Introduction
In our increasingly digital world, the importance of protecting sensitive data cannot be overstated. Every day, businesses collect and store vast amounts of personal and confidential information, from customer details to proprietary business data. Unfortunately, this wealth of information makes organizations prime targets for cybercriminals. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This staggering figure highlights the urgency for businesses to take proactive measures in protecting sensitive data from cyber threats.
When I first ventured into the online business landscape, I underestimated the risks associated with data security. I thought that as a small player, I wouldn’t attract attention from hackers. However, after hearing about a friend’s company that suffered a devastating data breach, I quickly realized that no organization is too small to be targeted. This incident was a wake-up call for me and many others in my network.
In this blog post, we will explore the various dimensions of protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. We’ll delve into what constitutes sensitive data, identify common cyber threats, and outline effective strategies for safeguarding your information. By understanding these concepts and implementing best practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of a data breach and protect your organization’s reputation. Are you ready to discover how to fortify your defenses against cyber threats? Let’s dive in!
What Are Cyber Threats and Why Should You Care?
In today’s digital world, the term “cyber threats” is thrown around a lot, but what does it really mean? Simply put, cyber threats are malicious acts aimed at compromising the integrity, confidentiality, or availability of your data. These threats can come in many forms, including malware, phishing attacks, ransomware, and insider threats. Understanding these risks is crucial for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats.
The Growing Landscape of Cyber Threats
I remember when I first started my online business; I thought I was too small to be a target. Boy, was I wrong! Just last year, a small company in my network fell victim to a ransomware attack. They lost access to their files and had to pay a hefty ransom to regain control. This incident opened my eyes to the reality that no one is immune. According to recent statistics from Business Ventures, global cybercrime damages are expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. That’s a staggering figure that should make any entrepreneur sit up and take notice.
Why You Should Care
So why should you care about protecting sensitive data from cyber threats? The consequences can be devastating. Data breaches can lead to financial losses, legal ramifications, and irreparable damage to your reputation. For instance, a study by IBM found that the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million! That’s not pocket change for most businesses.
Moreover, customer trust is hard-won but easily lost. If your customers believe their personal information is at risk, they won’t think twice about taking their business elsewhere. In fact, according to a survey by PwC, 85% of consumers will not do business with a company if they have concerns about its security practices.
Types of Cyber Threats You Should Know
- Malware: This is software designed to harm or exploit any programmable device or network. It includes viruses, worms, and Trojans that can steal data or cause damage.
- Phishing Attacks: These are deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in electronic communications. I once received an email that looked like it came from my bank, asking me to verify my account details. Thankfully, I recognized it as phishing and didn’t click on any links.
- Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts your files and demands payment for the decryption key. It’s like being held hostage—your data is locked away until you pay up.
- Insider Threats: Sometimes the biggest threat comes from within your organization. Whether intentional or accidental, employees can expose sensitive data through negligence or malicious intent.
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: These attacks overwhelm your servers with traffic, making your website unavailable to users.
How Can You Protect Your Business?
Now that you understand what cyber threats are and why they matter, let’s talk about how you can protect your sensitive data from these dangers.
- Educate Your Team: Regular training on recognizing phishing emails and safe internet practices can go a long way in preventing breaches.
- Invest in Technology: Use firewalls and antivirus software to protect against malware and unauthorized access.
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Encourage employees to use complex passwords and change them regularly.
- Regularly Update Software: Keeping your software updated ensures you have the latest security patches installed.
- Backup Your Data: Always have backups in place so you can recover quickly if something goes wrong.
Understanding cyber threats is the first step in protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. The digital landscape is fraught with dangers that can impact your business significantly if left unchecked. By staying informed and implementing robust security measures, you can safeguard your organization against these risks.

How Can You Identify Sensitive Data in Your Organization?
Identifying sensitive data within your organization is a crucial step in protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. But what exactly qualifies as sensitive data? It includes any information that, if disclosed, could harm individuals or the organization itself. This can range from personal identification numbers (PINs) and credit card information to proprietary business data and customer records.
Understanding What Constitutes Sensitive Data
Let’s break it down. Sensitive data typically falls into several categories:
- Personal Identifiable Information (PII): This includes names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and any other information that can identify an individual.
- Payment Information: Credit card numbers, bank account details, and any financial records fall under this category.
- Health Information: Medical records and health insurance information are considered highly sensitive due to privacy regulations like HIPAA.
- Intellectual Property: Trade secrets, patents, and proprietary algorithms are vital for businesses and should be safeguarded.
- Customer Data: Any information collected from customers for business purposes, including purchase history and preferences.
Why Identifying Sensitive Data Matters
You might wonder why this process is so important in the grand scheme of protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. Well, knowing where your sensitive data resides helps you implement targeted security measures. For instance, if you store customer payment information in a database without encryption, you’re leaving the door wide open for cybercriminals.
In my experience as a tech entrepreneur, I once overlooked a small database containing customer emails. It seemed harmless at the time until I learned that hackers often target email lists for phishing attacks. This incident taught me that every piece of data needs attention—no matter how insignificant it may seem.
Steps to Identify Sensitive Data
So how do you go about identifying sensitive data in your organization? Here are some actionable steps:
- Conduct a Data Inventory
Start by creating a comprehensive inventory of all the data your organization collects, processes, and stores. This includes databases, spreadsheets, cloud storage, and even physical documents.
- Tools to Use: Consider using data discovery tools like Varonis or Spirion that can automate this process by scanning your systems for sensitive information.
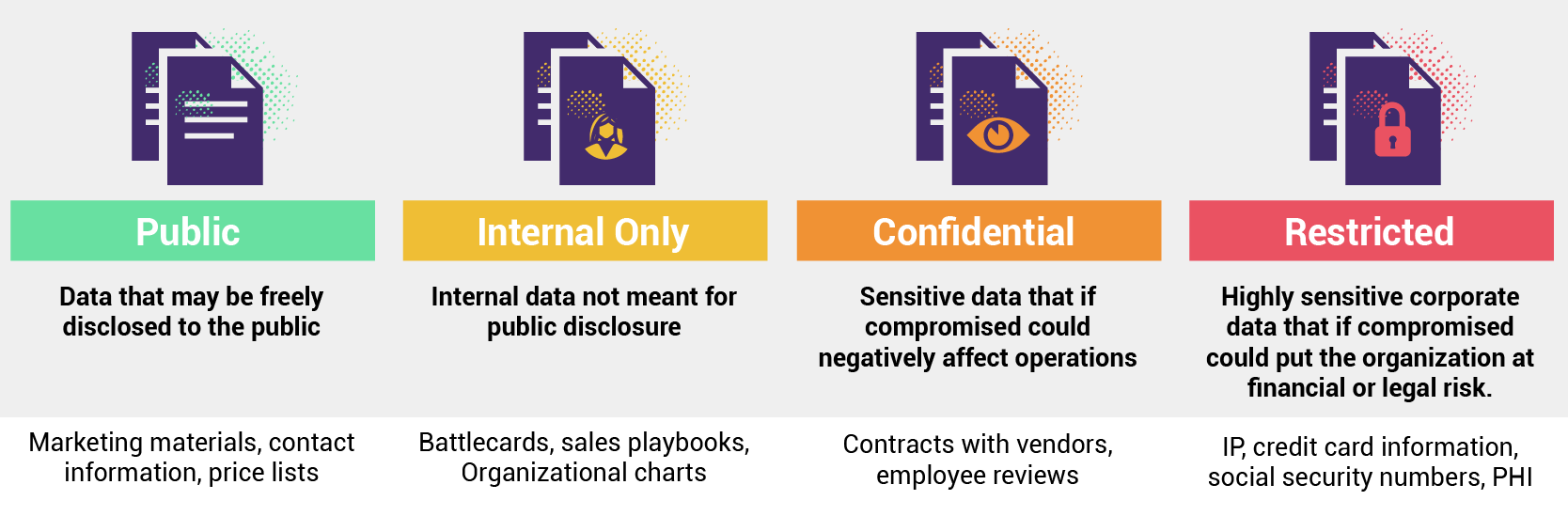
- Classify Your Data
Once you have an inventory, classify your data based on its sensitivity level. You might categorize it as public, internal use only, confidential, or highly confidential.
- Example: In my own business, I implemented a simple classification system that allowed my team to quickly identify which files required additional security measures.
- Assess Risk Levels
Evaluate the risks associated with each type of sensitive data. Ask yourself questions like:
- What would happen if this data were compromised?
- Who has access to this information?
- How is it currently being protected?
This risk assessment will help prioritize which data needs immediate attention in terms of security.
- Implement Access Controls
Once you’ve identified your sensitive data, implement access controls to limit who can view or modify it. Use role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure that employees only have access to the information necessary for their job functions.
- Personal Experience: After implementing RBAC in my organization, we significantly reduced the number of potential vulnerabilities because fewer people had access to critical information.
- Regularly Review and Update
Data identification isn’t a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. Regularly review your inventory and classification system to ensure it remains up-to-date with any changes in your business operations or regulations.
Identifying sensitive data is a foundational step in protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By understanding what constitutes sensitive information and taking proactive measures to manage it effectively, you can significantly reduce your risk of a data breach. Remember, knowledge is power—knowing where your sensitive data lies empowers you to secure it better.
What Are Effective Data Protection Strategies?
Once you’ve identified sensitive data within your organization, the next logical step is to implement effective data protection strategies. Protecting sensitive data from cyber threats requires a multi-layered approach that combines technology, policies, and employee training. In this section, we’ll explore various strategies that can significantly enhance your data security posture.
The Importance of Data Protection Strategies
Why should you invest time and resources into developing data protection strategies? The answer is simple: the consequences of a data breach can be catastrophic. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, 60% of small businesses close within six months of a cyber attack. This statistic alone should motivate you to take proactive measures.
In my own experience, I once faced a minor data breach due to inadequate protection strategies. While we managed to contain it quickly, the incident served as a wake-up call. It was clear that we needed to strengthen our defenses. Here are some effective strategies I implemented that can help you too.
- Implement Strong Access Control Measures
Access control is one of the most basic yet effective strategies for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By limiting access to sensitive information, you reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This method allows you to assign permissions based on job roles. For example, only finance team members should have access to payroll information.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security through MFA can significantly reduce the chances of unauthorized access. Even if someone gets hold of a password, they would still need a second form of verification—like a text message code—to gain entry.
- Utilize Data Encryption
Data encryption is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information both at rest and in transit. When data is encrypted, it becomes unreadable without the proper decryption key.
- Full Disk Encryption: Encrypting entire drives ensures that all data stored on them is protected. This is particularly important for laptops and mobile devices that can be easily lost or stolen.
- End-to-End Encryption: This method secures data during transmission. For instance, using secure protocols like HTTPS when transmitting sensitive information over the internet ensures that it cannot be intercepted by malicious actors.
In my early days, I neglected encryption for customer payment information stored in our database. When I realized this oversight, I immediately implemented encryption protocols and felt a huge weight lifted off my shoulders.
- Conduct Regular Vulnerability Assessments
Regularly assessing your systems for vulnerabilities is key to maintaining strong security measures. This involves scanning your network and applications for weaknesses that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
- Automated Tools: Use tools like Nessus or Qualys to perform regular vulnerability scans and identify potential risks.
- Penetration Testing: Consider hiring ethical hackers to test your systems’ defenses by simulating cyber-attacks. This proactive approach can reveal vulnerabilities before they are exploited by malicious actors.
- Provide Employee Training
Your employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Regular training on cybersecurity best practices can help them recognize and respond to potential threats effectively.
- Phishing Simulations: Conduct mock phishing attacks to test employees’ awareness and response to suspicious emails.
- Ongoing Education: Make cybersecurity training an ongoing part of your employee development program. Regular updates on new threats and best practices can keep security top-of-mind for everyone in your organization.
In my experience, after implementing regular training sessions, we noticed a significant decrease in successful phishing attempts within our company—proof that education pays off!
- Develop a Data Backup Strategy
Having a robust backup strategy is essential for recovering from any data loss incidents—whether due to cyber-attacks or accidental deletions.
- The 3-2-1 Backup Rule: This rule states you should have three copies of your data, on two different media types, with one copy stored offsite. This ensures that even if one backup fails or gets compromised, you still have additional copies available.
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Consider using reputable cloud storage providers that offer automatic backups and encryption features.
Implementing effective data protection strategies is vital for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By focusing on access control, encryption, vulnerability assessments, employee training, and backup solutions, you can create a robust defense against potential breaches. Remember, cybersecurity is not just an IT issue; it’s a business priority that requires ongoing attention and investment.
How Can Technology Enhance Your Data Protection Efforts?
In today’s digital landscape, leveraging technology is essential for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. With the right tools and solutions, you can significantly bolster your security posture and safeguard your organization against potential breaches. In this section, we’ll explore various technologies that can enhance your data protection efforts.
The Role of Technology in Data Protection
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern cybersecurity strategies. It helps automate processes, detect threats in real-time, and streamline compliance with regulations. However, it’s essential to remember that technology alone isn’t a silver bullet; it must be combined with effective policies and employee training for maximum effectiveness.
I’ve seen personally how adopting the right technologies can transform an organization’s approach to data security. When I first implemented advanced security measures in my business, it felt like putting on a suit of armor against cyber threats. Here are some key technologies that can help protect your sensitive data.
- Firewalls and VPNs
Firewalls act as a barrier between your internal network and external threats. They monitor incoming and outgoing traffic and can block unauthorized access to your systems.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW): These advanced firewalls offer additional features like intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and application awareness, providing more robust protection than traditional firewalls.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): A VPN encrypts internet traffic, making it difficult for cybercriminals to intercept sensitive information. This is especially important for remote workers who access company resources from various locations.
In my experience, implementing a VPN for remote employees significantly improved our data security. It ensured that sensitive information transmitted over public networks remained protected.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
IDS and IPS are critical components of a comprehensive security strategy. They monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can take action to block potential threats.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems alert you to potential threats by analyzing traffic patterns and identifying anomalies.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): An IPS not only detects threats but also takes action to prevent them by blocking malicious traffic in real-time.
Using IDS/IPS solutions in my organization helped us detect unusual activities early on, allowing us to respond swiftly before any significant damage occurred.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions
Data Loss Prevention tools help organizations monitor and control the movement of sensitive data across their networks. They can prevent unauthorized sharing or access to critical information.
- Endpoint DLP: This type of DLP focuses on protecting data on endpoints like laptops and mobile devices, ensuring that sensitive information is not leaked outside the organization.
- Network DLP: Network DLP solutions monitor data in transit across the network, preventing unauthorized transfers of sensitive information.
After implementing DLP solutions, I felt more confident that our sensitive data was secure from accidental leaks or intentional breaches.
- Endpoint Security Solutions
With the rise of remote work, endpoint security has become increasingly important. Endpoint security solutions protect devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets from cyber threats.
- Antivirus Software: While basic, up-to-date antivirus software is crucial for detecting and removing malware from devices.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection capabilities by continuously monitoring endpoint activities for signs of malicious behavior.
In my experience, deploying EDR solutions helped us identify potential threats before they could escalate into full-blown attacks.
- Cloud Security Solutions
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services, securing cloud environments is essential for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): CASBs act as intermediaries between users and cloud service providers, enforcing security policies and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Encryption in the Cloud: Many cloud providers offer built-in encryption features to protect data stored in their environments. Always ensure that your cloud provider implements strong encryption practices.
When we transitioned to cloud storage for our sensitive data, we made sure to choose a provider that offered robust security features, including encryption. This decision has been instrumental in maintaining our data integrity.
Leveraging technology is vital for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats effectively. By implementing firewalls, IDS/IPS systems, DLP solutions, endpoint security measures, and cloud security tools, you can create a comprehensive security framework that safeguards your organization’s most valuable assets. Remember that technology should complement your overall cybersecurity strategy—not replace it—and regular updates are essential to keep pace with evolving threats.

What Should Your Incident Response Plan Include?
An effective incident response plan (IRP) is crucial for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. When a cyber-incident occurs, having a well-defined plan can mean the difference between a minor hiccup and a full-blown crisis. An IRP outlines the steps your organization will take to prepare for, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents. In this section, we’ll explore the essential components of an effective incident response plan.
Why You Need an Incident Response Plan
You might be thinking, “Why do I need an incident response plan?” The answer is simple: preparation is key. According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, organizations with an incident response plan are able to contain breaches 27% faster than those without one. This speed can save your business significant time and money.In my experience, creating an IRP was one of the best decisions I made for my business. After witnessing a colleague’s company struggle through a data breach without a plan, I realized that having a structured approach could help mitigate damage and restore operations more swiftly.
Key Components of an Incident Response Plan
- Preparation
Preparation is the foundation of any successful incident response plan. This involves establishing policies, procedures, and training programs to ensure that everyone knows their roles during an incident.
- Incident Response Team: Form a dedicated team responsible for managing incidents. This team should include representatives from IT, legal, human resources, and public relations.
- Training and Drills: Regularly train your incident response team and conduct drills to simulate various scenarios. This practice helps ensure everyone knows their responsibilities when an actual incident occurs.
- Identification
The identification phase involves detecting and determining whether an incident has occurred. Quick identification is crucial for minimizing damage.
- Monitoring Tools: Utilize monitoring tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to analyze logs and detect anomalies in real-time.
- Incident Reporting Procedures: Establish clear procedures for employees to report potential incidents. Encourage a culture where staff feel comfortable reporting suspicious activity without fear of repercussions.
- Containment
Once an incident is identified, the next step is containment. This phase aims to limit the damage caused by the incident and prevent further compromise.
- Short-Term Containment: Implement immediate measures to stop the attack from spreading. This may involve isolating affected systems or disabling compromised accounts.
- Long-Term Containment: Develop strategies to maintain business operations while addressing the underlying issues that led to the incident.
- Eradication
After containing the incident, it’s essential to identify and eliminate the root cause of the breach. This step ensures that similar incidents don’t occur in the future.
- Malware Removal: If malware was involved, ensure it is completely removed from affected systems before bringing them back online.
- Vulnerability Patching: Address any vulnerabilities that were exploited during the incident by applying patches or updates as necessary.
- Recovery
The recovery phase focuses on restoring affected systems and services while ensuring that they are secure before going back online.
- System Restoration: Use backups to restore data lost during the incident, ensuring that all systems are functioning properly before reintroducing them into your network.
- Monitoring Post-Recovery: Continue monitoring systems for any signs of residual threats or unusual activity after recovery.
- Lessons Learned
After resolving an incident, it’s vital to conduct a post-incident review to evaluate what happened and how well your team responded.
- Debriefing Sessions: Hold debriefing sessions with your incident response team to discuss what went well and what could be improved.
- Update Your Plan: Use insights gained from the review to update your incident response plan accordingly. Continuous improvement is key to staying ahead of evolving threats.
A well-crafted incident response plan is essential for effectively protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By preparing in advance, establishing clear procedures for identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and learning from incidents, you can minimize damage and restore operations quickly when faced with a cyber-threat. Remember, being proactive rather than reactive is crucial in today’s ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.

How Can You Foster a Culture of Cybersecurity in Your Organization?
Creating a culture of cybersecurity within your organization is essential for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. A strong cybersecurity culture means that every employee, regardless of their role, understands the importance of data security and actively participates in protecting sensitive information. In this section, we’ll explore effective strategies for fostering this culture and ensuring that cybersecurity becomes a shared responsibility.
Why a Cybersecurity Culture Matters
You might be wondering why focusing on culture is so important. Well, even the most advanced security technologies can fail if employees are not vigilant. According to a study by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), 85% of data breaches involve human error. This statistic highlights the need for a proactive approach to cybersecurity that includes employee engagement and awareness.
In my early days as an entrepreneur, I realized that while I had invested in cutting-edge security tools, my team lacked awareness about basic cybersecurity practices. This gap left us vulnerable to attacks. By fostering a culture of cybersecurity, I was able to significantly reduce our risk profile and enhance our overall security posture.
Strategies to Foster a Cybersecurity Culture
- Leadership Commitment
The commitment of leadership sets the tone for the entire organization. When leaders prioritize cybersecurity, it sends a clear message that everyone should take it seriously.
-
- Lead by Example: As a leader, demonstrate good cybersecurity practices, such as using strong passwords and reporting suspicious emails. Your actions will encourage others to follow suit.
- Communicate the Importance: Regularly communicate the significance of cybersecurity to your team through meetings, newsletters, or internal communications. Share stories about real-world breaches and their consequences to emphasize the need for vigilance.
- Comprehensive Training Programs
Regular training is crucial for educating employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices.
-
- Onboarding Training: Include cybersecurity training as part of your onboarding process for new employees. This ensures they understand their responsibilities from day one.
- Ongoing Education: Offer continuous training sessions that cover new threats and emerging trends in cybersecurity. Consider using online platforms like Coursera or LinkedIn Learning for accessible training resources.
- Encourage Open Communication
Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable discussing cybersecurity concerns is vital for fostering a culture of security.
-
- Establish Reporting Procedures: Make it easy for employees to report suspicious activities or potential breaches without fear of judgment or repercussions.
- Feedback Loops: Encourage feedback on existing policies and procedures. Employees often have valuable insights into how security measures can be improved based on their day-to-day experiences.
- Gamify Cybersecurity Awareness
Making learning fun can significantly enhance engagement with cybersecurity training.
-
- Quizzes and Competitions: Organize quizzes or competitions related to cybersecurity best practices. Offering small prizes can motivate participation and make learning enjoyable.
- Simulated Phishing Attacks: Conduct simulated phishing attacks to test employees’ awareness and response capabilities. Provide immediate feedback on their performance to reinforce learning.
- Recognize and Reward Good Practices
Recognizing employees who demonstrate good cybersecurity practices can reinforce positive behavior across the organization.
-
- Spotlight Achievements: Highlight individuals or teams who successfully identify threats or contribute to improving security measures during company meetings or newsletters.
- Incentives: Consider implementing incentive programs that reward employees for completing training modules or reporting potential threats.
Fostering a culture of cybersecurity is essential for effectively protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By prioritizing leadership commitment, providing comprehensive training, encouraging open communication, gamifying awareness efforts, and recognizing good practices, you can create an environment where every employee feels responsible for data security. Remember, in today’s digital landscape, everyone plays a role in safeguarding sensitive information—make sure your team is equipped to do so!
Final Thoughts on Protecting Sensitive Data
As we wrap up this comprehensive guide on protecting sensitive data from cyber threats, it’s essential to reflect on the key takeaways and the proactive steps you can implement to safeguard your organization. In an age where data breaches are increasingly common, being prepared is not just an option; it’s a necessity.
The Cybersecurity Landscape
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging daily. Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a large corporation, understanding the risks and implementing effective strategies is crucial. The statistics are sobering: according to IBM, the average time to identify and contain a breach is 287 days. This delay can lead to significant financial losses and damage to your reputation.
In my journey as an entrepreneur, I’ve witnessed first-hand how quickly a cyber-incident can escalate. By prioritizing data protection and fostering a culture of cybersecurity within my organization, I’ve been able to mitigate risks and respond more effectively to potential threats.
Key Strategies for Protection
Throughout this article, we’ve discussed several strategies for protecting sensitive data, including:
- Identifying Sensitive Data: Knowing what constitutes sensitive information is the first step in safeguarding it.
- Effective Data Protection Strategies: Implementing access controls, encryption, regular vulnerability assessments, employee training, and backup solutions are all vital components of a robust security framework.
- Leveraging Technology: Utilizing firewalls, IDS/IPS systems, DLP solutions, endpoint security measures, and cloud security tools can significantly enhance your data protection efforts.
- Developing an Incident Response Plan: Having a well-defined incident response plan ensures that your organization can respond swiftly and effectively to cyber incidents.
- Fostering a Cybersecurity Culture: Engaging employees at all levels in cybersecurity practices creates a shared responsibility for protecting sensitive data.
Moving Forward
As you move forward in your cybersecurity journey, keep these principles in mind:
- Stay Informed: Cyber threats are constantly changing. Stay updated on the latest trends and best practices by following reputable cybersecurity blogs and news sources.
- Regularly Review Your Policies: Your data protection strategies should evolve as your organization grows and as new threats emerge. Regularly review and update your policies to ensure they remain effective.
- Invest in Training: Cybersecurity training should not be a one-time event. Make it an ongoing part of your organizational culture to keep employees informed and vigilant.
- Engage with Experts: Don’t hesitate to consult with cybersecurity professionals or hire third-party services for vulnerability assessments or penetration testing. Their expertise can provide valuable insights into your security posture.
In conclusion, protecting sensitive data from cyber threats is an ongoing commitment that requires vigilance, education, and proactive measures. By implementing the strategies discussed in this article and fostering a culture of cybersecurity within your organization, you can significantly reduce your risk of data breaches and ensure that your sensitive information remains secure. Remember, the cost of prevention is far less than the cost of recovery after a breach. Take action today to protect what matters most—your sensitive data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What types of data are considered sensitive?
Sensitive data includes personal identifiable information (PII) such as names, Social Security numbers, financial information like credit card details, health records, and proprietary business information. Understanding what constitutes sensitive data is crucial for protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. - How can I tell if my organization is at risk of a data breach?
Signs that your organization may be at risk include outdated software, lack of employee training on cybersecurity practices, and previous incidents of phishing or malware attacks. Regular vulnerability assessments can help identify weaknesses in your security posture. - What is multi-factor authentication, and why is it important?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a system. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised. - How often should I train my employees on cybersecurity practices?
Employee training should be conducted regularly—at least annually, with additional training sessions whenever new threats emerge or policies change. Ongoing education keeps cybersecurity top-of-mind for everyone in the organization. - What are some common signs of a cyber-attack?
Common signs include unusual network activity, unexpected system crashes, slow performance, unauthorized access attempts, and receiving strange emails or alerts. If you notice any of these signs, it’s essential to investigate immediately. - How can I ensure compliance with data protection regulations?
Familiarize yourself with relevant regulations such as GDPR or CCPA and implement necessary policies and procedures to comply. Regular audits and employee training can help maintain compliance and ensure that sensitive data is handled appropriately. - What should I do if I suspect a data breach has occurred?
If you suspect a breach, immediately activate your incident response plan. Contain the breach by isolating affected systems, assess the extent of the damage, notify relevant stakeholders, and report the incident to authorities if required. - Are there specific tools recommended for data encryption?
Yes! Some popular encryption tools include VeraCrypt for file encryption, BitLocker for full disk encryption (Windows), and FileVault for macOS. Additionally, many cloud storage providers offer built-in encryption features for data at rest and in transit. - What steps can I take to secure my home office network?
To secure your home office network, use strong passwords for your Wi-Fi network, enable WPA3 encryption if available, keep your router firmware updated, and consider using a VPN for added security when accessing company resources remotely. - How can I stay updated on the latest cybersecurity threats?
Follow reputable cybersecurity blogs and news sites like Krebs on Security or the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). Joining professional networks or forums can also provide valuable insights into emerging threats and best practices.
This FAQ section aims to address common concerns related to protecting sensitive data from cyber threats while providing actionable insights that resonate with readers at all levels of expertise.