Introduction
In an age where digital transformation is reshaping how businesses operate, the importance of robust security measures cannot be overstated. Understanding how to implement multi-factor authentication is critical. With increasing reliance on online platforms and cloud-based services, organizations are more vulnerable than ever to cyber threats.
Data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access have become common headlines, leaving businesses scrambling to protect their sensitive information and maintain customer trust. One of the most effective ways to bolster security in this digital landscape is through Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
MFA adds an essential layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods before granting access to accounts or systems. This means that even if a hacker manages to steal a password, they would still need additional verification—making it significantly harder for them to gain unauthorized access.
Why Multi-Factor Authentication Matters
The statistics surrounding cybercrime are alarming. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is expected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. Furthermore, the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report reveals that 81% of data breaches are caused by stolen or weak passwords. These figures underscore the urgent need for businesses to adopt stronger security measures.
In my own journey as a tech-savvy entrepreneur, I’ve witnessed the devastating impact of inadequate security practices. A few years back, a client of mine experienced a significant data breach due to weak password policies. It was a wake-up call for us all; we realized that relying solely on passwords was no longer sufficient. This experience catalyzed our commitment to implementing MFA across all our platforms—a decision that ultimately saved us from potential disasters.
What You Will Learn
In this blog post, we will explore the ins and outs of Multi-Factor Authentication, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its importance and implementation. We’ll cover:
- What MFA is and how it works: We’ll break down the different types of authentication factors and explain how they enhance account security.
- Why MFA is essential for businesses: We’ll discuss the various cyber threats organizations face and the regulatory requirements that make MFA indispensable.
- How to implement MFA: You’ll receive a step-by-step guide on assessing your organization’s needs, choosing the right solution, and rolling out MFA effectively.
- Best practices for enhancing account security with MFA: We’ll share actionable tips to ensure your MFA implementation is successful and user-friendly.
- Common challenges in MFA implementation: Learn about potential obstacles you may encounter and how to overcome them.
- Measuring the success of your MFA implementation: Discover key performance indicators (KPIs) to track effectiveness and areas for improvement.
- Future trends in MFA: Stay ahead of the curve by understanding emerging technologies and strategies in digital security.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid foundation in Multi-Factor Authentication and be well-equipped to enhance your organization’s security posture. Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a larger enterprise, implementing MFA can significantly reduce your risk of cyber threats and protect your valuable assets.
So let’s dive in and explore why Multi-Factor Authentication is the must-have security measure every business needs! Would you like me to assist with any other specific sections or details?
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA, is a security measure that adds an extra layer of protection when accessing accounts or systems. Instead of just relying on a password, MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access. This could be something they know (like a password), something they have (like a smartphone or hardware token), or something they are (like a fingerprint).
Why Use Multi-Factor Authentication?
In my experience, passwords alone just don’t cut it anymore. Think about it: how many times have you heard about someone getting their account hacked because their password was too weak or because they reused it across multiple sites? It’s scary!
According to a report by Verizon, 81% of data breaches are caused by stolen or weak passwords. That’s where MFA comes in. By implementing multi-factor authentication, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Even if someone manages to get hold of your password, they still need that second factor to log in. This makes it much harder for cybercriminals to succeed.
Types of Authentication Factors
There are three main types of factors used in MFA:
- Something You Know: This is typically your password or a PIN. It’s the first line of defense but not enough on its own.
- Something You Have: This could be your smartphone, a hardware token, or even an email account. For example, when you log into your bank account and receive a text message with a code, that’s using something you have.
- Something You Are: This involves biometrics like fingerprints or facial recognition. Many smartphones today use this technology to unlock devices.
Real-World Example
Let me share a quick story. A few years back, I was working with a client who had just experienced a data breach due to weak passwords across their organization. After the incident, we decided to implement MFA as part of our security strategy. We chose an MFA solution that used both SMS codes and biometric authentication. The results were fantastic! Not only did we see a significant drop in unauthorized access attempts, but employees also felt more secure knowing their accounts were better protected. It was a win-win situation!

For more detailed information on the types of authentication methods available and how they can enhance account security, check out this article on Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
Why is Multi-Factor Authentication Essential for Businesses?
In today’s digital landscape, security is more important than ever. Cyber threats are evolving rapidly, and businesses must stay ahead of the curve. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) plays a crucial role in this fight against cybercrime. Let’s dive into why MFA is essential for businesses and how it can protect your valuable assets.
How Does MFA Protect Against Cyber Threats?
Cyber threats are everywhere—phishing attacks, ransomware, and data breaches are just a few examples. In fact, according to the 2023 Cybersecurity Almanac, there will be an estimated 33 billion records stolen by cybercriminals by 2023. That’s staggering!
When I first started my journey in tech entrepreneurship, I underestimated the importance of strong security measures. I thought that having a solid password was enough. But after experiencing a phishing attack that compromised several accounts, I learned my lesson the hard way.
Implementing MFA was one of the best decisions I made for my business. MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Even if a hacker manages to steal your password through phishing or other means, they would still need that second factor to log in. This extra layer of security can deter many cybercriminals who are looking for easy targets.
What Are the Regulatory Requirements for MFA?
In addition to protecting against threats, many industries have regulatory requirements that mandate the use of MFA. For example:
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): If you handle credit card transactions, you’re required to implement MFA for remote access to your systems.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Healthcare organizations must secure patient information, and MFA is often a key component of compliance.
When I worked with a healthcare start-up, we had to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations. Implementing MFA not only helped us meet these requirements but also built trust with our clients. They knew we were serious about protecting their sensitive information.

For more insights on cybersecurity regulations and the importance of MFA, you can read this informative piece on NIST’s website.
How to Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) in your organization is a crucial step toward enhancing your security posture. While it may seem daunting at first, breaking it down into manageable steps can make the process smoother. In this section, I’ll share a comprehensive MFA implementation guide based on my experiences and best practices that can help you get started.
Step 1: Assess Your Organization’s Needs and Risks
Before diving into the implementation of MFA, it’s vital to assess your organization’s specific needs and the risks you face. Consider the following questions:
- What sensitive data do you handle?
- Who needs access to this data?
- What are the potential consequences of a data breach?
In my experience, conducting a risk assessment helped us identify which accounts needed MFA the most. For instance, administrative accounts or those with access to sensitive customer data should be prioritized.
Step 2: Choose the Right MFA Solution
Once you’ve assessed your needs, it’s time to choose an MFA solution that fits your organization. There are many options available, ranging from SMS-based authentication to more advanced biometric methods. Here are some popular types:
- SMS or Email Codes: Users receive a one-time code via text or email.
- Authenticator Apps: Applications like Google Authenticator or Authy generate time-sensitive codes.
- Hardware Tokens: Physical devices that generate codes or provide a secure way to log in.
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint scanners or facial recognition technology.
When selecting an MFA solution, consider factors like ease of use, integration capabilities with existing systems, and cost. I remember when we chose an authenticator app for our team; it was user-friendly and integrated seamlessly with our existing software.
Step 3: Define Your MFA Policies and Procedures
Having clear policies and procedures is essential for successful MFA implementation. This includes defining:
- Which accounts require MFA
- The types of authentication methods allowed
- How often users need to authenticate
Creating a policy document can help communicate these guidelines effectively. During our implementation process, we drafted a policy that outlined who was required to use MFA and under what circumstances. This clarity helped everyone understand their responsibilities.
Step 4: Educate Your Users on MFA Importance and Usage
User education is critical for successful adoption. Many employees may be resistant to change or unsure about how to use new technology. Here’s how to ease those concerns:
- Conduct Training Sessions: Organize workshops to explain what MFA is and how it protects them.
- Provide Resources: Create easy-to-follow guides or videos demonstrating how to set up and use MFA.
- Encourage Questions: Foster an environment where employees feel comfortable asking questions about security practices.
I recall hosting a training session where we demonstrated the setup process for our chosen authenticator app. It was great to see employees engaging and asking questions!
Step 5: Roll Out MFA in Phases (Pilot Testing)
Instead of implementing MFA across the board all at once, consider rolling it out in phases. Start with a pilot group—perhaps your IT department or a small team that is tech-savvy. This allows you to gather feedback and make adjustments before a full rollout. During our pilot phase, we discovered some technical issues that needed addressing before expanding access to the entire organization. This approach not only minimized disruption but also allowed us to refine our processes.
Step 6: Monitor and Adjust Based on Feedback and Performance
After implementing MFA, it’s important to monitor its effectiveness continuously. Keep track of metrics such as:
- Adoption rates among employees
- Number of unauthorized access attempts
- User feedback regarding their experience
Regularly reviewing these metrics will help you identify areas for improvement. For instance, if users are struggling with a particular authentication method, consider offering alternatives or additional training.
For further reading on choosing the right MFA solution and implementation strategies, check out this detailed guide on CSO Online.
Best Practices for Enhancing Account Security with MFA
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a significant step toward securing your business, but it’s just the beginning. To truly enhance account security, you need to follow best practices that ensure MFA is effective and user-friendly.
Here, I’ll share some of the best practices I’ve encountered in my journey as a tech entrepreneur, along with insights that can help you strengthen your security posture.
Use a Variety of Authentication Methods
One of the most effective ways to enhance account security is by using a variety of authentication methods. Relying solely on one method can create vulnerabilities. Consider implementing a mix of the following:
- SMS Codes: While convenient, SMS codes can be intercepted. It’s best to use them as part of a multi-layered approach rather than the only method.
- Authenticator Apps: Apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator generate time-sensitive codes that are more secure than SMS.
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint scans or facial recognition provide a high level of security and are increasingly user-friendly.
In my own experience, we started by using SMS codes for MFA. However, after learning about the risks associated with this method, we transitioned to authenticator apps and biometric methods for our most sensitive accounts. This layered approach made us feel much more secure.
Implement Conditional Access Policies
Not all users require the same level of access, and not every situation warrants the same authentication requirements. Conditional access policies allow you to make decisions based on user context. For example:
- Location-Based Access: If an employee tries to log in from an unusual location, require an additional authentication factor.
- Device-Based Access: If a user is attempting to access sensitive data from an unrecognized device, prompt for more verification.
When I worked with a financial services company, we implemented conditional access based on user roles and locations. This helped us tighten security without burdening users who were logging in from familiar devices and locations.
Regularly Review and Update MFA Configurations
MFA is not a set-it-and-forget-it solution. Regularly reviewing and updating your MFA configurations is essential to maintaining strong security. Here are some key areas to focus on:
- User Access Reviews: Periodically review who has access to sensitive systems and ensure that only necessary personnel have MFA enabled.
- Authentication Method Reviews: As technology evolves, so do authentication methods. Stay informed about new technologies and consider adopting them if they offer better security.
- Policy Updates: As your organization grows or changes, your MFA policies may need adjustments. Regularly revisit these policies to ensure they remain relevant.
I learned this lesson when our company underwent significant growth. We had to reassess our user access levels and update our MFA policies accordingly to accommodate new employees while ensuring that sensitive data remained protected.
Encourage Strong Password Practices Alongside MFA
While MFA adds an extra layer of security, it’s still important to encourage strong password practices among employees. Here are some tips you can share:
- Use Complex Passwords: Encourage employees to create passwords that are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid Password Reuse: Remind users not to reuse passwords across different accounts. A breach on one site can compromise others if passwords are reused.
- Utilize Password Managers: Recommend using password managers to help employees create and store complex passwords securely.
In my experience, combining strong password practices with MFA creates a robust defense against unauthorized access. It’s like having two locks on your door instead of one!
Provide Ongoing User Training and Support
Education doesn’t stop after the initial rollout of MFA. Ongoing training and support are crucial for maintaining high levels of security awareness among employees. Here’s how you can foster a culture of security:
- Regular Training Sessions: Schedule periodic training sessions to keep employees updated on best practices for using MFA effectively.
- Share Real-Life Examples: Use case studies or news articles about recent breaches to highlight the importance of MFA and good security habits.
- Create a Support System: Establish a help desk or point of contact for employees who have questions or encounter issues with MFA.
I found that regular training sessions not only kept everyone informed but also helped build a community focused on security within our organization. Employees felt empowered to ask questions and share their experiences—creating an environment where everyone was invested in protecting our data.
For more insights into best practices for implementing MFA effectively, check out this article on TechTarget.
Common Challenges in MFA Implementation
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a vital step toward enhancing your organization’s security, but it’s not without its challenges. Understanding these obstacles can help you navigate the implementation process more smoothly. In this section, I’ll share some common challenges I’ve encountered and provide practical solutions based on real-world experiences.
User Resistance and Education Challenges
One of the most significant hurdles in implementing MFA is user resistance. Many employees view MFA as an inconvenience, especially if they’re accustomed to logging in with just a password. This resistance can lead to pushback during the rollout phase. How to Overcome User Resistance:
- Communicate the Benefits: Clearly explain why MFA is necessary. Share statistics about data breaches and how MFA can protect sensitive information. When employees understand the risks, they’re more likely to embrace the change.
- Offer Incentives: Consider providing incentives for early adopters or those who successfully set up MFA. This could be as simple as recognition in a team meeting or a small reward.
- Make It Easy: Choose an MFA solution that is user-friendly. If the setup process is complicated or time-consuming, employees may resist using it altogether.
When we first rolled out MFA at my company, we faced significant pushback from some employees. By hosting a town hall meeting where we discussed the importance of security and shared real-life examples of breaches, we were able to alleviate concerns and encourage adoption.
Balancing Security with User Experience
Another challenge is finding the right balance between security and user experience. While MFA enhances security, it can also create friction in the login process. If users find it too cumbersome, they may seek ways to bypass it. How to Balance Security and User Experience:
- Tailor MFA Requirements: Implement different levels of MFA based on user roles and access needs. For example, high-level executives may need stricter authentication measures than regular employees accessing less sensitive data.
- Use Adaptive Authentication: Consider solutions that adjust authentication requirements based on risk factors such as location, device, or behavior patterns. This way, users who log in from familiar locations may not need to provide additional verification.
- Gather Feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from users about their experiences with MFA. Use this information to make adjustments that improve usability without compromising security.
In our organization, we adopted adaptive authentication for our executive team while keeping a straightforward MFA process for regular employees. This approach minimized friction while maintaining high security for sensitive accounts.
Technical Integration Issues with Existing Systems
Integrating MFA into existing systems can pose technical challenges, especially if your organization relies on legacy systems or uses multiple software platforms. Compatibility issues can lead to delays and frustration during implementation. How to Address Technical Integration Issues:
- Conduct a Compatibility Assessment: Before choosing an MFA solution, assess its compatibility with your current systems. This will help you avoid surprises during implementation.
- Engage IT Early: Involve your IT team from the beginning of the process. Their expertise can help identify potential integration challenges and streamline the setup process.
- Test Thoroughly: Before rolling out MFA organization-wide, conduct thorough testing within a controlled environment. This allows you to identify and resolve any technical issues before they affect all users.
I remember when we integrated an MFA solution with our customer relationship management (CRM) system. Initially, we faced some compatibility issues that delayed the rollout. By involving our IT team early on and conducting extensive testing before launch, we were able to resolve these challenges efficiently.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Once MFA is implemented, ongoing maintenance and support are crucial for ensuring its effectiveness over time. Without proper attention, even the best security measures can become outdated or ineffective. How to Ensure Ongoing Maintenance:
- Regularly Review Access Logs: Monitor access logs to identify any unusual activity or potential breaches. This proactive approach can help you catch issues before they escalate.
- Stay Informed About Updates: Keep your MFA solutions updated with the latest security patches and features. Cyber threats evolve rapidly, so staying current is essential for maintaining strong defenses.
- Provide Continuous Support: Establish a support system for users who encounter issues with MFA. Quick resolution of problems will encourage continued use and foster a culture of security awareness.
At my company, we set up regular check-ins to review access logs and discuss any potential issues related to MFA usage. This not only kept us informed but also reinforced our commitment to maintaining strong security practices across the organization.
Measuring the Success of Your MFA Implementation
Once you’ve implemented Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), it’s essential to measure its effectiveness. This not only helps you understand how well your security measures are working but also identifies areas for improvement. In this section, I’ll share practical strategies for evaluating the success of your MFA implementation based on my experiences.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Monitor
To gauge the effectiveness of your MFA strategy, you should establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with your security goals. Here are some important KPIs to consider:
- Adoption Rate: Track how many users have successfully set up MFA. A low adoption rate may indicate resistance or confusion among employees.
- Number of Unauthorized Access Attempts: Monitor the frequency of unauthorized access attempts before and after implementing MFA. A significant decrease would indicate that your MFA strategy is effective.
- User Feedback and Satisfaction: Regularly survey users about their experiences with MFA. This qualitative data can provide insights into how well the system is working and where improvements are needed.
- Support Ticket Volume: Keep an eye on the number of support tickets related to MFA issues. A high volume may suggest that users are struggling with the process or experiencing technical difficulties.
When we rolled out MFA at my company, we established these KPIs and reviewed them monthly. This allowed us to quickly identify any issues and make necessary adjustments.
Conducting Regular Security Audits
In addition to monitoring KPIs, conducting regular security audits can provide a comprehensive view of your MFA implementation’s effectiveness. Here’s how to approach this:
- Schedule Periodic Audits: Set a schedule for regular audits—quarterly or biannually—to review your MFA processes and policies.
- Assess Compliance with Policies: Ensure that all users are following established MFA policies and procedures. This includes verifying that all required accounts have MFA enabled.
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Use audits to identify any potential weaknesses in your MFA setup, such as outdated authentication methods or gaps in user training.
During one of our audits, we discovered that a small percentage of our team had not enabled MFA on their accounts due to lack of awareness. This prompted us to conduct additional training sessions focused on the importance of compliance with our security policies.
Importance of User Feedback
User feedback is invaluable in measuring the success of your MFA implementation. Engaging employees can help you identify pain points and areas for improvement. Here’s how to effectively gather feedback:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Create anonymous surveys to encourage honest feedback about the MFA process. Ask specific questions about usability and any challenges faced during setup or daily use.
- Focus Groups: Organize focus groups with a diverse set of employees to discuss their experiences with MFA in detail. This can provide deeper insights than surveys alone.
- Open Communication Channels: Encourage employees to share their thoughts and experiences openly, whether through company meetings or dedicated communication platforms.
After implementing an anonymous survey about our MFA experience, we received constructive feedback that led us to simplify the onboarding process for new employees. This change resulted in higher adoption rates moving forward.
Adjusting Based on Performance Data
Once you’ve gathered data from KPIs and user feedback, it’s crucial to act on this information. Here’s how to adjust your strategy based on performance:
- Identify Trends: Look for patterns in your data that may indicate broader issues, such as a spike in support tickets related to a specific authentication method.
- Implement Changes: Use insights gained from audits and feedback to make necessary adjustments—whether it’s enhancing user training, changing authentication methods, or refining policies.
- Communicate Changes: Keep users informed about any changes made based on their feedback. This not only fosters trust but also encourages continued engagement with security practices.
For example, after noticing an uptick in support tickets related to SMS codes, we decided to phase out this method in favor of authenticator apps and biometric options. We communicated this change clearly, explaining the reasons behind it and providing additional training resources.
For more insights into measuring the effectiveness of your security measures, check out this article on Security Magazine.
Future Trends in Multi-Factor Authentication
As technology evolves, so do the methods and strategies for securing sensitive information. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is no exception. Staying informed about the latest trends in MFA can help your organization adapt to emerging threats and improve overall security. In this section, I’ll explore some future trends in MFA that I believe will shape the landscape of digital security.
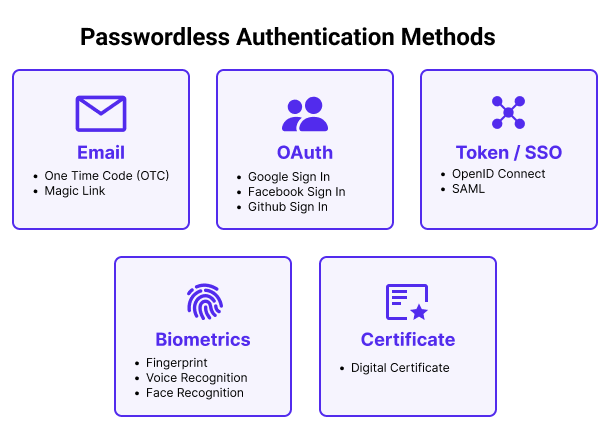
The Rise of Passwordless Authentication
One of the most significant trends we’re seeing is the shift toward passwordless authentication. As cybercriminals continue to exploit weak passwords, many organizations are looking for alternatives that eliminate passwords altogether. Passwordless authentication methods include:
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice recognition are becoming more common as secure and user-friendly alternatives to traditional passwords.
- Magic Links: Some services send users a one-time link via email or SMS, allowing them to log in without entering a password.
- Security Keys: Hardware tokens like YubiKey provide a secure way to authenticate without relying on passwords.
In my experience, transitioning to passwordless methods can significantly enhance user experience while also improving security. We piloted biometric authentication for our mobile app, and users loved the convenience of logging in with their fingerprints instead of remembering complex passwords.
Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is making its way into MFA solutions, helping organizations enhance their security measures. AI can analyze user behavior and identify patterns that may indicate suspicious activity. Here’s how AI is being integrated into MFA:
- Behavioral Biometrics: This technology analyzes how users interact with devices—such as typing speed or mouse movements—to create a unique profile. If a login attempt deviates significantly from this profile, additional authentication may be required.
- Risk-Based Authentication: AI can assess risk factors in real-time during login attempts, adjusting authentication requirements based on the perceived risk level. For example, if a user logs in from a new location or device, the system may prompt for additional verification.
I’ve seen firsthand how AI can bolster security measures. Implementing risk-based authentication allowed us to streamline the login process for regular users while maintaining heightened security for high-risk scenarios.
Integration with Identity and Access Management (IAM) Solutions
The integration of MFA with Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions is becoming increasingly important. IAM systems manage user identities and access rights across an organization, and combining these with MFA can enhance security significantly.
- Centralized Management: By integrating MFA into IAM solutions, organizations can manage user access and authentication methods from a single platform, simplifying administration and monitoring.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Many IAM solutions offer SSO capabilities combined with MFA, allowing users to log in once and gain access to multiple applications securely without needing to re-enter credentials.
When we integrated our MFA solution with our IAM system, it streamlined our processes significantly. Employees could access various applications without repeated logins while still benefiting from robust security measures.
Growing Focus on User Experience
As organizations adopt more advanced security measures, there’s a growing emphasis on maintaining a positive user experience. Security shouldn’t come at the expense of usability. Here are some ways companies are focusing on user experience:
- Simplified Processes: Organizations are working to make MFA setup and usage as seamless as possible. This includes offering clear instructions and support during onboarding.
- User-Centric Design: MFA solutions are increasingly designed with the end-user in mind, ensuring that they are intuitive and easy to navigate.
- Adaptive Security Measures: By implementing adaptive authentication methods that adjust based on user context, organizations can provide a smoother experience while still maintaining high security standards.
I’ve learned that prioritizing user experience during our MFA implementation led to higher adoption rates and fewer support requests. Employees appreciated having a straightforward process that didn’t feel cumbersome.
Embracing Decentralized Identity Solutions
Decentralized identity solutions are emerging as a potential game-changer in the realm of digital identity management. These solutions allow users to control their own identities without relying on centralized authorities or databases. Here’s how they work:
- Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI): Users can create and manage their own digital identities using blockchain technology, providing a secure way to authenticate without relying on traditional methods.
- Verifiable Credentials: Users can present verifiable credentials (like age or employment status) without sharing sensitive personal information, enhancing privacy while still allowing for secure access.
While still in its infancy, I believe decentralized identity solutions have the potential to reshape how we think about authentication and data privacy. As these technologies mature, they could offer even more secure options for businesses looking to implement MFA.
Final Thoughts on Multi-Factor Authentication as a Security Measure
As we’ve explored throughout this blog post, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is no longer just an optional security measure; it’s a necessity for businesses of all sizes in today’s digital landscape. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats make it imperative to adopt robust security practices to protect sensitive data and maintain customer trust. Here are some key takeaways that highlight the importance of MFA and its role in enhancing security.
The Importance of Proactive Security Measures
In my experience, waiting for a security breach to occur before taking action is a recipe for disaster. MFA serves as a proactive measure that can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. By requiring multiple forms of verification, you create a formidable barrier against cybercriminals who rely on stolen credentials.
For instance, after implementing MFA at my company, we noticed a dramatic decrease in unauthorized access attempts. It was evident that our proactive approach was paying off. This shift not only protected our sensitive data but also instilled confidence in our clients, knowing we were serious about safeguarding their information.
Building a Culture of Security Awareness
Implementing MFA is just one piece of the puzzle. To truly enhance security, organizations must foster a culture of security awareness among employees. This means providing ongoing training, encouraging open discussions about security practices, and making security a shared responsibility.
I’ve seen how creating an environment where employees feel empowered to ask questions and share concerns can lead to better security outcomes. When everyone understands the importance of MFA and their role in maintaining security, it becomes a collective effort rather than an isolated task.
Embracing Continuous Improvement
Security is not static; it’s an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Regularly reviewing your MFA implementation, staying informed about emerging threats, and adapting your strategies accordingly are essential for maintaining strong defenses.
For example, as new authentication methods emerge—such as biometric options or AI-driven solutions—consider how they can enhance your existing MFA strategy. I’ve found that staying ahead of the curve by adopting innovative technologies not only improves security but also enhances user experience.
The Future is Bright for MFA
As we look to the future, it’s clear that MFA will continue to evolve alongside advancements in technology. The rise of passwordless authentication, AI integration, and decentralized identity solutions are just a few trends that promise to reshape how we think about digital security.
By embracing these innovations and adapting your MFA strategy accordingly, you can ensure that your organization remains resilient against evolving threats. The journey toward enhanced security may have its challenges, but the benefits far outweigh the hurdles.
Take Action Today
If you haven’t already implemented Multi-Factor Authentication in your organization, now is the time to take action. Start by assessing your current security posture, choosing the right MFA solution, and educating your employees about its importance. Remember, every step you take toward improving security contributes to safeguarding your organization’s future.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.s)
-
What is multi-factor authentication?
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security measure requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to accounts or systems.
-
How does multi-factor authentication work?
- MFA works by combining something you know (like a password), something you have (like a smartphone), and something you are (like a fingerprint) for secure access.
-
Why should my business use multi-factor authentication?
- MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access by adding an extra layer of protection beyond just passwords.
-
What are the different types of factors used in MFA?
- The three main types are knowledge factors (passwords), possession factors (smartphones or tokens), and inherence factors (biometrics).
-
How do I choose an MFA vendor?
- Consider factors such as ease of integration with existing systems, user experience, cost, and support options when selecting an MFA vendor.
-
Can I implement MFA without disrupting my current workflows?
- Yes! By rolling out MFA in phases and providing user training, you can minimize disruptions during implementation.
-
What are common challenges businesses face when implementing MFA?
- Challenges include user resistance, balancing security with user experience, technical integration issues, and ongoing maintenance needs.
-
How can I educate my employees about multi-factor authentication?
- Conduct training sessions, provide resources like guides or videos, and encourage open communication about security practices.
-
What are the best practices for maintaining an effective MFA system?
- Regularly review access logs, keep solutions updated with patches, provide continuous support, and gather user feedback for improvements.
-
How often should I review my multi-factor authentication policies?
- It’s advisable to review your policies at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in your organization or technology landscape.
This concludes our comprehensive guide on Multi-Factor Authentication! If you have any questions or need further assistance on how to implement multi-factor authentication in your organization, feel free to reach out!