Introduction
In today’s hyper-connected digital landscape, the threat of cyber incidents looms larger than ever. This is where creating a cybersecurity incident response plan becomes crucial. From small businesses to large enterprises, organizations are increasingly vulnerable to a wide array of cyber threats, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and phishing scams. The consequences of these incidents can be devastating—not just in terms of financial loss but also regarding reputational damage and customer trust.
Think of it as your organization’s emergency plan for the digital world. Just like you wouldn’t wait for a fire to break out before deciding how to escape, you shouldn’t wait for a cyber incident to figure out how to respond. An incident response plan provides a structured approach for detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity threats.
Having experienced the chaos of a cyber incident firsthand, I can attest to the importance of being prepared. In my early days as a tech entrepreneur, our company faced a significant data breach that caught us completely off guard. Without a clear plan in place, our team scrambled to figure out what to do while our customers were left in the dark. The aftermath was not only costly but also damaging to our reputation—a hard lesson learned too late.
This blog post will guide you through the essential steps for creating an effective cybersecurity incident response plan. We will explore the key components of incident response strategies, discuss how to build an effective incident response team, and delve into practical tools and frameworks that can enhance your organization’s readiness against cyber threats.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to prepare for the worst and protect your organization from potential cyber disasters. So let’s dive in and start building a solid foundation for your cybersecurity incident response plan! Would you like me to proceed with any specific section next or make any adjustments?
What is Creating a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan?
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan is like having a fire drill for your digital assets. Just as you wouldn’t wait for a fire to break out before deciding how to escape, you shouldn’t wait for a cyber incident to figure out how to respond. An effective incident response plan is crucial for any organization that wants to protect its data and maintain its reputation in the face of increasing cyber threats.
Understanding the Basics
At its core, creating a cybersecurity incident response plan outlines the steps your organization will take when a cyber incident occurs. This includes everything from identifying the incident to recovering from it. The goal? To minimize damage, reduce recovery time, and limit the impact on your business operations.
I remember when I first started my journey in tech entrepreneurship. We faced a significant data breach that caught us completely off guard. We didn’t have a plan in place, and the chaos that followed was overwhelming. Our team scrambled to figure out what to do while our customers were left in the dark. It was a learning experience that taught me just how essential it is to have a solid plan in place.
Why is It Important?
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan is essential for several reasons:
- Minimizing Damage: When an incident occurs, every second counts. Having a predefined plan allows your team to act quickly and effectively, minimizing potential damage.
- Reducing Recovery Time: The faster you can respond, the quicker you can return to normal operations. A well-structured plan helps streamline recovery efforts.
- Building Trust: Customers want to know that their data is safe with you. By demonstrating that you have a solid incident response plan, you can build trust and confidence in your brand.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries have regulations requiring organizations to have an incident response plan in place. Not having one could lead to legal issues and hefty fines.
Key Components of an Incident Response Plan
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan involves several key components:
- Preparation: This is where you define your policies and procedures for handling incidents. You’ll want to establish roles and responsibilities within your team and ensure everyone knows their part.
- Detection and Analysis: This phase involves identifying potential incidents and assessing their impact. Utilizing threat intelligence can help improve your detection capabilities.
- Containment, Eradication, and Recovery: Once an incident is confirmed, your team needs to contain it to prevent further damage, eradicate the threat, and recover systems back to normal operations.
Real-World Application
In my experience, creating a cybersecurity incident response plan isn’t just about writing down procedures; it’s about building a culture of preparedness within your organization. For instance, we conducted regular training sessions where team members participated in simulated cyber incidents. These drills helped everyone understand their roles better and highlighted areas where we needed improvement.
I found that involving different departments—like IT, HR, and PR—was crucial in crafting an effective plan. Each department brings unique insights into how incidents might affect their areas, which ultimately leads to a more comprehensive strategy.
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan is not just a checkbox on your compliance list; it’s an essential strategy for protecting your organization from cyber threats. By preparing ahead of time, you can minimize damage, reduce recovery time, and build trust with your customers.
Why is Creating a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan Essential?
In today’s digital landscape, creating a cybersecurity incident response plan is not just a good idea; it’s a necessity. Cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and the consequences of not being prepared can be devastating. Let’s explore why having an effective incident response plan is essential for every organization.
The Growing Threat Landscape
Cybersecurity incidents are on the rise. According to a report from Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is expected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. Just think about that for a moment—$10.5 trillion! This staggering figure highlights the urgency for businesses to take proactive measures.
I recall the time when our company was targeted by a phishing attack that nearly compromised our sensitive data. Thankfully, we had just begun developing our incident response plan, which allowed us to quickly identify the threat and mitigate the damage. If we hadn’t been working on that plan, the outcome could have been catastrophic.

The Role of Incident Response Plans
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan plays a critical role in minimizing damage and recovery time during an incident. Here’s how:
- Quick Identification: With an established plan, your team knows exactly what steps to take when an incident occurs. This allows for quicker identification of the issue, which is crucial in preventing further damage.
- Streamlined Communication: A well-defined plan includes communication protocols that ensure everyone knows their roles and responsibilities during an incident. This reduces confusion and helps maintain order.
- Damage Control: The faster you can contain an incident, the less damage it will cause. An effective response plan outlines containment strategies that can be implemented immediately.
- Recovery Strategies: After an incident has been contained, your team needs to focus on recovery. A solid plan provides clear steps for restoring systems and data to their normal state.
Real-Life Examples of Consequences
The consequences of not having a cybersecurity incident response plan can be severe. For instance, consider the infamous Equifax data breach in 2017, which exposed the personal information of approximately 147 million people. The breach was attributed to a failure in responding quickly to known vulnerabilities, resulting in significant financial losses and reputational damage for the company.
In my own experience, I’ve seen smaller companies suffer similar fates due to inadequate preparation. One startup I worked with faced a ransomware attack that paralyzed their operations for weeks because they didn’t have a clear response strategy in place. They lost not only money but also customer trust—a hard lesson learned too late.
Building Trust with Stakeholders
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan also helps build trust with your customers and stakeholders. In today’s world, consumers are increasingly concerned about their data privacy and security. When they see that your organization has taken proactive steps to protect their information, it fosters confidence. I remember when we communicated our incident response strategy to our customers during a routine update. We received positive feedback from clients who appreciated our transparency and commitment to security. This trust can translate into customer loyalty, which is invaluable in competitive markets.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Many industries are subject to regulations that require organizations to have an incident response plan in place. For example, businesses in finance or healthcare must comply with regulations like HIPAA or PCI DSS, which mandate specific security measures and protocols. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to hefty fines and legal repercussions. In my experience, it’s always better to be proactive rather than reactive when it comes to compliance issues.
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan is essential for protecting your organization from the growing threat of cybercrime. By preparing ahead of time, you can minimize damage, streamline recovery efforts, build trust with stakeholders, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
To learn more about building trust through cybersecurity measures, check out this article on customer data protection or this guide on compliance requirements.
What are the Key Components of Incident Response Strategies?
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan is more than just writing down procedures; it’s about understanding the key components that make your strategy effective. When you think about incident response strategies, it’s essential to break them down into manageable parts. This not only helps in creating a comprehensive plan but also ensures that your team knows exactly what to do when an incident occurs.
Incident Response Strategies: What Should Be Included?
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan involves several critical components that work together to ensure a swift and effective response to any cyber incident. Let’s explore these components in detail.

Preparation Phase
The preparation phase is the foundation of your incident response strategy. It’s where you lay the groundwork for everything that follows. Here’s what you need to focus on:
- Establishing Policies and Procedures: Develop clear policies that outline how your organization will respond to various types of incidents. This includes defining what constitutes an incident and the steps to take when one occurs.
- Team Roles and Responsibilities: Identify who will be part of your incident response team. Each member should have clearly defined roles, whether they are responsible for technical analysis, communication, or recovery efforts.
- Training and Awareness: Regular training sessions are crucial for keeping your team prepared. I remember conducting our first training session; it was eye-opening to see how many gaps we had in our knowledge. Simulating incidents helped us understand our weaknesses and improve our response capabilities.
- Resource Allocation: Ensure that your team has access to the tools and resources they need to respond effectively. This might include software for monitoring threats, communication tools, and access to external experts if necessary.
Detection and Analysis
Once you’ve prepared your team, the next step is detection and analysis. This phase is critical for identifying incidents early and understanding their impact:
- Monitoring Systems: Implement continuous monitoring of your systems to detect anomalies or suspicious activities. Tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can be invaluable here.
- Threat Intelligence: Leverage threat intelligence to stay informed about emerging threats relevant to your industry. This proactive approach can help you identify potential incidents before they escalate.
- Incident Classification: When an incident is detected, classify it based on its severity and type. This classification will guide your response strategy and help prioritize actions.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of any detected incidents, including timestamps, affected systems, and initial assessments. This documentation will be crucial for later analysis and reporting.
Containment, Eradication, and Recovery
After detecting an incident, the next steps are containment, eradication, and recovery:
- Containment Strategies: Quickly isolate affected systems to prevent further damage. For example, during a ransomware attack we faced, we immediately disconnected infected machines from the network—this simple step saved us from a much larger disaster.
- Eradication Process: Once contained, work on eradicating the threat from your systems. This might involve removing malware or closing vulnerabilities that were exploited during the attack.
- Recovery Steps: After eradication, focus on restoring systems back to normal operations. This includes recovering data from backups and ensuring that all systems are secure before bringing them back online.
- Post-Incident Analysis: After recovery, conduct a thorough analysis of the incident to understand what happened and why. This is where you can identify lessons learned and areas for improvement in your incident response plan.
Real-World Application
In my experience with developing incident response strategies, I’ve found that each component plays a vital role in ensuring overall effectiveness. For instance, during our last simulated attack drill, we discovered that our detection capabilities were lacking due to outdated monitoring tools.
This prompted us to invest in better technology that ultimately improved our response time during real incidents. Moreover, involving cross-departmental teams in these drills helped us identify communication gaps between IT and management—something we hadn’t considered before! It was a game-changer for us because it highlighted the importance of having clear lines of communication during an actual crisis.
Understanding the key components of incident response strategies is essential for creating a robust cybersecurity incident response plan. By focusing on preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery, you can ensure that your organization is well-equipped to handle cyber incidents effectively.
How to Build an Effective Incident Response Team?
Building an effective incident response team is one of the most critical steps in creating a cybersecurity incident response plan. Your team is the frontline defense against cyber threats, and their ability to respond quickly and efficiently can make all the difference when an incident occurs. Let’s explore how to build a team that’s ready to tackle any cyber challenge.
Roles and Responsibilities in Crisis Management in IT
The first step in building your incident response team is defining clear roles and responsibilities. Each member should know their specific duties during an incident, which helps streamline the response process. Here are some key roles to consider:
- Incident Response Manager: This person oversees the entire incident response process. They coordinate efforts, communicate with stakeholders, and ensure that the plan is executed effectively. I’ve found that having a dedicated manager can significantly improve response times, as they serve as the central point of contact.
- Technical Lead: This role is filled by someone with deep technical knowledge of your systems and networks. The technical lead is responsible for identifying vulnerabilities, analyzing threats, and implementing technical solutions during an incident.
- Communication Officer: Effective communication is crucial during a crisis. The communication officer handles internal and external communications, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed about the situation and any actions being taken.
- Legal Advisor: Cyber incidents can have legal implications, so having a legal advisor on your team is essential. They can help navigate compliance issues and advise on any legal actions that may be necessary after an incident.
- Human Resources Representative: In cases where employees are involved or affected by an incident, having an HR representative ensures that employee concerns are addressed sensitively and appropriately.
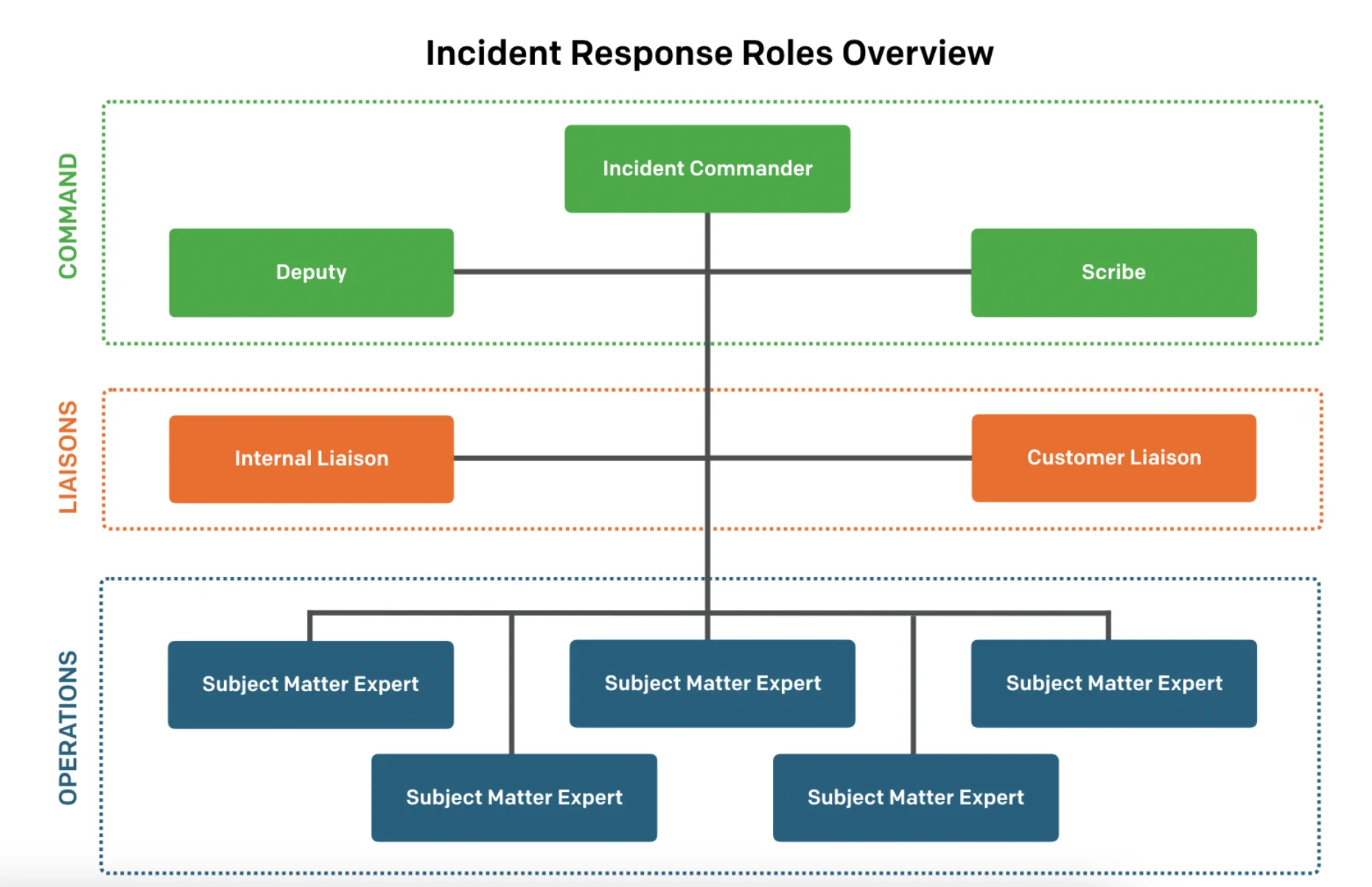
Importance of Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Creating a successful incident response team isn’t just about filling roles; it’s also about fostering collaboration across departments. Cybersecurity isn’t solely the responsibility of the IT department; it requires input from various areas of your organization:
- IT Department: Naturally, your IT team will play a crucial role in detecting and responding to incidents. They need to work closely with other departments to understand how incidents may affect their operations.
- Legal and Compliance Teams: These teams help ensure that your organization adheres to laws and regulations related to data protection and cybersecurity.
- Public Relations: In the event of a significant incident, your PR team will need to manage communications with the media and public to maintain trust in your brand.
I’ve seen firsthand how cross-departmental collaboration can enhance our response efforts. During one incident, our PR team was able to craft timely messages that reassured our customers while our IT team worked on containment strategies. This unified approach not only minimized confusion but also helped maintain customer confidence.
Training and Simulations
Once you’ve established your team, regular training sessions are essential for keeping everyone sharp. Here’s how you can effectively train your incident response team:
- Conduct Regular Drills: Simulated cyber incidents allow your team to practice their roles in a controlled environment. I remember our first drill; it was eye-opening to see how different members responded under pressure. We identified gaps in our plan that we hadn’t noticed before.
- Stay Updated on Threats: Cyber threats evolve rapidly, so it’s important for your team to stay informed about new tactics used by cybercriminals. Encourage ongoing education through webinars, workshops, and industry conferences.
- Review Lessons Learned: After each drill or real incident, conduct a debriefing session where team members can share insights on what worked well and what didn’t. This continuous improvement mindset strengthens your team’s capabilities over time.
Building a Culture of Preparedness
Creating an effective incident response team goes beyond just training; it involves fostering a culture of preparedness within your organization:
- Encourage Open Communication: Make sure all employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities or potential threats without fear of repercussions.
- Promote Cyber Hygiene: Regularly educate all staff on best practices for cybersecurity—like using strong passwords and recognizing phishing attempts—to minimize risks at every level of your organization.
- Celebrate Successes: When your team successfully handles an incident or completes a training exercise, celebrate those wins! This boosts morale and reinforces the importance of their work.
Building an effective incident response team requires careful planning, clear role definitions, cross-departmental collaboration, ongoing training, and fostering a culture of preparedness. By investing in your team’s capabilities, you’ll be better equipped to handle any cyber incident that comes your way.
For additional insights on building effective teams in cybersecurity, check out this article on teamwork in cybersecurity or this guide on training for incident response.
What Frameworks Can Guide Your Incident Response Plan?
When it comes to creating a cybersecurity incident response plan, frameworks can provide invaluable guidance. These frameworks offer structured approaches to managing incidents and help ensure that your organization is prepared for any cyber threat. By leveraging established frameworks, you can enhance your incident response strategies and improve your overall security posture.
Overview of Popular Frameworks
Several widely recognized frameworks can guide the development of your incident response plan. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most effective ones:
1. NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework is one of the most comprehensive guidelines available. It consists of five core functions:
- Identify: Understand your organization’s environment and the risks you face.
- Protect: Implement safeguards to limit the impact of potential incidents.
- Detect: Develop and implement activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event.
- Respond: Take action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident.
- Recover: Maintain plans for resilience and restore any capabilities or services that were impaired.
I remember when we first adopted the NIST framework; it provided a clear roadmap for our incident response efforts. The structured approach helped us identify gaps in our existing processes and prioritize our actions effectively.
2. SANS Institute Incident Handling Steps
The SANS Institute offers a straightforward approach to incident handling, which consists of six key steps:
- Preparation: Establish and train your incident response team.
- Identification: Determine whether an incident has occurred.
- Containment: Limit the damage from the incident.
- Eradication: Remove the cause of the incident.
- Recovery: Restore systems to normal operations.
- Lessons Learned: Analyze the incident to improve future responses.
This framework is particularly useful for organizations looking for practical, actionable steps. During our implementation of SANS guidelines, we found that focusing on lessons learned was crucial for continuous improvement.
3. ISO/IEC 27035
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides a standard specifically focused on information security incident management—ISO/IEC 27035. This framework emphasizes:
- Planning: Preparing for incidents by establishing policies and procedures.
- Detection and Reporting: Identifying incidents through monitoring and reporting mechanisms.
- Assessment and Decision Making: Evaluating incidents to determine appropriate responses.
- Response: Implementing actions based on assessments.
- Review: Conducting post-incident reviews to improve future responses.
Adopting ISO standards helped us align our practices with international best practices, which was particularly beneficial when dealing with clients in regulated industries.
How These Frameworks Can Help Structure Your Incident Response Efforts
Using these frameworks as a foundation for your incident response plan can significantly enhance your organization’s preparedness:
- Standardization: Frameworks provide standardize processes that help ensure consistency in how incidents are handled across your organization.
- Clarity in Roles: Many frameworks outline specific roles and responsibilities, making it easier for team members to understand their contributions during an incident.
- Comprehensive Coverage: By following a recognized framework, you can ensure that all aspects of incident management are addressed—from preparation to recovery.
- Continuous Improvement: Frameworks emphasize the importance of learning from past incidents, allowing organizations to refine their processes over time.
Comparison of Incident Response Frameworks
To help you choose the right framework for your organization, here’s a comparison table outlining key features:
| Framework | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| NIST | Comprehensive guidelines with five core functions | Organizations seeking detailed processes |
| SANS | Focus on practical steps with six key phases | Teams needing actionable playbooks |
| ISO | International standards emphasizing information security | Organizations aiming for compliance |

Real-World Application
In my experience, adopting a framework has been transformative for our incident response efforts. For instance, after implementing NIST guidelines, we conducted regular tabletop exercises that simulated various cyber incidents. These exercises not only improved our response times but also fostered better communication among team members. Moreover, using frameworks has allowed us to benchmark our practices against industry standards, providing reassurance to our clients about our commitment to cybersecurity.
Leveraging established frameworks like NIST, SANS, and ISO can significantly enhance your cybersecurity incident response plan. By providing structured approaches and best practices, these frameworks help organizations prepare for, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents effectively.
How to Develop Incident Response Playbooks?
Developing incident response playbooks is a critical step in creating an effective cybersecurity incident response plan. These playbooks serve as detailed guides that outline the specific actions your team should take in response to various types of incidents. By having these playbooks in place, you can ensure a swift and organized response, minimizing confusion and maximizing efficiency during a crisis.
Creating Playbooks for Common Threats
When developing incident response playbooks, it’s essential to focus on the most common threats your organization may face. Here’s how to create effective playbooks for these scenarios:
1. Identify Common Threats
Start by identifying the types of incidents that are most likely to occur in your organization. Common threats include:
- Ransomware Attacks: Malicious software that encrypts data and demands payment for decryption.
- Phishing Attempts: Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to confidential data, often resulting in data theft or exposure.
In my experience, we began developing playbooks after analyzing our past incidents and industry reports. This analysis helped us focus on the threats that posed the highest risk to our operations.
2. Outline Step-by-Step Procedures
Once you’ve identified the threats, outline step-by-step procedures for responding to each incident type. Here’s an example of what a ransomware attack playbook might include:
- Detection: Identify signs of ransomware activity, such as unusual file access or alerts from security software.
- Containment:
- Disconnect affected systems from the network.
- Inform relevant team members about the incident.
- Eradication:
- Determine the source of the attack (e.g., phishing email).
- Remove the ransomware and any associated malware from affected systems.
- Recovery:
- Restore data from backups.
- Monitor systems for any signs of lingering threats.
- Post-Incident Analysis:
- Conduct a thorough review of the incident.
- Update the playbook based on lessons learned.
I remember when we first drafted our playbook for ransomware attacks; it was a collaborative effort involving multiple departments. This collaboration ensured we covered all angles and didn’t miss any critical steps.
Best Practices for Developing Playbooks
To create effective incident response playbooks, consider these best practices:
1. Keep It Simple and Clear
Your playbooks should be easy to understand and follow, even under pressure. Use clear language and avoid technical jargon where possible. Short, actionable steps will help your team respond quickly without getting bogged down in details.
2. Include Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly define who is responsible for each action within the playbook. This helps eliminate confusion during an incident and ensures accountability.
3. Regularly Update Playbooks
Cyber threats evolve rapidly, so it’s crucial to keep your playbooks up-to-date. Schedule regular reviews—at least annually or after significant incidents—to ensure that your procedures reflect current best practices and threat landscapes.
4. Test Your Playbooks
Conduct regular drills using your playbooks to test their effectiveness. I’ve found that running simulations not only helps identify gaps but also builds confidence among team members in their ability to respond effectively.
Real-World Application
In my experience, having well-developed incident response playbooks has been invaluable during real incidents. For example, when we faced a phishing attack that compromised several employee accounts, our phishing response playbook guided us through each step—ensuring we contained the threat quickly and communicated effectively with affected employees. Moreover, after every incident, we would gather feedback from team members involved in executing the playbook. This feedback loop allowed us to continuously refine our procedures based on real-world experiences.
Developing incident response playbooks is essential for ensuring a swift and effective response to cyber incidents. By identifying common threats, outlining clear procedures, keeping your playbooks updated, and regularly testing them, you can enhance your organization’s preparedness and resilience against cyber threats.

What Communication Strategies Should Be Implemented?
Effective communication during a cybersecurity incident is crucial for minimizing damage and ensuring a coordinated response. When an incident occurs, clear and timely communication can make all the difference in how well your organization manages the situation. Let’s explore the key communication strategies that should be implemented as part of your incident response plan.
Crisis Management in IT: Communicating During an Incident
When a cyber incident occurs, it’s essential to have a well-defined communication strategy in place. Here are some critical components to consider:
1. Establish a Communication Plan
A robust communication plan outlines how information will be shared during an incident. This plan should include:
- Internal Communication: Define how information will be communicated within your organization. This includes notifying team members, management, and other relevant departments.
- External Communication: Determine how you will communicate with external stakeholders, including customers, partners, and the media. Transparency is key here; stakeholders need to know what happened and how you’re addressing it.
I remember when our company experienced a data breach; we had a communication plan that allowed us to quickly inform our employees and clients about the situation. This proactive approach helped maintain trust during a challenging time.
2. Designate Spokespersons
Identify specific individuals who will serve as spokespersons during an incident. These individuals should be trained in crisis communication and equipped to handle inquiries from both internal and external parties.
- Primary Spokesperson: Typically, this is someone from senior management or the communications team who can speak on behalf of the organization.
- Technical Spokesperson: In cases where technical details are required, having a technical expert available to answer questions can be beneficial.
Having designated spokespeople helped us present a unified message during our data breach incident, reducing confusion and misinformation.
3. Use Multiple Communication Channels
During a cyber incident, it’s essential to use various communication channels to reach your audience effectively:
- Email Alerts: Send out timely emails to keep employees informed about the situation and any actions they need to take.
- Intranet Updates: Use your company intranet or internal messaging system to provide real-time updates for employees.
- Social Media: If necessary, use social media platforms to communicate with external stakeholders and customers about the incident.
In our experience, utilizing multiple channels ensured that our message reached everyone promptly. For example, we used email for detailed updates while leveraging social media for broader announcements.
Best Practices for Incident Communication
To enhance your communication strategies during an incident, consider these best practices:
1. Be Transparent
Transparency is critical during a crisis. Share what you know about the incident, including its impact and the steps you’re taking to address it. This builds trust with your stakeholders and helps prevent misinformation from spreading.
2. Provide Regular Updates
Keep stakeholders informed with regular updates throughout the incident response process. Even if there’s no new information, communicating that you’re still actively working on the issue reassures everyone involved.
3. Tailor Your Message
Different audiences may require different levels of detail in their communications. For example, technical teams may need more in-depth information about the incident’s nature, while customers may only need reassurance that their data is safe.
4. Prepare for Questions
Be ready for questions from both internal and external parties during an incident. Having pre-prepared responses can help streamline communication and ensure consistency in messaging.
Real-World Application
In my experience managing communications during cybersecurity incidents, I’ve learned that preparation is key. For instance, after our data breach, we had prepared FAQs ready to address common concerns from both employees and customers. This proactive measure allowed us to respond quickly and effectively to inquiries without causing further panic.
Additionally, conducting post-incident reviews of our communication strategies helped us identify areas for improvement. We realized that our initial updates were too technical for our general audience; as a result, we adjusted our messaging approach in subsequent communications.
Implementing effective communication strategies during a cybersecurity incident is vital for successful crisis management. By establishing a clear communication plan, designating spokespersons, using multiple channels, and following best practices, you can ensure that your organization responds effectively while maintaining trust with stakeholders.
How to Evaluate and Improve Your Incident Response Plan?
Creating a cybersecurity incident response plan is just the beginning; the real work lies in continually evaluating and improving that plan. Cyber threats evolve rapidly, and your incident response strategies must adapt accordingly. Regularly assessing your plan helps ensure that it remains effective and relevant. Let’s explore how to evaluate and improve your incident response plan effectively.
Continuous Improvement in Incident Response Strategies
The concept of continuous improvement is vital in cybersecurity. Here’s how to implement it effectively:
1. Conduct Post-Incident Reviews
After every incident, it’s essential to conduct a thorough review. This process involves analyzing the incident from start to finish, including how it was detected, contained, and resolved. Here are some key questions to consider during the review:
- What went well during the response?
- What challenges did the team face?
- Were there any gaps in communication or procedures?
- How effective were the tools and technologies used?
I recall after one significant incident where we faced a DDoS attack; our post-incident review revealed that our detection systems had alerted us too late. This led us to upgrade our monitoring tools and refine our detection processes.
2. Gather Feedback from Team Members
Involve all team members who participated in the incident response in the review process. Their insights can provide valuable perspectives on what worked and what didn’t. Encourage open discussions about their experiences and any suggestions they have for improvement. For example, during a recent tabletop exercise, team members shared their thoughts on how certain procedures could be streamlined, which led to significant enhancements in our playbooks.
3. Track Metrics for Evaluation
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your incident response plan. Some useful metrics include:
- Time to Detect: How quickly did your team identify the incident?
- Time to Respond: How long did it take to contain the incident?
- Time to Recover: How long did it take to restore normal operations?
- Number of Incidents: Track the frequency of incidents over time to identify trends.
By analyzing these metrics, you can identify areas for improvement and set benchmarks for future performance.
Regular Updates and Training Sessions
To keep your incident response plan effective, regular updates and training sessions are crucial:
1. Schedule Regular Reviews
Set a schedule for reviewing your incident response plan—ideally at least once a year or after significant incidents. During these reviews, update procedures based on lessons learned from previous incidents and any changes in your organization’s structure or technology.
2. Conduct Ongoing Training
Regular training sessions help ensure that your team is prepared for various scenarios. Incorporate lessons learned from past incidents into these training sessions to reinforce best practices. For instance, we hold quarterly training sessions where we simulate different types of cyber incidents. These exercises not only help keep skills sharp but also allow us to practice updated procedures based on our latest evaluations.
Embrace New Technologies
As technology evolves, so do cyber threats. Stay informed about new tools and technologies that can enhance your incident response capabilities:
- Automation Tools: Consider implementing automation tools that can help streamline detection and response processes. Automation can significantly reduce response times by handling routine tasks.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: Utilize threat intelligence platforms that provide real-time data on emerging threats relevant to your organization’s industry.
- Incident Management Software: Invest in software designed specifically for managing incidents. These tools can help track incidents, document responses, and analyze performance metrics more efficiently.
Real-World Application
In my experience, evaluating and improving our incident response plan has been an ongoing journey rather than a one-time task. After implementing new technologies like automated monitoring systems, we noticed a significant reduction in our time to detect incidents—an improvement that was reflected in our KPIs. Moreover, by fostering a culture of continuous improvement within our team, we’ve created an environment where everyone feels empowered to contribute ideas for enhancing our processes.
Evaluating and improving your incident response plan is crucial for maintaining its effectiveness in the face of evolving cyber threats. By conducting post-incident reviews, gathering feedback from team members, tracking metrics, scheduling regular updates, embracing new technologies, and providing ongoing training, you can ensure that your organization is well-prepared for any cyber incident.
What Tools Are Essential for Effective Incident Response?
In the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, having the right tools at your disposal is crucial for effective incident response. These tools not only help in detecting and responding to incidents but also streamline communication and documentation throughout the process. Let’s explore some essential tools that can enhance your incident response capabilities.
Selecting the Right Tools for Incident Management
When it comes to incident management, there are several categories of tools to consider. Each category serves a specific purpose in the incident response lifecycle.
1. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
SIEM tools are essential for monitoring and analyzing security events in real-time. They aggregate data from various sources, such as servers, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, allowing your team to identify potential threats quickly.
- Key Features:
- Real-time monitoring of security events
- Correlation of logs from multiple sources
- Automated alerts for suspicious activities
I remember when we implemented a SIEM solution; it transformed our ability to detect incidents early. The centralized logging allowed us to see patterns and anomalies that would have otherwise gone unnoticed.
2. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions
EDR solutions focus on monitoring endpoints—like laptops, desktops, and servers—for suspicious activities. They provide advanced threat detection capabilities and allow for rapid response actions.
- Key Features:
- Continuous monitoring of endpoint activities
- Behavioral analysis to identify anomalies
- Automated response actions, such as isolating affected devices
During a recent incident involving malware on employee laptops, our EDR tool was instrumental in identifying the infected machines quickly. The automated isolation feature helped contain the threat before it spread.
3. Incident Management Software
Incident management software helps organize and manage the entire incident response process. These tools provide a centralized platform for tracking incidents, documenting responses, and analyzing performance metrics.
- Key Features:
- Incident tracking and documentation
- Workflow automation for response processes
- Reporting and analytics capabilities
Using incident management software has streamlined our response efforts significantly. We can easily assign tasks, track progress, and generate reports after incidents, which aids in our post-incident reviews.
Additional Essential Tools
Beyond SIEM, EDR, and incident management software, there are other tools that can enhance your incident response capabilities:
1. Threat Intelligence Platforms
Threat intelligence platforms provide real-time information about emerging threats relevant to your organization’s industry. By leveraging this data, you can proactively defend against potential attacks.
- Key Features:
- Aggregation of threat data from various sources
- Alerts for new vulnerabilities or exploits
- Integration with existing security tools for enhanced visibility
Incorporating threat intelligence into our security strategy has allowed us to stay ahead of potential threats. For example, when we learned about a new phishing campaign targeting our sector, we were able to implement additional training for employees before any incidents occurred.
2. Communication Tools
Effective communication is vital during an incident. Having reliable communication tools ensures that your team can coordinate their efforts seamlessly.
- Key Features:
- Real-time messaging capabilities
- Video conferencing options for remote teams
- Document sharing features for collaboration
During a recent cyber incident, we relied heavily on our communication platform to keep everyone informed about developments in real-time. This facilitated quick decision-making and ensured that all team members were aligned in their response efforts.
3. Forensic Analysis Tools
Forensic analysis tools are essential for investigating incidents after they occur. These tools help recover data, analyze malware, and understand how an attack happened.
- Key Features:
- Data recovery capabilities
- Malware analysis functions
- Timeline reconstruction of events leading up to an incident
After experiencing a significant breach, we utilized forensic analysis tools to understand how attackers gained access to our systems. This analysis was crucial in preventing similar incidents in the future.
Real-World Application
In my experience managing cybersecurity incidents, having the right tools has been a game-changer. For instance, during a recent ransomware attack simulation, our SIEM tool provided immediate alerts that allowed us to practice containment strategies effectively. Moreover, integrating these various tools into a cohesive incident response strategy has improved our overall efficiency. The combination of SIEM for monitoring, EDR for endpoint protection, and incident management software for tracking has created a robust framework that enhances our readiness against cyber threats.
Selecting the right tools is essential for effective incident response. By leveraging SIEM solutions, EDR systems, incident management software, threat intelligence platforms, communication tools, and forensic analysis tools, you can significantly enhance your organization’s ability to detect and respond to cyber incidents swiftly and efficiently.
Final Thoughts: Preparing for Future Cyber Threats
As we navigate an increasingly digital world, the importance of being prepared for cyber threats cannot be overstated. Creating a robust cybersecurity incident response plan is not just an exercise in compliance; it’s a vital strategy for protecting your organization’s assets, reputation, and future. Let’s summarize the key takeaways and emphasize the importance of ongoing preparedness.
Importance of a Proactive Approach
In today’s landscape, cyber threats are evolving at an unprecedented pace. Organizations face a myriad of risks, from ransomware attacks to sophisticated phishing schemes. A proactive approach to cybersecurity is essential for mitigating these risks effectively. Here are some critical aspects to consider:
- Anticipate Threats: Understanding the types of threats your organization may face is the first step in preparing for them. Conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities in your systems and processes.
- Invest in Training: Your employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Regular training on recognizing phishing attempts, understanding data privacy, and following security protocols can significantly reduce the risk of incidents.
- Stay Informed: The cybersecurity landscape is constantly changing. Stay updated on the latest threats and trends by subscribing to industry newsletters, attending webinars, and participating in professional organizations.
I remember when our team started attending cybersecurity conferences; it opened our eyes to emerging threats and innovative solutions that we could implement in our organization.
Building a Culture of Cybersecurity
Creating a culture of cybersecurity within your organization is crucial for long-term success. This means making security a priority at every level—from the executive team to entry-level employees. Here are some strategies to foster this culture:
- Leadership Commitment: Leadership should actively promote cybersecurity initiatives and demonstrate their importance through actions and investments. When employees see that management prioritizes security, they are more likely to take it seriously themselves.
- Encourage Open Communication: Create an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities without fear of repercussions. This openness can lead to quicker detection and response to potential threats.
- Recognize and Reward Good Practices: Acknowledge employees who demonstrate good cybersecurity practices or identify potential threats. This not only reinforces positive behavior but also encourages others to follow suit.
Regularly Review and Update Your Incident Response Plan
Your incident response plan should be a living document that evolves as your organization grows and as new threats emerge. Regularly reviewing and updating your plan ensures that it remains relevant and effective:
- Post-Incident Analysis: After every incident, conduct a thorough review to identify what worked well and what could be improved. Use these insights to refine your plan continuously.
- Engage with External Experts: Sometimes, bringing in external consultants or experts can provide fresh perspectives on your incident response strategies and help identify areas for improvement.
- Test Your Plan: Regularly conduct drills and simulations to test your incident response plan in real-world scenarios. These exercises help ensure that everyone knows their roles and responsibilities during an actual incident.
Preparing for future cyber threats requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses proactive measures, ongoing training, a strong culture of cybersecurity, and regular evaluations of your incident response plan. By investing time and resources into these areas, you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience against cyber incidents. Remember, cybersecurity is not just an IT issue; it’s a business imperative that affects everyone in your organization. By fostering a culture of preparedness and continuous improvement, you can protect your organization from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.s)
- What is an incident response plan?
- An incident response plan is a documented strategy that outlines the processes and procedures an organization follows to detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents. It serves as a roadmap for managing incidents effectively and minimizing damage.
- Why is it important to have an incident response team?
- Having an incident response team is crucial because it ensures that there are designated individuals responsible for managing cybersecurity incidents. This team can act quickly, coordinate responses, and minimize the impact of incidents on the organization.
- What are common types of cyber incidents organizations face?
- Common types of cyber incidents include ransomware attacks, phishing attempts, data breaches, denial-of-service attacks, and insider threats. Each type requires specific response strategies.
- How often should an incident response plan be updated?
- An incident response plan should be reviewed and updated at least annually or after significant incidents. Regular assessments ensure that the plan remains effective in addressing current threats and organizational changes.
- What metrics should organizations track during an incident?
- Organizations should track metrics such as time to detect an incident, time to respond, time to recover systems, and the number of incidents over time. These metrics help evaluate the effectiveness of the incident response plan.
- How can organizations train their staff on incident response?
- Organizations can train their staff through regular training sessions, tabletop exercises, and simulated cyber incidents. Providing resources and encouraging participation helps build awareness and preparedness among employees.
- What role does communication play during a cybersecurity incident?
- Communication is vital during a cybersecurity incident as it ensures that all stakeholders are informed about the situation, actions being taken, and any necessary precautions. Clear communication helps maintain trust and minimizes confusion.
- Can small businesses benefit from having an incident response plan?
- Yes, small businesses can greatly benefit from having an incident response plan. Even though they may face different threats than larger organizations, being prepared can help minimize damage and recovery time in the event of an incident.
- What are the challenges in implementing an effective incident response strategy?
- Challenges may include a lack of resources, insufficient training for staff, outdated technology, and difficulty in coordinating between departments. Overcoming these challenges requires commitment from leadership and ongoing investment in cybersecurity.
- How do I choose the right tools for my organization’s needs?
- To choose the right tools, assess your organization’s specific needs based on its size, industry, and threat landscape. Conduct research on available tools, consider user reviews, and seek recommendations from industry experts to find solutions that align with your requirements.
This concludes the blog post titled “Prepare for the Worst: How to Create an Effective Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan!” If you have any further requests or need additional sections or modifications, feel free to let me know!