Introduction
Every day, businesses face threats from hackers and cybercriminals who target unsecured devices. We will review best practices for mobile device security. According to a recent report by Cybersecurity Ventures, mobile malware attacks are expected to reach 256 billion by 2031. This staggering number highlights the urgent need for businesses to adopt best practices for mobile device security.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, mobile devices have become essential tools for businesses. From smartphones to tablets, these gadgets allow us to work from anywhere, communicate instantly, and access vital information on the go. However, with this convenience comes a significant risk: mobile device security.
Having experienced a security breach firsthand in my early entrepreneurial days, I can attest to the chaos that ensues when mobile devices are not secured properly. It was a wake-up call that led me to prioritize mobile security in my business strategy. I learned that securing mobile devices isn’t just about protecting data; it’s about safeguarding your entire business reputation.
In this blog post, we will explore the best practices for mobile device security that every business should implement now. We’ll cover everything from strong authentication measures to employee training programs. By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure that your business operates smoothly.

As we dive deeper into this topic, remember that securing mobile devices is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing commitment. Let’s get started by understanding why securing mobile devices is essential for your business.
What Are the Best Practices for Mobile Device Security?
When we talk about best practices for mobile device security, it’s essential to understand that these practices are not just guidelines; they are necessary actions that can protect your business from potential threats. In my experience, implementing these best practices for mobile device security has made a significant difference in how secure our operations are.
Understanding the Importance of Best Practices
The term, best practices for mobile device security, refers to a set of strategies designed to mitigate risks associated with mobile devices. As businesses increasingly rely on these devices, it becomes crucial to adopt effective measures. These practices help in securing mobile devices against unauthorized access, data breaches, and malware attacks.
The Five Key Practices
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
One of the most effective best practices for mobile device security is enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA). This adds an extra layer of protection beyond just a password. For instance, when I implemented MFA in my business, I noticed a significant decrease in unauthorized access attempts. With MFA, even if someone gets hold of a password, they still need another form of verification—like a text message or an authentication app—to gain access.

- Use Strong Passwords and Biometric Authentication
Another critical aspect of best practices for mobile device security is using strong passwords combined with biometric authentication methods like fingerprint scanning or facial recognition. In my early days, I often used simple passwords, thinking they were sufficient. However, after experiencing a minor breach, I realized the importance of creating complex passwords and utilizing biometric options wherever possible. This not only secures mobile devices but also makes it easier for employees to access their accounts without compromising security. - Keep Software and Applications Updated
Regularly updating software and applications is one of the most straightforward yet impactful best practices for mobile device security. Updates often include patches that fix vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit. I’ve seen firsthand how neglecting updates can lead to security gaps. For example, after a significant update rolled out for our operating system, we noticed a reduction in malware attempts on our devices. - Avoid Unsecured Public Wi-Fi Networks
Using unsecured public Wi-Fi can be a major risk factor for businesses. It’s one of those common mistakes that many make without realizing the potential dangers involved. I remember once connecting to public Wi-Fi at a café and later finding out that sensitive data had been intercepted by hackers. To combat this risk, it’s best to avoid public networks altogether or use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when connecting. - Conduct Regular Training and Awareness Programs
Finally, one of the most crucial best practices for mobile device security is educating employees about potential threats and safe practices. Regular training sessions can help staff recognize phishing attempts and understand the importance of securing their devices. In my experience, when we conducted training sessions on securing mobile devices, employees became more vigilant about their online activities.
Implementing these best practices for mobile device security is essential for any business aiming to protect its data and reputation. By focusing on securing mobile devices through strong authentication measures, regular updates, and employee education, you create a robust defense against cyber threats.
Why Is Securing Mobile Devices Essential for Businesses?
In our increasingly mobile world, understanding the importance of securing mobile devices is crucial for every business. With employees accessing sensitive company data from their smartphones and tablets, the risks associated with unsecured devices can lead to devastating consequences. In my journey as an entrepreneur, I’ve personally witnessed how a single security breach can disrupt operations and tarnish a company’s reputation.
The Growing Threat Landscape
Best practices for mobile device security become even more relevant when we consider the alarming statistics surrounding mobile security threats. According to a report by IBM, mobile malware attacks have surged by over 50% in just a year. This statistic underscores the need for businesses to prioritize securing mobile devices as part of their overall cybersecurity strategy.
When I first started my business, I underestimated the risks associated with mobile devices. I thought that having basic antivirus software was enough. However, after learning about various types of attacks—like phishing and ransomware—I realized that securing mobile devices requires a more comprehensive approach.
The Impact of Data Breaches
Data breaches can have severe repercussions for businesses. Not only do they result in financial losses, but they can also lead to loss of customer trust and legal consequences. A study by Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of a data breach is around $4.24 million. Imagine the impact this could have on a small business!

In my experience, I’ve seen companies struggle to recover after a breach. One client lost critical customer data due to an unsecured mobile device, leading to lawsuits and a damaged reputation. This incident served as a wake-up call for many businesses in our network, emphasizing the importance of implementing best practices for mobile device security.
Employee Mobility and Security Risks
With remote work becoming more common, employees often use personal devices for work-related tasks. This trend increases the risk of exposing sensitive information if those devices are not properly secured. It’s essential to recognize that every employee’s device is a potential entry point for cybercriminals.
To mitigate these risks, businesses must adopt best practices for mobile device security tailored to their specific needs. For instance, establishing clear policies regarding acceptable use of personal devices can help protect company data. I remember drafting a policy that required employees to use secure connections and avoid public Wi-Fi when accessing sensitive information. This simple step significantly reduced our vulnerability.
The Role of Compliance
Many industries are subject to regulations that mandate specific security measures for handling sensitive data. For example, healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA regulations, while financial institutions must adhere to PCI DSS standards. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to hefty fines and additional scrutiny from regulatory bodies.
In my experience working with clients in regulated industries, I’ve seen how crucial it is to integrate securing mobile devices into compliance strategies. By adopting best practices for mobile device security, businesses can not only protect their data but also ensure they remain compliant with industry standards.
Securing mobile devices is not just an IT issue; it’s a fundamental business concern that affects every aspect of operations. By understanding the significance of securing mobile devices, businesses can take proactive steps to protect themselves from potential threats. Implementing best practices for mobile device security will not only safeguard sensitive information but also enhance overall business resilience in an increasingly digital landscape.
How Can Businesses Implement Strong Authentication Measures?
When it comes to best practices for mobile device security, one of the most effective strategies is implementing strong authentication measures. This approach not only protects sensitive data but also significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. In my experience, adopting robust authentication methods has been a game-changer for businesses looking to enhance their mobile security posture.
Understanding Strong Authentication
Best practices for mobile device security emphasize the need for strong authentication as a critical component. Strong authentication involves verifying a user’s identity through multiple means, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information. This multi-layered approach is essential in today’s threat landscape, where cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to bypass security measures.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
One of the most effective methods for strong authentication is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access. For instance, after entering a password, users may need to enter a code sent to their mobile device or use a biometric scan. This process adds an extra layer of security that is crucial in securing mobile devices.
When I first implemented MFA in my business, I noticed an immediate drop in unauthorized access attempts. It was eye-opening to see how many potential breaches were thwarted simply by requiring an additional verification step. According to a report by Microsoft, MFA can block 99.9% of automated attacks, making it one of the best practices for mobile device security that businesses should adopt immediately.
Password Management
Another vital aspect of strong authentication is effective password management. Weak passwords are one of the easiest ways for hackers to gain access to sensitive data. Therefore, businesses must encourage employees to create complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols.
In my experience, I’ve found that using password managers can significantly simplify this process. These tools help employees generate and store strong passwords securely, reducing the temptation to reuse simple passwords across multiple accounts. By promoting strong password practices as part of your best practices for mobile device security, you can greatly enhance your overall security posture.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication methods—such as fingerprint recognition and facial recognition—are becoming increasingly popular as part of strong authentication strategies. These methods provide a unique way to verify user identity and are often more secure than traditional passwords.
I recall attending a cybersecurity conference where experts discussed the future of biometric technology in mobile security. The consensus was clear: biometrics offer convenience without sacrificing security. Implementing biometric authentication can be a significant step toward securing mobile devices, making it one of the essential best practices for mobile device security.
Employee Training on Authentication Practices
While implementing strong authentication measures is crucial, educating employees about these practices is equally important. Many breaches occur not because of weak technology but due to human error. Employees must understand how to use MFA effectively and recognize the importance of maintaining strong passwords.
In my business, we conduct regular training sessions focused on best practices for mobile device security and strong authentication measures. During these sessions, we share real-world examples of breaches caused by weak authentication practices and demonstrate how simple changes can make a significant difference.
Implementing strong authentication measures is one of the most impactful best practices for mobile device security that businesses can adopt today. By utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), promoting effective password management, incorporating biometric options, and educating employees on these practices, you create a robust defense against unauthorized access and data breaches.
What Role Do Strong Passwords Play in Mobile Security?
When discussing best practices for mobile device security, one of the most fundamental yet often overlooked aspects is the role of strong passwords. A password is often the first line of defense against unauthorized access to sensitive information. In my experience, the strength of your passwords can significantly impact your overall mobile security strategy.
The Importance of Strong Passwords
The best practices for mobile device security, highlight that strong passwords are essential for safeguarding your business’s data. Weak passwords are akin to leaving the front door of your office wide open; they invite trouble. According to a study by Verizon, 81% of data breaches are caused by stolen or weak passwords. This statistic underscores the critical need for businesses to prioritize strong password practices as part of their securing mobile devices strategy.
Characteristics of Strong Passwords
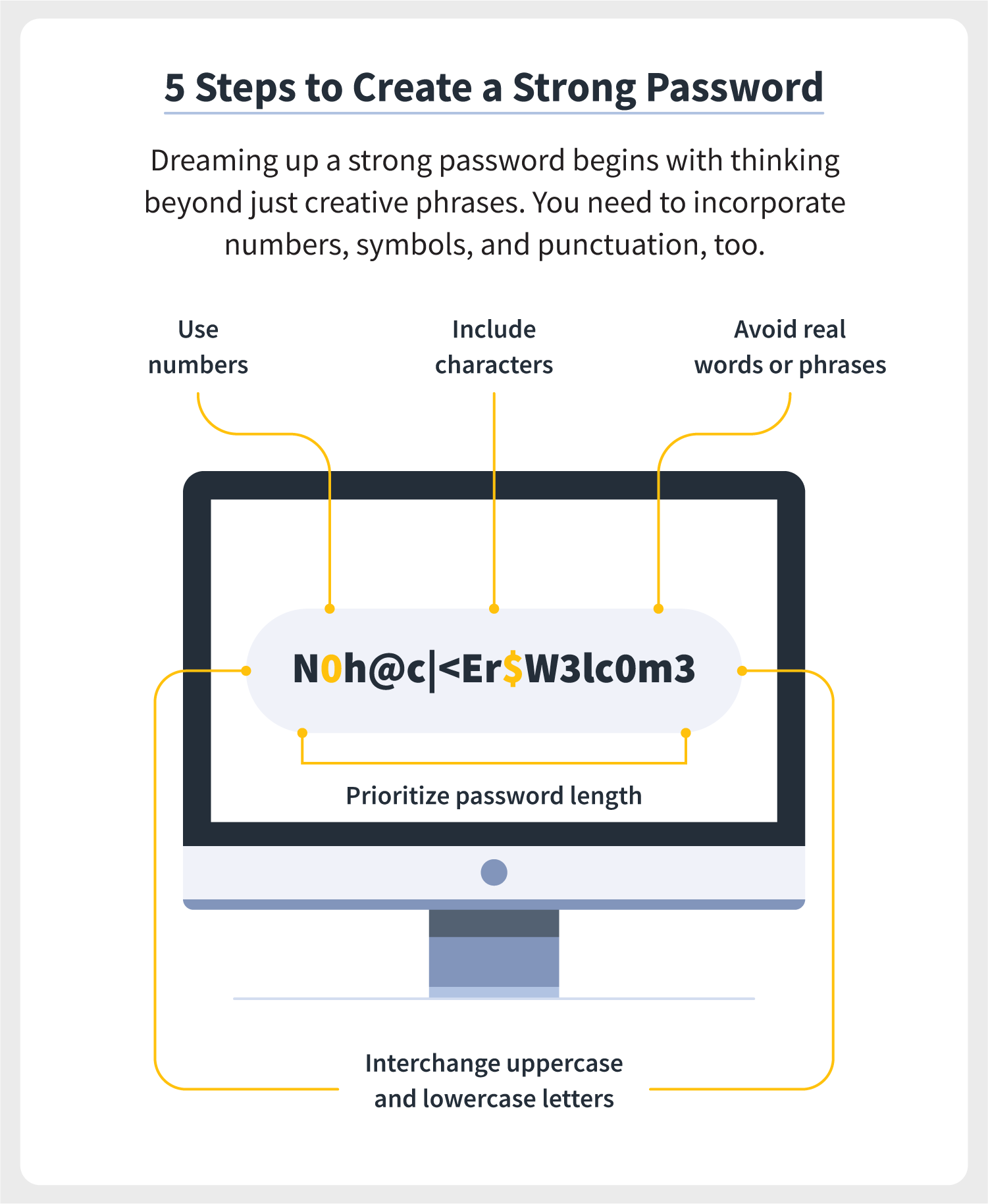
So, what constitutes a strong password? A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common words. In my early days as an entrepreneur, I often used simple passwords because I thought they were easy to remember.
However, after a close call with a phishing attempt that nearly compromised my accounts, I learned the hard way that complexity is key. I began using passphrases—longer combinations of words that are easier to remember but harder to crack. For example, instead of “password123,” I might use “SunnyDay!2024&Coffee.” This method not only strengthens security but also makes it easier for employees to recall their passwords.
Password Management Tools
To further enhance your password security, consider using password management tools. These applications can generate complex passwords and securely store them, allowing users to access their accounts without needing to memorize every password. When I introduced a password manager in my business, I noticed a significant improvement in our overall security posture. Employees no longer reused passwords across multiple accounts, reducing our vulnerability to breaches.
Additionally, many password managers offer features like automatic password updates and alerts for potential breaches, making them invaluable tools in the realm of best practices for mobile device security.
Biometric Authentication as an Alternative
While strong passwords are crucial, they can be complemented by biometric authentication methods such as fingerprint scanning or facial recognition. These technologies offer an additional layer of security and can simplify the login process for users. In my experience, incorporating biometric options into our mobile security strategy has been beneficial. Employees appreciate the convenience of logging in with their fingerprints rather than remembering complex passwords. However, it’s important to note that biometric authentication should not replace strong passwords but rather serve as an additional safeguard.
Employee Training on Password Practices
Educating employees about the importance of strong passwords is vital for maintaining securing mobile devices. Regular training sessions can help employees understand why weak passwords pose risks and how they can create stronger ones. I remember hosting a workshop focused on password security where we discussed common mistakes people make and shared tips on creating strong passwords. The feedback was overwhelmingly positive; employees felt more empowered to take control of their own security practices.
Strong passwords play a critical role in best practices for mobile device security. By emphasizing the importance of creating complex passwords, utilizing password management tools, incorporating biometric authentication methods, and providing employee training on these practices, businesses can significantly enhance their mobile security posture.
How Can Regular Updates Enhance Mobile Security?
When we think about best practices for mobile device security, one of the most straightforward yet often neglected strategies is keeping software and applications updated. Regular updates are crucial for maintaining the integrity of mobile devices and protecting sensitive information from emerging threats. In my experience, neglecting updates can lead to vulnerabilities that cybercriminals eagerly exploit.
The Importance of Software Updates
Regular updates are essential in a world where cyber threats are constantly evolving and are emphasized. Software developers frequently release updates to patch security vulnerabilities, improve functionality, and enhance user experience. Failing to install these updates leaves devices exposed to potential attacks.
According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, 60% of data breaches involve vulnerabilities for which a patch was available but not applied. This statistic highlights the critical need for businesses to prioritize regular updates as part of their securing mobile devices strategy.
Types of Updates
- Operating System Updates
Operating system (OS) updates are among the most critical updates you can install on your mobile devices. These updates often include security patches that protect against newly discovered vulnerabilities. For example, when Apple or Android releases an OS update, it typically addresses known security flaws that could be exploited by hackers. In my early days, I often delayed OS updates, thinking they were unnecessary. However, after learning about a severe vulnerability that was patched in a recent update, I realized the importance of acting promptly. Now, I make it a point to ensure all devices in my organization are updated as soon as new versions are released. - Application Updates
Just like operating systems, applications also require regular updates to maintain security and functionality. Many apps collect sensitive data and are prime targets for cybercriminals. When app developers release updates, they often fix security vulnerabilities that could be exploited. I remember a time when one of our commonly used applications had a significant vulnerability that was addressed in an update. We had several employees using the outdated version, which left us exposed until we enforced an update policy across the organization.
Automating Updates
To simplify the process of keeping software up-to-date, consider enabling automatic updates on all devices. This feature allows devices to download and install updates without requiring manual intervention from users. In my experience, automating updates has significantly reduced the risk of running outdated software. Employees often forget to check for updates regularly; however, with automation in place, we ensure that all devices remain secure without additional effort from staff.
Employee Training on Update Importance
Educating employees about the importance of regular updates is crucial for maintaining best practices for mobile device security. Many employees may not understand why these updates matter or may see them as an inconvenience. I’ve found that conducting training sessions focused on the significance of software updates can help foster a culture of security awareness within the organization. During these sessions, we discuss real-world examples of breaches caused by outdated software and demonstrate how easy it is to enable automatic updates.
Regularly updating software and applications is one of the most effective best practices for mobile device security that businesses can adopt. By prioritizing operating system and application updates, automating the update process, and educating employees about their importance, you create a formidable defense against potential cyber threats.
What Are the Risks of Public Wi-Fi and How to Mitigate Them?
In today’s mobile-centric world, many of us rely on public Wi-Fi networks to stay connected while on the go. However, when discussing best practices for mobile device security, it’s crucial to address the significant risks associated with using unsecured public Wi-Fi. In my experience, being aware of these risks and implementing effective mitigation strategies can make a world of difference in protecting sensitive information.
The Dangers of Public Wi-Fi
According to the best practices for mobile device security, public Wi-Fi networks are often prime targets for cybercriminals. These networks are typically unsecured, meaning that anyone within range can access them without a password. This lack of security makes it easy for hackers to intercept data transmitted over these networks.
According to a study by Norton, 70% of people use public Wi-Fi without taking any precautions. This statistic is alarming because it shows how many individuals unknowingly expose themselves to threats. I remember once connecting to a public Wi-Fi network at an airport café, thinking it was harmless. Little did I know that my connection could have been monitored by someone sitting just a few tables away.
Common Threats on Public Wi-Fi
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
One of the most common threats on public Wi-Fi networks is the man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack. In this scenario, a hacker intercepts communication between two parties, allowing them to eavesdrop on sensitive information such as login credentials and financial data. I learned about MitM attacks during a cybersecurity workshop, where experts shared stories of businesses that suffered breaches due to unsecured connections. It was a wake-up call that underscored the importance of following best practices for mobile device security when using public networks. - Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing is another method hackers use to capture data transmitted over unsecured networks. By using specialized software, they can monitor network traffic and collect sensitive information without the user’s knowledge. After hearing horror stories about packet sniffing at that same workshop, I made it a personal mission to educate my team about the dangers of using public Wi-Fi without proper precautions. It became clear that we needed to adopt stronger measures to secure mobile devices against such threats.
Mitigation Strategies
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
One of the most effective ways to protect your data when using public Wi-Fi is by utilizing a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it much harder for hackers to intercept your data. When I started using a VPN while traveling for business, I felt much more secure accessing sensitive information over public networks. It became one of my go-to best practices for mobile device security that I recommend to everyone in my network.

- Avoid Accessing Sensitive Information
If possible, avoid accessing sensitive information—such as banking details or confidential company data—while connected to public Wi-Fi. This precaution is one of the simplest yet most effective best practices for mobile device security. During my travels, I’ve made it a habit to wait until I’m on a secure network before logging into sensitive accounts. This small change has helped me avoid potential pitfalls and maintain better control over my data. - Turn Off Sharing Settings
Before connecting to public Wi-Fi, ensure that sharing settings are turned off on your devices. This includes file sharing and printer sharing options that could expose your device to unauthorized access. I remember once connecting my laptop to a public network and inadvertently leaving sharing settings enabled. Thankfully, nothing happened, but it was a valuable lesson in ensuring all settings are properly configured before connecting to unsecured networks.
Understanding the risks associated with public Wi-Fi is vital for maintaining best practices for mobile device security. By recognizing the dangers of man-in-the-middle attacks and packet sniffing, and by implementing mitigation strategies like using VPNs and avoiding sensitive transactions on public networks, you can significantly enhance your mobile security posture.
How Can Businesses Educate Employees on Mobile Security?
When it comes to best practices for mobile device security, one of the most crucial aspects is employee education. No matter how robust your security measures are, if employees are not aware of the risks and best practices, your business remains vulnerable. In my experience, investing time and resources in training programs can significantly enhance the security posture of any organization.
The Importance of Employee Education
International best practices for mobile device security confirm that educating employees is essential for safeguarding sensitive information. Cybercriminals often exploit human error, making it vital for employees to understand how to recognize threats and respond appropriately. According to a report by IBM, 95% of cybersecurity breaches are due to human error. This statistic highlights the need for effective training programs focused on securing mobile devices.
Key Topics for Training Programs
- Recognizing Phishing Attempts
One of the most common tactics used by cybercriminals is phishing, where they attempt to trick employees into revealing sensitive information through deceptive emails or messages. Training employees to recognize phishing attempts is a critical component of best practices for mobile device security. I remember when my team participated in a phishing simulation exercise. The results were eye-opening; many employees fell for the fake emails. Afterward, we held a workshop to discuss how to identify red flags in emails, such as suspicious links or unexpected attachments. This training significantly improved our ability to spot potential threats. - Safe Browsing Habits
Educating employees about safe browsing habits is another essential topic in any training program focused on securing mobile devices. Many employees may not realize that visiting unsecured websites can expose them to malware and other threats. During our training sessions, we emphasize the importance of looking for “HTTPS” in URLs and avoiding clicking on unfamiliar links. Sharing real-life examples of businesses that suffered breaches due to unsafe browsing practices has made this point resonate with my team. - Using Strong Passwords and MFA
As discussed in previous sections, using strong passwords and enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are critical best practices for mobile device security. Employees should be trained on how to create strong passwords and use MFA effectively. We conducted a workshop where we shared tips on creating complex passwords and demonstrated how MFA works. After this session, I noticed an increase in employees adopting these practices, which helped bolster our overall security.
Regular Training Sessions
One-time training isn’t enough; ongoing education is vital for maintaining awareness around best practices for mobile device security. Regular training sessions can help reinforce key concepts and keep employees informed about new threats. In my organization, we schedule quarterly training sessions focused on different aspects of mobile security. These sessions include guest speakers from cybersecurity firms who share the latest trends and tactics used by hackers. This approach not only keeps our team informed but also fosters a culture of security awareness.
Creating a Culture of Security
To effectively educate employees about securing mobile devices, businesses must create a culture that prioritizes security at all levels. This means encouraging open communication about potential threats and empowering employees to report suspicious activities without fear of repercussions. I’ve found that when employees feel responsible for their own security, they are more likely to adhere to best practices for mobile device security. In our organization, we celebrate “Security Champions”—employees who go above and beyond in promoting safe practices within their teams.
Educating employees about mobile security is one of the most effective ways to implement best practices for mobile device security within any organization. By focusing on recognizing phishing attempts, safe browsing habits, strong password usage, and fostering a culture of security awareness, businesses can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats.
What Additional Mobile Security Tips Should Businesses Consider?
While implementing the best practices for mobile device security we’ve discussed is essential, there are several additional mobile security tips that businesses should consider. These tips can further enhance your organization’s defenses and help ensure that sensitive information remains protected. In my experience, small changes can lead to significant improvements in overall security.
The Importance of Additional Security Measures
A multi-layered approach is crucial for effective protection when looking at best practices for mobile device security. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and relying solely on basic security measures may leave your business vulnerable. By incorporating additional mobile security tips, you can create a more robust defense against potential attacks.
1. Enable Device Encryption
One of the most effective additional tips for securing mobile devices is enabling device encryption. Encryption converts data into a code that can only be accessed with the correct credentials. This means that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains protected. I learned about the importance of encryption when a colleague’s phone was stolen during a business trip. Thankfully, they had encryption enabled, which prevented unauthorized access to sensitive company data. This incident reinforced the need to prioritize encryption as part of our best practices for mobile device security.
2. Implement Remote Wipe Capabilities
Another valuable tip is to implement remote wipe capabilities on all mobile devices used for work. This feature allows administrators to remotely erase all data from a lost or stolen device, ensuring that sensitive information does not fall into the wrong hands. In my organization, we have a policy in place that requires all devices to have remote wipe capabilities enabled. I remember when an employee misplaced their tablet at a conference; we were able to remotely wipe it within minutes, safeguarding our data and preventing potential breaches.
3. Use Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Installing reputable antivirus and anti-malware software is another critical step in securing mobile devices. These tools can help detect and remove malicious software that could compromise your data. Initially, I was skeptical about the need for antivirus software on mobile devices, thinking they were primarily for computers. However, after attending a seminar where experts discussed rising threats targeting mobile platforms, I quickly changed my mind. Now, every device in our organization has antivirus software installed as part of our best practices for mobile device security.
4. Regularly Review App Permissions
Many employees may not realize that apps often request permissions that could expose sensitive information. Regularly reviewing app permissions is an additional tip that can enhance your mobile security efforts. In my experience, I’ve found that conducting periodic audits of app permissions helps identify any unnecessary access granted to apps. We encourage employees to limit permissions to only what is necessary for the app’s functionality, reinforcing our commitment to best practices for mobile device security.
5. Keep an Eye on Device Usage Policies
Establishing clear device usage policies is essential for maintaining secure operations within your organization. These policies should outline acceptable use of personal devices for work purposes and provide guidelines on how to handle sensitive information. When I first drafted our device usage policy, I included sections on acceptable apps, public Wi-Fi usage, and password management. This comprehensive approach has helped create awareness among employees about their responsibilities in maintaining securing mobile devices.
Incorporating additional mobile security tips into your strategy is vital for implementing effective best practices for mobile device security. By enabling device encryption, implementing remote wipe capabilities, using antivirus software, regularly reviewing app permissions, and establishing clear usage policies, businesses can significantly enhance their defenses against cyber threats.
How Can Businesses Monitor and Manage Mobile Device Security?
Monitoring and managing mobile device security is a critical aspect of implementing best practices for mobile device security. As mobile devices become increasingly integrated into business operations, it’s essential to have robust systems in place to oversee their security. In my experience, proactive monitoring can help identify vulnerabilities before they lead to significant issues.
The Importance of Monitoring Mobile Security
The global best practices for mobile device security, highlights that ongoing monitoring is essential for maintaining a secure environment. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and without proper oversight, businesses may find themselves vulnerable to attacks. According to a report by Gartner, organizations that implement comprehensive mobile device management (MDM) solutions can reduce the risk of security breaches by up to 50%. This statistic underscores the importance of actively monitoring and managing mobile devices.
Implementing Mobile Device Management (MDM)
One of the most effective ways to monitor and manage mobile device security is through Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions. MDM allows organizations to enforce security policies, deploy applications, and monitor device compliance from a centralized platform. When I first implemented an MDM solution in my organization, I was amazed at how much control we gained over our devices. We could remotely wipe lost devices, push updates, and ensure that all devices complied with our best practices for mobile device security. This centralized approach significantly improved our ability to secure mobile devices against potential threats.

Key Features of MDM Solutions
- Device Inventory and Tracking
A key feature of any MDM solution is the ability to maintain an inventory of all devices connected to your network. This functionality allows businesses to track which devices are in use and ensure they meet security standards. In my experience, having a complete inventory has helped us identify unauthorized devices accessing our network. By regularly reviewing this inventory, we can take immediate action if we detect any suspicious activity. - Policy Enforcement
MDM solutions enable organizations to enforce security policies across all devices. This includes requiring strong passwords, enabling encryption, and mandating regular software updates. I remember when we first set up policy enforcement through our MDM solution; it was a game-changer. Employees were automatically prompted to change weak passwords or update their software, ensuring compliance with our best practices for mobile device security. - Remote Management Capabilities
Remote management capabilities are essential for responding quickly to potential threats. With MDM, administrators can remotely lock or wipe devices if they are lost or stolen, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. There was a time when one of our employees lost their phone during a business trip. Thanks to our MDM solution, we were able to remotely wipe the device within minutes, ensuring that no company data fell into the wrong hands.
Regular Security Audits
In addition to using MDM solutions, conducting regular security audits is another critical component of monitoring and managing mobile device security. These audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with established policies. I’ve found that conducting bi-annual security audits has been invaluable in maintaining our best practices for mobile device security. During these audits, we review device configurations, assess compliance with security policies, and identify any areas for improvement.
Employee Training on Monitoring Practices
While technology plays a significant role in monitoring mobile device security, employee awareness is equally important. Training employees on how to recognize potential threats and report suspicious activities can enhance your organization’s overall security posture. In my organization, we’ve implemented training sessions that focus on how employees can contribute to monitoring efforts. This includes recognizing phishing attempts or reporting unusual behavior on their devices—key elements in securing mobile devices effectively.
Monitoring and managing mobile device security is a vital aspect of implementing effective best practices for mobile device security. By utilizing Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions, conducting regular audits, and training employees on monitoring practices, businesses can significantly enhance their defenses against cyber threats.
Final Thoughts on Strengthening Mobile Device Security
As we conclude our exploration of best practices for mobile device security, it’s essential to recognize that securing mobile devices is a continuous process that requires commitment from everyone in the organization. In my experience, adopting a proactive approach to mobile security not only protects sensitive information but also fosters a culture of security awareness among employees.
The Ongoing Nature of Mobile Security
The regulatory best practices for mobile device security, serves as a reminder that these practices are not one-time efforts but ongoing commitments. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and businesses must adapt their strategies accordingly. Regularly reviewing and updating security measures ensures that you remain one step ahead of potential threats.
Building a Security-First Culture
Creating a culture that prioritizes security is crucial for successful implementation of best practices for mobile device security. When employees understand the importance of securing mobile devices and feel empowered to take action, they become valuable assets in the fight against cyber threats. In my organization, we’ve made it a point to celebrate employees who demonstrate exceptional awareness of mobile security. This recognition not only motivates others but also reinforces the idea that everyone plays a role in securing mobile devices.
Continuous Training and Awareness
Regular training sessions are vital for maintaining awareness around best practices for mobile device security. As new threats emerge, it’s essential to keep employees informed about the latest tactics used by cybercriminals and how to counteract them. I’ve found that incorporating real-world examples into our training sessions makes the information more relatable and impactful. Employees are more likely to remember lessons learned from actual incidents than from theoretical discussions.
Leveraging Technology
Utilizing technology effectively is another essential aspect of strengthening mobile device security. Implementing tools like Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions, encryption software, and antivirus programs can significantly enhance your organization’s defenses. In my experience, investing in the right technology pays off in the long run. It not only simplifies compliance with best practices for mobile device security but also provides peace of mind knowing that sensitive data is protected.
Regular Assessment and Improvement
Finally, regularly assessing your mobile security strategy is critical for identifying areas for improvement. Conducting audits, reviewing policies, and gathering feedback from employees can help you refine your approach over time. I recommend scheduling regular reviews of your mobile security measures to ensure they align with current best practices and address any emerging threats. This proactive approach is key to maintaining effective securing mobile devices strategies.
Strengthening mobile device security requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates ongoing education, technology, and a culture of awareness. By implementing best practices for mobile device security, businesses can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats and protect their sensitive information. As you move forward, remember that securing mobile devices is not just an IT responsibility; it’s a collective effort that involves everyone in your organization. By fostering a culture of security awareness and continuously improving your strategies, you can ensure that your business remains resilient in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.s)
1. What is mobile device security?
Mobile device security refers to the measures and practices implemented to protect mobile devices—such as smartphones and tablets—from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. It encompasses a range of strategies, including strong authentication, encryption, and regular software updates.
2. Why is multi-factor authentication important?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors before accessing an account. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised. Implementing MFA is one of the best practices for mobile device security that businesses should adopt.
3. How often should I update my mobile device software?
It’s crucial to update your mobile device software as soon as updates become available. Regular updates help patch security vulnerabilities and improve functionality. Following the best practices for mobile device security, you should enable automatic updates whenever possible to ensure your devices are always protected.
4. What are the signs that my mobile device has been compromised?
Signs of a compromised mobile device may include unusual behavior such as unexpected pop-ups, slow performance, unfamiliar apps, or excessive data usage. If you notice any of these indicators, it’s essential to take immediate action to secure your device and investigate potential breaches.
5. Can using a VPN improve my mobile device security?
Yes, using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can significantly enhance your mobile device security when connected to public Wi-Fi networks. A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it much harder for hackers to intercept your data. This is an important aspect of securing mobile devices in public spaces.
6. What should I do if I lose my mobile device?
If you lose your mobile device, immediately report it to your IT department or service provider. Utilize remote wipe capabilities if available to erase sensitive data from the device. Following best practices for mobile device security, ensure that you have a plan in place for such scenarios.
7. Are there specific antivirus apps recommended for mobile devices?
While there are many antivirus apps available, it’s essential to choose reputable options from trusted developers. Look for antivirus solutions that offer real-time protection, malware scanning, and features tailored for mobile devices. Always check reviews and ratings before installing any app.
8. How can I educate my employees about mobile security risks?
Educating employees about mobile security risks can be done through regular training sessions that cover topics like recognizing phishing attempts, safe browsing habits, and proper password management. Incorporating real-world examples and interactive exercises can make the training more engaging and effective.
9. What is the difference between MDM and MAM?
Mobile Device Management (MDM) focuses on managing and securing devices themselves, while Mobile Application Management (MAM) specifically targets managing applications on those devices. Both are essential components of a comprehensive mobile security strategy.
10. How can small businesses implement these best practices effectively?
Small businesses can implement best practices for mobile device security by prioritizing employee education, utilizing affordable MDM solutions, enforcing strong password policies, and regularly updating software on all devices. It’s vital to create a culture of security awareness that encourages proactive measures among all employees. This concludes the blog post on “Mobile Device Security: 5 Best Practices Every Business Should Implement Now!”



