Introduction
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is not just a concern for large corporations; it’s a pressing issue for small businesses too. Did you know that nearly 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses? This staggering statistic highlights the urgency for small business owners to understand and address the common cybersecurity threats for small businesses.
As an entrepreneur who has navigated the treacherous waters of digital transformation, I can tell you that the stakes are high. I remember when my own small business faced a phishing attempt that could have led to significant financial loss. Thankfully, we had implemented some basic security measures, which allowed us to catch the scam before it caused any damage. But not every small business is as fortunate.
In this article, we will explore the top cyber threats that small businesses face today, including ransomware, business email compromise (BEC), phishing scams, malware, and insider threats. By understanding these threats and recognizing the vulnerabilities in small businesses, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your company.

Understanding these common cybersecurity threats for small businesses is crucial because they can lead to severe consequences, including financial losses, legal issues, and damage to your reputation. With the right knowledge and tools, you can build a robust defense against these threats. Let’s dive deeper into what these top cyber threats are and how they can impact your business.
What Are the Common Cybersecurity Threats for Small Businesses?
Understanding the common cybersecurity threats for small businesses is the first step in protecting your business. Small businesses often lack the resources and expertise to defend against sophisticated cyberattacks, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. Below, we’ll explore some of the most prevalent threats that small businesses face today.
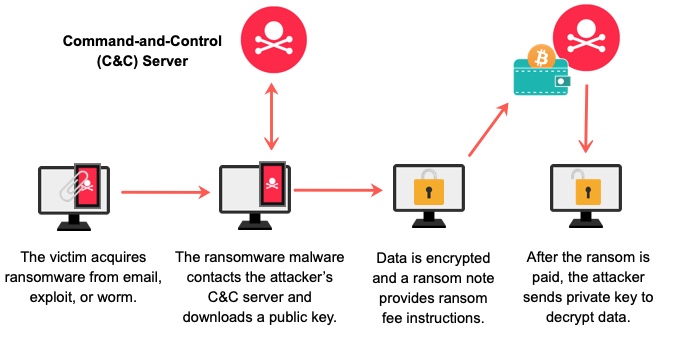
Ransomware
Ransomware is one of the most notorious top cyber threats affecting small businesses. In a ransomware attack, hackers encrypt your data and demand a ransom for its release. This can be devastating for a small business that relies on access to its data to operate. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, ransomware attacks are expected to occur every 11 seconds by 2021, and small businesses are often caught in the crossfire.
I recall a situation where a fellow entrepreneur in my network fell victim to a ransomware attack. His business was crippled overnight, and he faced a tough decision: pay the ransom or risk losing critical data. He ultimately decided to pay, but not without significant financial strain and anxiety. This experience taught me the importance of regular data backups and having a solid recovery plan in place.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Another alarming threat is Business Email Compromise (BEC). This type of attack involves cybercriminals impersonating an executive or trusted partner to trick employees into transferring money or sensitive information. BEC scams can be incredibly convincing, often using information gathered from social media or previous communications.
In my own experience, I’ve received emails that looked strikingly similar to those from my business partners, asking for urgent wire transfers. Thankfully, I had established protocols for verifying such requests through secondary communication methods, which helped us avoid falling into this trap.
Phishing Scams
Phishing scams are perhaps the most common form of cyberattack targeting small businesses. These scams typically come in the form of deceptive emails that appear legitimate but are designed to steal sensitive information like login credentials or financial data. According to the Anti-Phishing Working Group, there were over 200,000 phishing attacks reported each month in 2020 alone.
I once received an email that claimed to be from my bank, asking me to verify my account information. The email looked real—complete with logos and official language—but something felt off. I decided to call my bank directly instead of clicking any links. It turned out to be a phishing attempt aimed at stealing my personal information.
Malware
Malware encompasses various malicious software types designed to harm your computer systems or steal data. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, and spyware. Small businesses often fall victim to malware due to outdated software or lack of security measures.
For instance, I had an experience where one of my employees accidentally downloaded malware disguised as a legitimate software update. It caused significant disruptions in our operations until we managed to remove it and restore our systems. This incident underscored the importance of keeping all software up-to-date and ensuring that employees are trained on safe browsing practices.
Insider Threats
Insider threats can be one of the most challenging common cybersecurity threats for small businesses to detect and manage. These threats can come from disgruntled employees or even unintentional mistakes made by well-meaning staff members. According to a study by Cybersecurity Insiders, 70% of organizations believe insider threats are becoming more frequent.
In my early days as an entrepreneur, I had an employee who unintentionally shared sensitive customer data with an outside vendor due to a lack of understanding about our data-sharing policies. It was a wake-up call for me about how crucial it is to have clear guidelines and training for employees regarding data security.
By understanding these top cyber threats, you can take proactive steps to protect your business from falling victim to them. Awareness is key; knowing what you’re up against is half the battle won.
What Are the Top Cyber Threats Facing Small Businesses?
As we delve deeper into the landscape of cybersecurity, it’s essential to identify and understand the top cyber threats that specifically target small businesses. These threats can have devastating effects on operations, finances, and reputation. Below, we will explore five significant threats in detail, providing insights and strategies for mitigating their impact.
1. Ransomware
Ransomware continues to be a leading threat for small businesses. In a ransomware attack, hackers encrypt your files and demand a ransom payment to restore access. The rise of ransomware-as-a-service has made it easier for cybercriminals to launch attacks without advanced technical skills.
In my experience, I’ve seen businesses lose not just money but also customer trust due to ransomware incidents. For example, a local restaurant I know faced a ransomware attack that paralyzed its operations for days. They ended up paying the ransom, but the damage was done—customers were hesitant to return, fearing their data might be compromised. To protect against ransomware:
- Regularly back up your data: Ensure backups are stored offline or in a secure cloud environment.
- Educate employees: Training staff on recognizing suspicious emails can help prevent initial breaches.
- Implement robust security measures: Use firewalls and antivirus software that can detect and block ransomware attempts.
2. Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is another prevalent threat that exploits human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals impersonate high-ranking officials or trusted partners to trick employees into transferring funds or sensitive information.
A friend of mine once received an email that appeared to be from his CEO requesting an urgent wire transfer for a “confidential project.” Luckily, he decided to verify the request through a phone call before proceeding. This simple step saved the company from losing thousands of dollars.To defend against BEC:
- Verify requests through multiple channels: Always confirm unusual requests via phone or in-person.
- Train employees on BEC tactics: Awareness is crucial; employees should know what to look for.
- Use email authentication protocols: Implement DMARC, DKIM, and SPF to help prevent email spoofing.
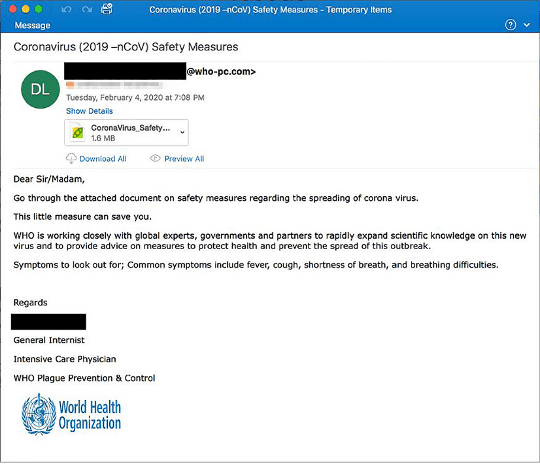
3. Phishing Scams
Phishing scams remain one of the most common top cyber threats affecting small businesses. These scams often come disguised as legitimate emails from trusted sources, tricking employees into revealing sensitive information.
I vividly remember receiving an email that looked like it was from my internet service provider, asking me to update my billing information. The urgency in the message almost convinced me to click the link. However, I took a moment to examine the sender’s email address and noticed it was slightly off—an easy red flag that could have saved me from potential identity theft. To combat phishing:
- Educate employees about phishing tactics: Regular training sessions can help staff recognize suspicious emails.
- Use spam filters: Invest in email security solutions that filter out potential phishing attempts.
- Encourage reporting of suspicious emails: Create a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting potential threats.
4. Malware
Malware is a broad category of malicious software designed to disrupt or damage systems. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, and spyware that can steal sensitive data or cause operational disruptions.
One time, an employee accidentally downloaded what they thought was a software update but turned out to be malware. It infiltrated our systems and caused significant downtime while we worked to remove it. This incident highlighted the importance of having strong antivirus software and conducting regular system scans. To protect against malware:
- Keep software updated: Regularly update operating systems and applications to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use reputable antivirus software: Invest in comprehensive security solutions that include real-time protection.
- Limit user permissions: Restrict administrative access to only those who need it for their roles.
5. Insider Threats
Insider threats can be particularly challenging because they originate from within your organization. Whether intentional or accidental, these threats can lead to significant data breaches or financial losses.
I once had an employee who unknowingly shared sensitive information with an outside vendor due to poor understanding of our data-sharing policies. This incident served as a wake-up call about the need for clear guidelines and training regarding data security practices. To mitigate insider threats:
- Implement strict access controls: Limit access to sensitive information based on job roles.
- Conduct regular training sessions: Educate employees about data security policies and best practices.
- Monitor user activity: Use tools that track user behavior and flag unusual activities.
By understanding these top cyber threats, small business owners can take proactive measures to protect their organizations from potential harm. Awareness is key; knowing what you’re up against is half the battle won.
How Do Vulnerabilities in Small Businesses Exacerbate Cybersecurity Risks?
Small businesses often operate with limited resources, which can expose them to various vulnerabilities in small businesses that exacerbate cybersecurity risks. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for developing effective strategies to protect your business from cyber threats. Here, we will explore some common vulnerabilities that small businesses face and how they can increase the likelihood of a successful cyberattack.
1. Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness
One of the most significant vulnerabilities in small businesses is a general lack of cybersecurity awareness among employees. Many small business owners assume that cyber threats are only a concern for larger corporations, leading to complacency. However, this mindset can be dangerous.
In my early days as an entrepreneur, I didn’t prioritize cybersecurity training for my team. This oversight came back to haunt me when an employee clicked on a phishing link, compromising our company’s sensitive data. It was a harsh lesson learned, and I quickly realized that regular training sessions were essential.
Solution: Implement ongoing cybersecurity training programs for all employees. Make it a part of your onboarding process and conduct regular refresher courses to keep everyone informed about the latest threats and best practices.
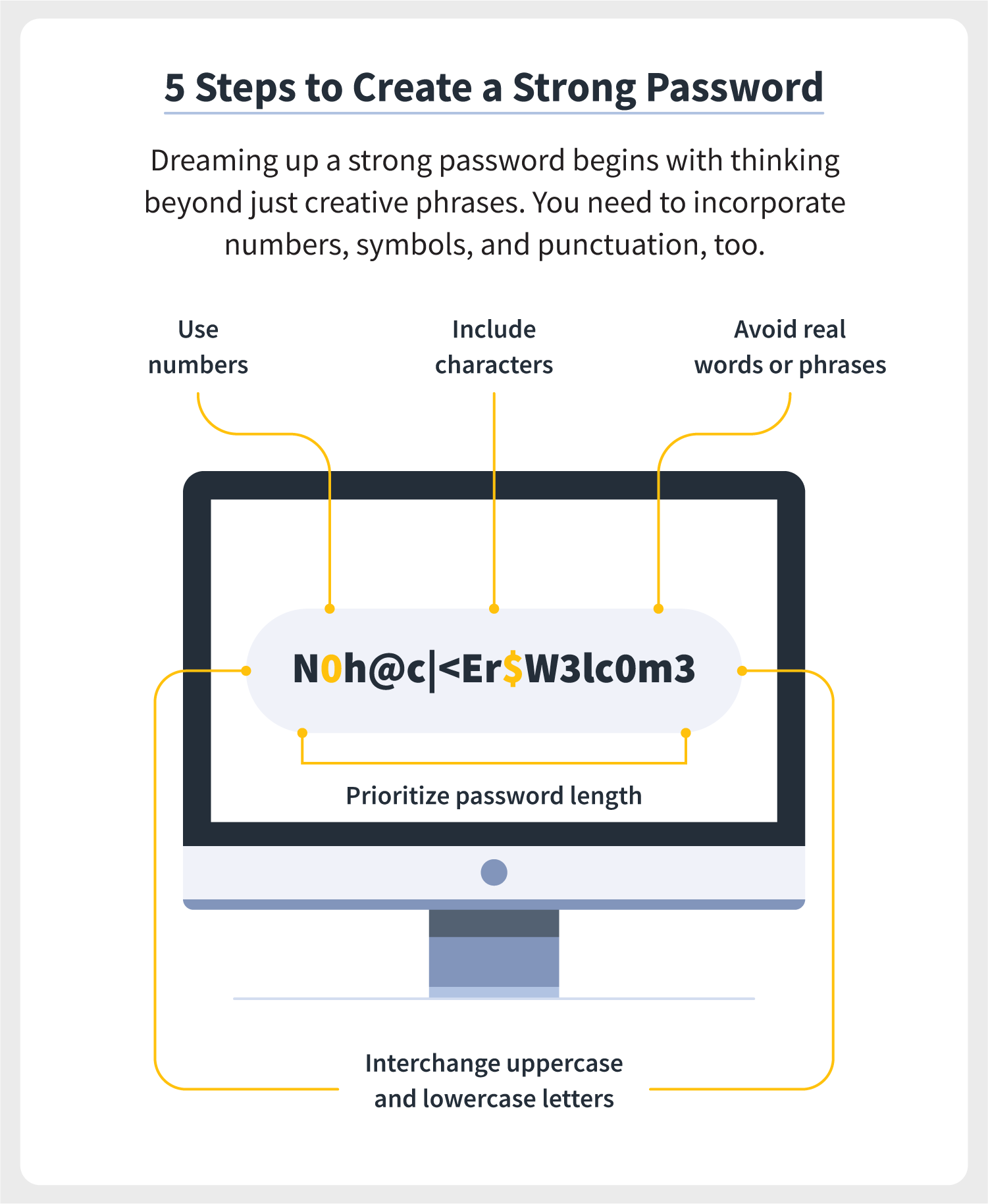
2. Weak Password Practices
Weak passwords are another common vulnerability that can lead to significant security breaches. Many employees use easily guessable passwords or reuse the same password across multiple accounts, making it easier for cybercriminals to gain access.
I remember a time when I discovered that several team members were using “password123” as their login credentials. It was shocking! After changing our password policy to require complex passwords and implementing two-factor authentication (2FA), we significantly reduced our risk of unauthorized access.
Solution: Establish strong password policies that require complex passwords and regular updates. Encourage the use of password managers to help employees create and store unique passwords securely.
3. Outdated Software and Systems
Many small businesses operate on outdated software or systems due to budget constraints or lack of IT support. This can create significant vulnerabilities, as outdated software often lacks the latest security patches needed to protect against known threats.
In my experience, I once neglected to update our accounting software for several months. When I finally did, I discovered that a critical security patch had been released that could have protected us from a recent wave of malware attacks. This incident reinforced the importance of staying current with software updates.
Solution: Regularly review all software and systems in use within your organization. Set up automatic updates whenever possible and establish a routine schedule for manual updates.
4. Insufficient Data Backup Procedures
Many small businesses fail to implement adequate data backup procedures, leaving them vulnerable to data loss from cyberattacks like ransomware or hardware failures. Without proper backups, recovering lost data can be nearly impossible.
I learned this lesson the hard way when a server failure wiped out critical customer data. Fortunately, we had recently implemented a cloud backup solution, which allowed us to restore our data quickly. It was a close call that highlighted how essential it is to have reliable backup systems in place.
Solution: Develop a comprehensive data backup strategy that includes regular backups to secure cloud storage or external drives. Test your backup restoration process periodically to ensure you can recover data when needed.
5. Inadequate Incident Response Plans
Many small businesses lack formal incident response plans, leaving them unprepared for potential cyber incidents. Without a clear plan in place, the response to an attack can be chaotic and ineffective, exacerbating the situation.
When my business faced its first cyber incident—a minor data breach—we scrambled to figure out what steps to take. It was stressful and disorganized, which ultimately delayed our response time and increased the damage done.
Solution: Create an incident response plan that outlines specific steps to take in the event of a cyber incident. Ensure all employees are familiar with the plan and conduct regular drills to practice your response.
By addressing these vulnerabilities in small businesses, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyber threats. Awareness and proactive measures are key components in building a robust cybersecurity posture for your organization.
Why Is Cybersecurity Essential for Small Businesses?
In an era where digital transformation is reshaping how businesses operate, understanding why cybersecurity is essential for small businesses is crucial. Cybersecurity is not just about protecting data; it’s about safeguarding your entire business model and reputation. Here are several compelling reasons why investing in cybersecurity should be a top priority for small business owners.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Small businesses often handle sensitive information, such as customer data, financial records, and proprietary business information. A breach can expose this data to cybercriminals, leading to identity theft, fraud, and financial loss.
I remember when a small online retailer I know experienced a data breach that compromised thousands of customer credit card details. The fallout was devastating—not only did they face immediate financial repercussions, but they also lost the trust of their customers. This incident serves as a reminder that protecting sensitive data is paramount.
Solution: Implement strong data protection measures, including encryption and access controls, to safeguard sensitive information.
Financial Implications of Cyberattacks
The financial impact of cyberattacks on small businesses can be staggering. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach for a small business can exceed $120,000. This cost includes not only the immediate financial loss but also potential legal fees, regulatory fines, and damage to your brand reputation.

When my own business faced a minor cyber incident, we incurred costs related to forensic investigations and public relations efforts to mitigate the damage. It quickly became clear that even small incidents could lead to significant financial burdens.
Solution: Consider investing in cyber insurance to help cover potential costs associated with cyber incidents. Additionally, conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities that could lead to costly breaches.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have strict regulations regarding data protection and privacy. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes severe penalties on businesses that mishandle personal data.
I once consulted for a small healthcare provider that faced fines due to non-compliance with HIPAA regulations after a data breach. The financial penalties were substantial, but the reputational damage was even more significant as patients lost trust in their ability to protect sensitive health information.
Solution: Stay informed about relevant regulations in your industry and ensure your cybersecurity practices align with compliance requirements.
Maintaining Customer Trust
Trust is the foundation of any successful business relationship. Customers expect their personal information to be protected when they engage with your business. A single cybersecurity incident can erode that trust and drive customers away.
For instance, after the data breach incident I mentioned earlier involving the online retailer, many customers voiced their concerns on social media and chose to shop elsewhere. Rebuilding that trust took time and effort—something every small business should strive to avoid.
Solution: Communicate openly with customers about your cybersecurity practices and any incidents that may occur. Transparency can help maintain trust even in challenging situations.
Competitive Advantage
In today’s digital landscape, having robust cybersecurity measures can serve as a competitive advantage. Customers are increasingly aware of cybersecurity issues and often prefer businesses that prioritize their security.
I’ve seen companies gain new clients simply because they could demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer data through certifications or robust security practices. This competitive edge can set you apart from others in your industry.
Solution: Invest in cybersecurity certifications or partnerships with reputable cybersecurity firms to showcase your commitment to security.
By recognizing the importance of cybersecurity for small businesses, you can take proactive steps to protect your organization from potential threats. Investing in cybersecurity is not just a technical necessity; it’s a strategic business decision that can safeguard your future.
How Can Small Businesses Protect Themselves Against Cyber Threats?
Protecting your small business from cyber threats is a critical responsibility that requires a proactive approach. By implementing effective cybersecurity measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to the common cybersecurity threats for small businesses. Here are several actionable strategies to help safeguard your organization.
1. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Regular security assessments are essential for identifying vulnerabilities in your systems and processes. These assessments can help you understand where your weaknesses lie and how to address them effectively.
In my experience, conducting a thorough security audit revealed several outdated systems and practices that needed immediate attention. This proactive step allowed us to strengthen our defenses before any potential attacks occurred.
Action Steps:
- Schedule regular security audits with an IT professional or cybersecurity consultant.
- Use vulnerability scanning tools to identify weaknesses in your network.
- Review and update your security policies based on assessment findings.
2. Implement Strong Password Policies
Weak passwords are one of the easiest ways for cybercriminals to gain access to your systems. Establishing strong password policies can significantly enhance your security posture.
I learned this lesson when I discovered that many employees were using simple passwords like “123456” or “password.” After implementing a policy requiring complex passwords and regular changes, we saw a noticeable decrease in unauthorized access attempts.
Action Steps:
- Require employees to create complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Implement two-factor authentication (2FA) for an extra layer of security.
- Encourage the use of password managers to help employees generate and store unique passwords securely.
3. Provide Cybersecurity Training for Employees
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Providing regular training can empower them to recognize and respond to potential threats effectively.
I remember when we held our first cybersecurity training session; it was eye-opening for many team members. They learned about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and how to handle suspicious emails. This knowledge made them more vigilant and less likely to fall victim to attacks.
Action Steps:
- Develop a comprehensive cybersecurity training program for all employees.
- Conduct regular refresher courses to keep staff updated on the latest threats.
- Create a culture of security awareness by encouraging employees to report suspicious activities.
4. Keep Software and Systems Updated
Outdated software is a significant vulnerability that cybercriminals often exploit. Regularly updating your software ensures you have the latest security patches and features.
In my own business, I once neglected to update our antivirus software, which left us exposed during a malware attack. After that incident, I made it a priority to establish a routine for checking and updating all software regularly.
Action Steps:
- Enable automatic updates for operating systems and applications whenever possible.
- Regularly review software licenses and ensure all programs are up-to-date.
- Consider using managed IT services that can handle software updates on your behalf.
5. Backup Data Regularly
Regular data backups are crucial for recovering from cyber incidents like ransomware attacks or hardware failures. Without proper backups, you risk losing valuable data permanently.
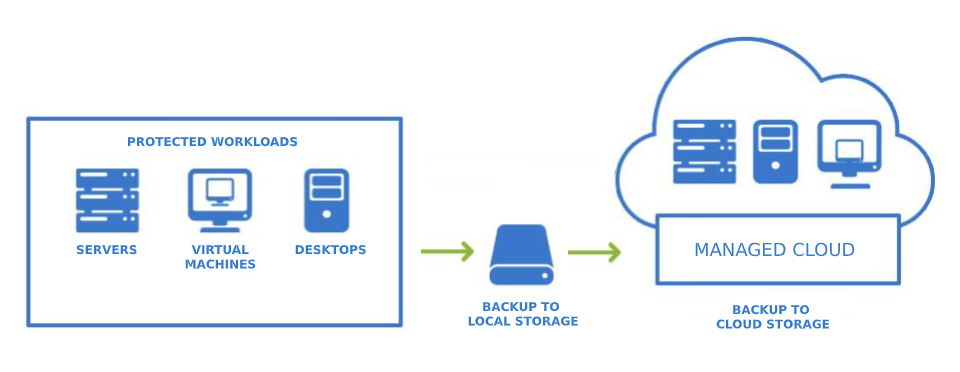
After experiencing a server failure in my business, I quickly realized the importance of having reliable backup solutions in place. We implemented both local and cloud-based backups, ensuring we could recover our data quickly in case of an incident.
Action Steps:
- Develop a data backup strategy that includes both local and cloud storage options.
- Schedule automatic backups at regular intervals (daily or weekly).
- Test your backup restoration process periodically to ensure data can be recovered when needed.
6. Establish an Incident Response Plan
Having an incident response plan is essential for minimizing the impact of a cyber incident when it occurs. This plan should outline specific steps to take during an attack and designate roles for team members involved in the response.
When my business faced its first minor data breach, we lacked a formal incident response plan, which led to confusion and delays in our response. Since then, we’ve developed a clear plan that outlines communication protocols, containment strategies, and recovery steps.
Action Steps:
- Create an incident response plan that details procedures for various types of incidents.
- Designate team members responsible for executing the plan during an attack.
- Conduct regular drills to practice the incident response process and identify areas for improvement.
By taking these proactive measures, small businesses can significantly enhance their defenses against common cybersecurity threats for small businesses. Remember, cybersecurity is not just about technology; it’s about creating a culture of awareness and preparedness within your organization.
What Are the Consequences of Ignoring Cybersecurity?
Ignoring cybersecurity can have dire consequences for small businesses, often leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. In an increasingly digital world, the risks associated with neglecting cybersecurity are too significant to overlook. Here are some of the most severe consequences that small businesses may face if they fail to prioritize their cybersecurity measures.
1. Financial Losses
One of the most immediate and tangible consequences of a cyberattack is financial loss. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach for small businesses can exceed $120,000. This figure includes costs related to recovery efforts, legal fees, regulatory fines, and lost revenue due to downtime.
I’ve seen first-hand how quickly costs can escalate after a cyber incident. A friend who owns a small retail store experienced a ransomware attack that demanded a $10,000 ransom. While he ultimately decided to pay it to regain access to his systems, the total costs—including lost sales during downtime—amounted to over $50,000.
Action Steps:
- Develop a budget for cybersecurity investments to mitigate potential losses.
- Consider cyber insurance to help cover costs associated with data breaches or cyber incidents.
2. Damage to Reputation
The reputation of your business can take a significant hit following a cyber incident. Customers expect their personal information to be protected; if they feel that you’ve failed in this regard, they may choose to take their business elsewhere.

After the data breach incident involving my friend’s retail store, many customers voiced their concerns on social media and opted to shop at competitors instead. Rebuilding that trust took time and effort—something every small business should strive to avoid.
Action Steps:
- Be transparent with customers about your cybersecurity practices and any incidents that may occur.
- Communicate openly about steps you’re taking to enhance security and protect customer data.
3. Legal Repercussions
Many industries are subject to strict regulations regarding data protection and privacy. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes severe penalties on businesses that mishandle personal data.
I once consulted for a healthcare provider that faced fines due to non-compliance with HIPAA regulations after a data breach. The financial penalties were substantial, but the reputational damage was even more significant as patients lost trust in their ability to protect sensitive health information.
Action Steps:
- Stay informed about relevant regulations in your industry and ensure your cybersecurity practices align with compliance requirements.
- Conduct regular audits to assess compliance with data protection laws and regulations.
4. Loss of Intellectual Property
For many small businesses, intellectual property (IP) is one of their most valuable assets. Cyberattacks can lead to the theft of proprietary information, trade secrets, or product designs, which can have long-term consequences for your business’s competitive edge.
I remember speaking with an entrepreneur who had developed an innovative software application. After falling victim to a cyberattack that compromised their source code, they struggled to regain their market position as competitors quickly capitalized on the stolen information.
Action Steps:
- Implement strong access controls and encryption measures for sensitive intellectual property.
- Regularly review and update your IP protection strategies as part of your overall cybersecurity plan.
5. Operational Disruption
Cyberattacks can cause significant disruptions in daily operations, leading to downtime and loss of productivity. This disruption can affect not only your internal processes but also your ability to serve customers effectively.
For instance, when my business experienced a minor malware infection, our systems were down for several hours while we worked on removal and recovery. During that time, we lost sales opportunities and frustrated customers who were unable to access our services.
Action Steps:
- Develop an incident response plan that includes strategies for minimizing operational disruption.
- Invest in backup systems and redundancy measures to ensure continuity of operations during an incident.
By understanding these potential consequences of ignoring cybersecurity, small business owners can better appreciate the importance of implementing effective security measures. Taking proactive steps now can save your business from devastating repercussions in the future.
What Resources Are Available for Small Businesses to Enhance Cybersecurity?
As a small business owner, you might feel overwhelmed by the complexities of cybersecurity. However, numerous resources are available to help you strengthen your defenses against common cybersecurity threats for small businesses. Here’s a guide to some valuable tools, services, and organizations that can assist you in enhancing your cybersecurity posture.
1. Cybersecurity Tools and Software
Investing in the right cybersecurity tools is essential for protecting your business from cyber threats. Here are some categories of software to consider:
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: These programs help detect and remove malicious software from your systems. Popular options include Norton, McAfee, and Bitdefender.
- Firewalls: A firewall acts as a barrier between your internal network and external threats. Consider using both hardware and software firewalls for comprehensive protection.
- Password Managers: Tools like LastPass or Dashlane can help employees create and store strong, unique passwords securely.
- Encryption Software: Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it’s stolen, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key. Tools like VeraCrypt can be useful for this purpose.
In my experience, implementing antivirus software significantly reduced the number of malware incidents we faced. It’s a simple yet effective first line of defense.
2. Cybersecurity Training Programs
Regular training is crucial for keeping employees informed about the latest cyber threats and best practices. Here are some resources for cybersecurity training:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning offer various courses on cybersecurity awareness tailored for businesses.
- Workshops and Webinars: Many organizations provide free or low-cost workshops that cover essential cybersecurity topics. Check local business associations or chambers of commerce for offerings.
- Phishing Simulations: Services like KnowBe4 allow you to conduct phishing simulations to test your employees’ ability to recognize suspicious emails. This hands-on approach can be highly effective in reinforcing training.
I remember attending a workshop hosted by our local chamber of commerce that focused on cybersecurity best practices. It was incredibly informative and provided actionable insights that we implemented immediately.
3. Government Resources
Various government agencies offer resources to help small businesses enhance their cybersecurity efforts:
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA): CISA provides a wealth of information on cybersecurity best practices, including guides specifically designed for small businesses.
- Small Business Administration (SBA): The SBA offers resources on how to protect your business from cyber threats, including funding options for improving cybersecurity measures.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): NIST has developed a Cybersecurity Framework that provides guidelines for managing cybersecurity risks. Their resources are especially useful for businesses looking to establish a comprehensive security program.
I found CISA’s resources particularly helpful when we were developing our incident response plan. Their templates made it much easier to get started.
4. Professional Cybersecurity Services
If your budget allows, consider hiring professional cybersecurity services to assess and enhance your security posture:
- Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs): MSSPs can monitor your systems 24/7, providing real-time threat detection and response services. They often offer comprehensive packages tailored to small businesses.
- Cybersecurity Consultants: Hiring a consultant can provide you with expert guidance on identifying vulnerabilities and developing effective security strategies tailored to your specific needs.
When my business faced increasing cyber threats, we decided to hire a consultant who helped us conduct a thorough risk assessment and implement necessary changes. It was an investment that paid off quickly by significantly reducing our risk exposure.
5. Community Support and Networking
Building relationships with other small business owners can be invaluable when it comes to sharing knowledge about cybersecurity:
- Local Business Associations: Joining local business groups or chambers of commerce can provide networking opportunities where you can learn from others’ experiences regarding cybersecurity challenges.
- Online Forums and Groups: Platforms like Reddit or LinkedIn have groups dedicated to small business owners discussing cybersecurity issues and solutions.
I’ve found that sharing experiences with other entrepreneurs has been incredibly beneficial. We often exchange tips on what works—and what doesn’t—when it comes to protecting our businesses from cyber threats.
By leveraging these resources, small businesses can enhance their defenses against the top cyber threats they face today. Remember, investing in cybersecurity is not just about technology; it’s about building a culture of awareness and preparedness within your organization.
Moving Forward: Building a Resilient Cybersecurity Framework
As small businesses navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, building a resilient cybersecurity framework is essential for protecting against the common cybersecurity threats for small businesses. A strong framework not only safeguards your data but also fosters trust among customers and partners. Here’s how to create a robust cybersecurity strategy that can adapt to evolving threats.
1. Assess Your Current Cybersecurity Posture
The first step in building a resilient cybersecurity framework is to assess your current security posture. This involves evaluating your existing policies, tools, and practices to identify strengths and weaknesses.
In my experience, conducting a thorough assessment revealed several gaps in our security measures that we hadn’t previously recognized. This included outdated software and insufficient employee training. By understanding where we stood, we could prioritize improvements effectively.
Action Steps:
- Conduct a comprehensive security audit with the help of an IT professional or cybersecurity consultant.
- Use vulnerability scanning tools to identify weaknesses in your network and systems.
- Document your findings to create a baseline for future improvements.
2. Develop a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Policy
A well-defined cybersecurity policy serves as the foundation of your security framework. This policy should outline the protocols and procedures for protecting sensitive information and responding to incidents.
When I first drafted our cybersecurity policy, I included guidelines on acceptable use of technology, password management, data protection measures, and incident response protocols. Having this document in place provided clarity for employees and helped establish accountability.
Action Steps:
- Create a written cybersecurity policy that covers all aspects of your security practices.
- Ensure that all employees have access to the policy and understand its importance.
- Review and update the policy regularly to reflect changes in technology and emerging threats.
3. Foster a Culture of Cybersecurity Awareness
Creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness within your organization is vital for reducing risks associated with human error. Employees should feel empowered to recognize potential threats and take appropriate action.
I remember when we implemented regular cybersecurity training sessions; it transformed how our team approached security. Employees began to actively report suspicious emails and behaviors, which significantly reduced our vulnerability to phishing attacks.
Action Steps:
- Schedule regular training sessions on cybersecurity best practices for all employees.
- Encourage open communication about security concerns and potential threats.
- Recognize employees who demonstrate strong security awareness to reinforce positive behavior.
4. Implement Multi-Layered Security Measures
A multi-layered approach to security ensures that if one layer fails, others remain in place to protect your business. This strategy involves combining various security tools and practices to create a comprehensive defense system.
For example, at my company, we use antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption together. This multi-layered approach has proven effective in preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive information.
Action Steps:
- Invest in a combination of security tools tailored to your business needs (e.g., antivirus software, firewalls, encryption).
- Regularly update all security software to ensure you have the latest protections.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activity that may indicate a breach.
5. Establish an Incident Response Plan
Having an incident response plan is crucial for minimizing damage when a cyber incident occurs. This plan should outline specific steps for detecting, responding to, and recovering from incidents.
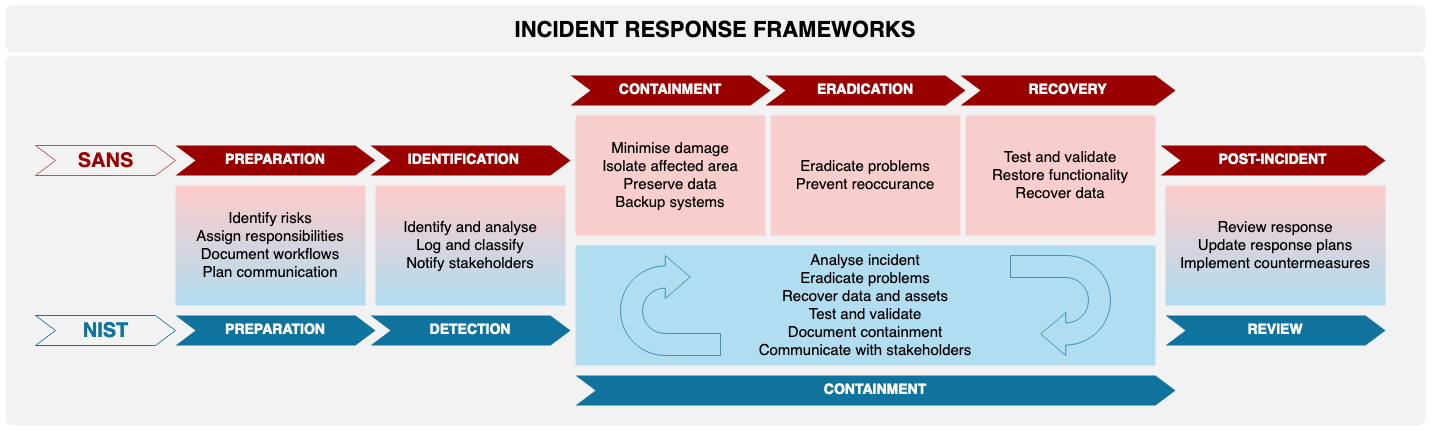
When my business faced its first cyber incident—a minor data breach—we lacked a formal incident response plan. The confusion during that time taught me the importance of having clear protocols in place.
Action Steps:
- Create an incident response plan that details procedures for various types of incidents (e.g., data breaches, ransomware attacks).
- Designate team members responsible for executing the plan during an incident.
- Conduct regular drills to practice the incident response process and identify areas for improvement.
6. Continuously Monitor and Improve Your Security Posture
Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort; it requires ongoing monitoring and improvement. Regularly reviewing your security measures helps you stay ahead of emerging threats and adapt to changing circumstances.
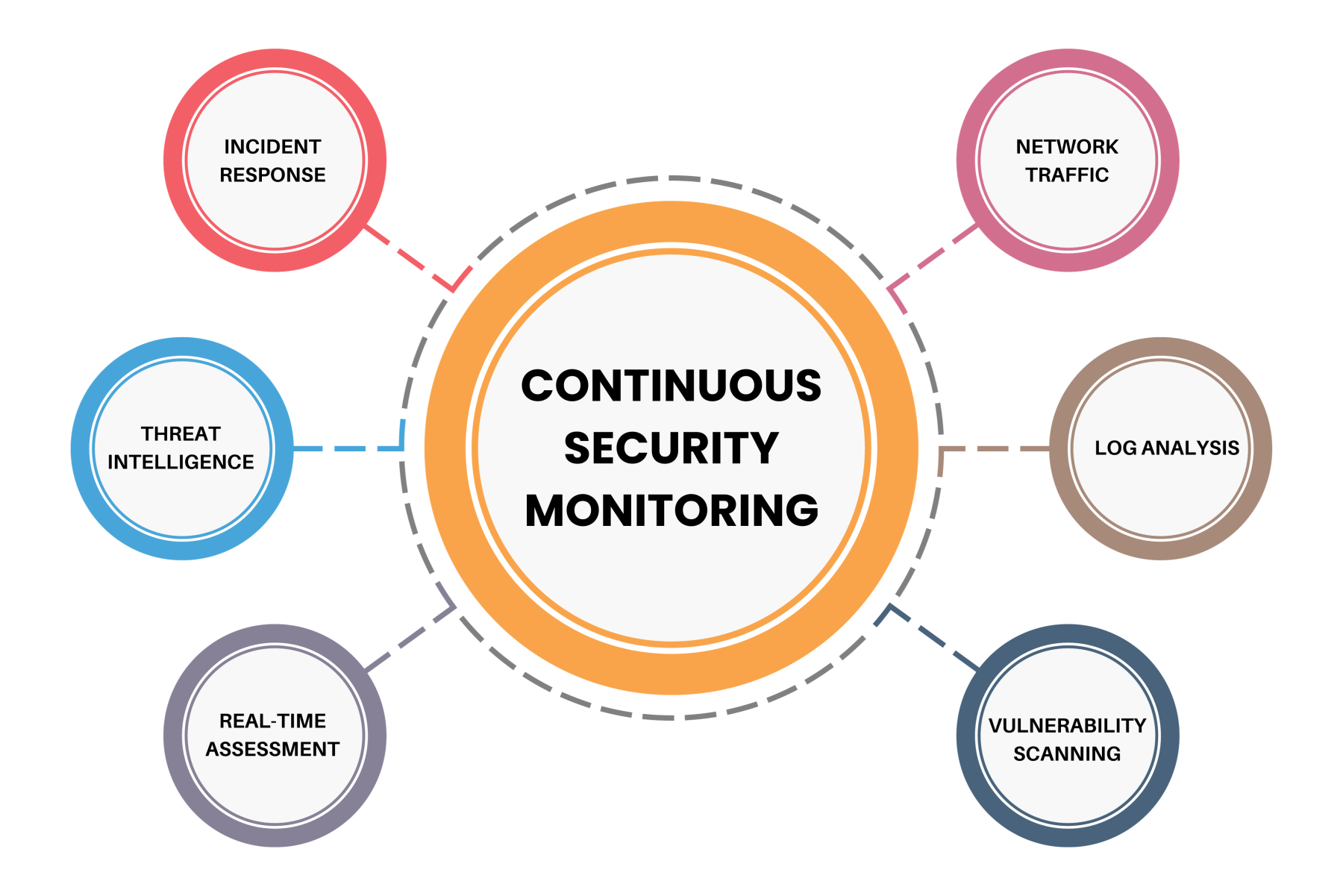
I’ve found that setting up regular reviews of our cybersecurity practices has been invaluable. It allows us to identify new vulnerabilities as they arise and adjust our strategies accordingly.
Action Steps:
- Schedule regular reviews of your cybersecurity policies and practices (e.g., quarterly or biannually).
- Stay informed about emerging threats through industry news, webinars, or professional organizations.
- Adjust your strategies based on lessons learned from incidents or changes in technology.
By taking these proactive steps to build a resilient cybersecurity framework, small businesses can significantly enhance their defenses against top cyber threats. Remember that investing in cybersecurity is not just about technology; it’s about fostering a culture of awareness and preparedness within your organization.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Digital Transformation with Security in Mind
As we conclude our exploration of the common cybersecurity threats for small businesses, it’s essential to recognize that embracing digital transformation does not mean compromising on security. In fact, the two should go hand in hand. With the right strategies and resources, small businesses can leverage technology to enhance their operations while maintaining a strong security posture.
Recognizing Cybersecurity as an Ongoing Journey
Cybersecurity is not a destination; it’s an ongoing journey that requires continuous effort and adaptation. As technology evolves, so do the tactics used by cybercriminals. Small businesses must remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to security.
Action Steps:
- Regularly revisit your cybersecurity policies and practices to ensure they remain effective against emerging threats.
- Stay informed about new technologies and trends that can enhance your security measures.
- Foster a mindset of continuous improvement within your organization.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Security
Digital transformation offers numerous opportunities to enhance your cybersecurity efforts. From advanced threat detection systems to automated backup solutions, technology can help you stay one step ahead of cyber threats.
Action Steps:
- Explore new technologies that can bolster your cybersecurity efforts (e.g., AI-driven threat detection, cloud security solutions).
- Invest in training for employees to ensure they understand how to use these technologies effectively.
- Regularly assess the effectiveness of your current tools and consider upgrades as needed.
Building Strong Relationships with Cybersecurity Partners
Collaboration is key when it comes to cybersecurity. Building strong relationships with trusted cybersecurity partners can provide valuable insights and resources that strengthen your defenses.
Action Steps:
- Identify reputable cybersecurity firms or consultants that align with your business needs.
- Engage in regular communication with partners to stay informed about best practices and emerging threats.
- Consider joining industry groups or associations focused on cybersecurity to expand your network and resources.
Empowering Employees as Cybersecurity Advocates
Your employees play a crucial role in your organization’s cybersecurity efforts. By empowering them with knowledge and resources, you can transform them into advocates for security within your business.
Action Steps:
- Encourage open dialogue about cybersecurity concerns and ideas within your organization.
- Recognize employees who demonstrate strong security awareness or identify potential threats.
- Create opportunities for employees to participate in cybersecurity initiatives or training programs.
Committing to a Secure Future
Ultimately, committing to a secure future means recognizing that cybersecurity is an essential part of doing business today. By prioritizing security alongside digital transformation efforts, small businesses can thrive in an increasingly connected world. As you move forward, remember that investing in cybersecurity is not just about protecting your data; it’s about safeguarding your reputation, financial stability, and customer trust. The steps you take today will lay the foundation for a secure tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.s)
- What is the most common cybersecurity threat for small businesses?
- Ransomware is often cited as one of the most common threats facing small businesses today.
- How can I protect my business from ransomware attacks?
- Regularly back up your data, educate employees about phishing scams, and implement strong security measures like firewalls and antivirus software.
- What steps should I take if my business falls victim to a cyberattack?
- Immediately contain the attack, assess the damage, notify affected parties if necessary, and begin recovery efforts based on your incident response plan.
- How often should I train my employees on cybersecurity best practices?
- Conduct regular training sessions at least once or twice a year, with additional refresher courses as needed based on emerging threats.
- Are small businesses more vulnerable to cyberattacks than larger companies?
- Yes, many cybercriminals target small businesses due to their often limited resources and weaker security measures.
- What are some signs that my business may be experiencing a phishing attack?
- Look out for unexpected emails requesting sensitive information or urgent actions, especially if they contain poor grammar or unusual sender addresses.
- How can I identify insider threats within my organization?
- Monitor user activity for unusual behavior patterns and establish clear data access policies to reduce risks associated with insider threats.
- What tools can help protect against malware infections?
- Use reputable antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to protect against malware infections effectively.
- Is cyber insurance worth it for small businesses?
- Yes, cyber insurance can help cover costs associated with data breaches or cyber incidents, making it a valuable investment for small businesses.
- Where can I find additional resources to improve my business’s cybersecurity?
- Government agencies like CISA and the SBA provide valuable resources, as well as online courses from platforms like Coursera or Udemy focused on cybersecurity training.
This concludes our comprehensive guide on understanding and addressing the common cybersecurity threats for small businesses. By taking action today, you can help secure your business’s future against potential cyber risks!



