Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, the security of your business is more critical than ever. I’ve witnessed firsthand the devastating effects that a security breach can have on an organization—financial loss, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions. This is why conducting regular security assessments is not just a best practice; it’s a necessity for any business that values its integrity and customer trust.
But what exactly are security assessments? At their core, these assessments are systematic evaluations of your organization’s security posture. They help identify vulnerabilities in your systems, applications, and processes before they can be exploited by malicious actors. Think of it as a health check for your digital infrastructure; just as you would regularly visit a doctor to ensure your physical well-being, your business needs regular security assessments to maintain its cybersecurity health.
In this blog post, we will explore the importance of conducting regular security assessments and how they can protect your organization from potential threats. We will dive into the key components of effective assessments, including vulnerability assessments and security audit checklists, and discuss how to prepare for an assessment to maximize its effectiveness.
Furthermore, we’ll address the common vulnerabilities that organizations face and provide actionable steps for remediation. We’ll also highlight the role compliance plays in security assessments and how fostering a culture of continuous improvement can enhance your organization’s overall security posture.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of why regular security assessments are essential for your business and how to implement them effectively. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, prioritizing security is crucial in today’s threat landscape. So let’s embark on this journey together to strengthen your business against potential vulnerabilities and ensure a secure future.
What Does Conducting Regular Security Assessments Involve?
As an experienced entrepreneur and S.E.O expert, I’ve learned firsthand the importance of conducting regular security assessments for my business. It’s not just about protecting our digital assets, but also safeguarding our reputation and the trust of our clients. Regular security assessments involve a comprehensive evaluation of your organization’s security posture, covering various aspects such as network infrastructure, systems, applications, and even physical security measures.
The goal is to identify potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, or gaps in your security controls that could be exploited by malicious actors. One of the key components of conducting regular security assessments is the security audit checklist. This comprehensive document serves as a guide for the assessment process, ensuring that no critical area is overlooked. The security audit checklist typically includes sections on:
- Network security: Evaluating the configuration and security of routers, switches, firewalls, and other network devices.
- System security: Assessing the security of servers, workstations, and other computing devices, including operating system patches and configurations.
- Application security: Reviewing the security of web applications, databases, and other software used by the organization.
- Physical security: Inspecting the physical security measures in place, such as access controls, surveillance systems, and environmental controls.
- Personnel security: Evaluating the security awareness and training of employees, as well as access controls and policies related to user accounts and privileges.
By following a structured security audit checklist, you can ensure that your regular security assessments are thorough and consistent, allowing you to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. In my experience, conducting regular security assessments has been crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of our systems. It has helped us detect and mitigate potential threats, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, and data breaches.
By proactively addressing security issues, we’ve been able to avoid costly downtime, data loss, and reputational damage. To illustrate the importance of regular security assessments, consider the case of a small e-commerce business that failed to update its web application software. Attackers exploited a known vulnerability, gained access to the system, and stole customer data.
The breach resulted in significant financial losses, legal liabilities, and a loss of customer trust that ultimately led to the business closing down. This example highlights the need for businesses of all sizes to prioritize conducting regular security assessments as part of their overall security strategy. By staying vigilant and proactive, you can significantly reduce the risk of such incidents and protect your organization’s valuable assets. In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into the specific benefits of vulnerability assessments and why they are essential for your business.
Why Are Vulnerability Assessments Essential for Your Business?
When it comes to protecting your business, understanding the importance of vulnerability assessments is critical. These assessments are a vital part of conducting regular security assessments and serve as a proactive approach to identifying weaknesses in your security posture. From my experience, neglecting this aspect can lead to dire consequences.
What Are Vulnerability Assessments?
A vulnerability assessment is a systematic review of security weaknesses in an information system. This process involves identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing vulnerabilities in your systems, networks, and applications. The ultimate goal is to reduce the risk of exploitation by malicious actors. In my own journey as an entrepreneur, I’ve seen how conducting regular security assessments, including thorough vulnerability assessments, can make a significant difference. For instance, during one assessment, we discovered outdated software on several devices that could have been easily exploited. By addressing these vulnerabilities promptly, we avoided what could have been a costly data breach.
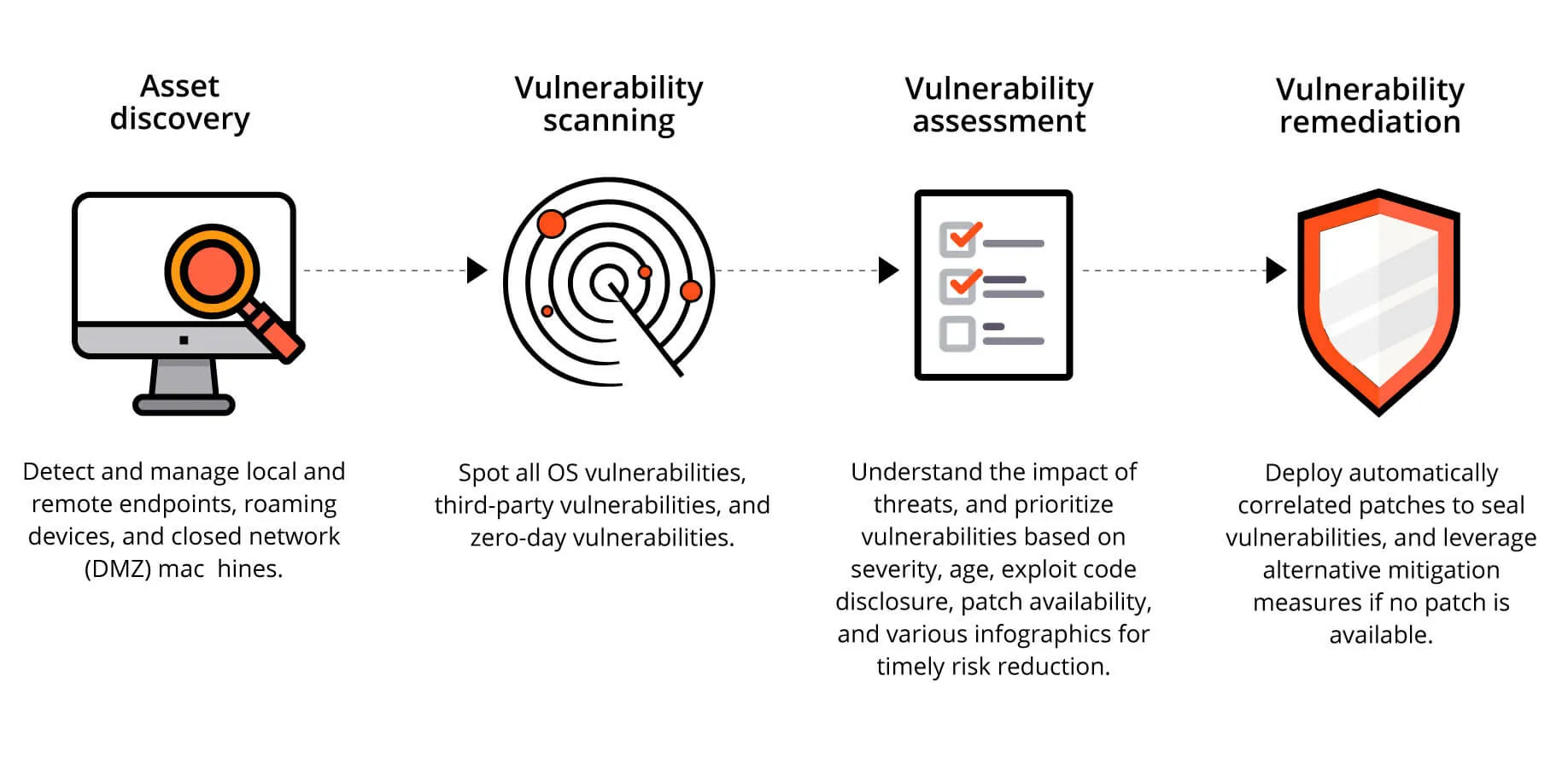
Key Benefits of Conducting Regular Vulnerability Assessments
- Proactive Threat Identification
- One of the most significant advantages of vulnerability assessments is their ability to identify potential threats before they can be exploited. By regularly scanning your systems for vulnerabilities, you can stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
- Many industries have specific regulations that require regular security assessments and vulnerability testing. For example, businesses handling sensitive customer data must comply with standards like GDPR or PCI DSS. Failing to meet these requirements can result in hefty fines and legal issues.
- Enhanced Security Posture
- Regularly conducting vulnerability assessments helps strengthen your overall security posture. By identifying and remediating vulnerabilities, you build a more resilient defense against potential attacks.
- Cost Savings
- Addressing vulnerabilities early can save your business significant costs associated with data breaches, including legal fees, recovery costs, and reputational damage. In fact, according to a study by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was around $4.45 million! By investing in conducting regular security assessments, you can potentially avoid these expenses.
- Informed Decision-Making
- Vulnerability assessments provide valuable insights that help you make informed decisions about your security strategy. Understanding where your weaknesses lie allows you to allocate resources effectively and prioritize remediation efforts.
Real-World Impact
Let me share a quick story from my experience that illustrates the importance of vulnerability assessments. A colleague of mine ran a small tech startup that experienced rapid growth. They were so focused on scaling their operations that they overlooked their cybersecurity measures. After conducting a vulnerability assessment, they discovered multiple critical vulnerabilities in their software infrastructure. Thanks to this proactive approach, they were able to patch those vulnerabilities before any damage occurred. This not only saved them from potential financial loss but also strengthened their reputation as a secure service provider in the market.
Make Vulnerability Assessments Part of Your Routine
Integrating vulnerability assessments into your routine is essential for maintaining a strong security posture. These assessments are not just about compliance; they are about safeguarding your business against potential threats and ensuring the trust of your clients. As we move forward in this blog post, we’ll discuss how often you should conduct these vital assessments to keep your business secure and thriving.
How Often Should You Conduct Security Assessments?
Determining how often to conduct security assessments is crucial for maintaining a robust security posture. In my experience, the frequency of conducting regular security assessments can vary based on several factors, including the size of your business, the nature of your operations, and the sensitivity of the data you handle. Let’s explore these factors in detail and establish a guideline for your organization.
Factors Influencing Assessment Frequency
- Business Size and Complexity
- Larger organizations with complex infrastructures may require more frequent assessments. For instance, if your business operates across multiple locations or has a diverse range of applications and systems, you should consider conducting security assessments quarterly or even monthly. In contrast, smaller businesses might find that semi-annual assessments suffice.
- Industry Standards and Compliance Requirements
- Certain industries have specific regulations that dictate how often security assessments must be conducted. For example, companies in finance or healthcare are often required to perform assessments annually or more frequently to comply with regulations like PCI DSS or HIPAA. Staying compliant not only protects your business but also builds trust with clients.
- Changes in Technology and Infrastructure
- If your organization frequently updates its technology, adds new applications, or undergoes significant changes in infrastructure, it’s wise to conduct security assessments more often. Each new addition can introduce vulnerabilities that need to be identified and mitigated promptly.
- Threat Landscape
- The cybersecurity threat landscape is constantly evolving. If there’s been an uptick in cyber threats targeting your industry or if you’ve experienced a recent incident (even if it was minor), it’s essential to conduct a security assessment as soon as possible to identify any potential weaknesses.
- Business Operations
- If your business handles sensitive data or engages in high-risk activities (like online transactions), you should prioritize conducting regular security assessments more frequently—at least quarterly or even monthly—to ensure that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed promptly.
Recommended Frequency for Security Assessments
Based on the factors mentioned above, here’s a general guideline for how often you should conduct security assessments:
- Monthly: For organizations with high-risk operations, sensitive data handling, or rapidly changing technology environments.
- Quarterly: For medium-sized businesses or those in regulated industries where compliance is critical.
- Semi-Annually: For smaller businesses with stable operations and lower risk profiles.
- Annually: For organizations with minimal changes in technology and lower compliance requirements.
Real-Life Example
Let me share an experience from my own business journey that highlights the importance of assessment frequency. A few years ago, we decided to conduct a comprehensive security assessment after experiencing a minor phishing attempt. Initially, we planned for an annual assessment; however, after realizing how quickly threats evolve, we shifted to quarterly assessments. During one of our quarterly reviews, we discovered outdated software that could have been exploited by attackers. By addressing this vulnerability immediately, we not only secured our systems but also gained peace of mind knowing we were proactively managing our risks.
Make Security Assessments a Habit
Establishing a routine for conducting regular security assessments is essential for protecting your business from potential threats. By considering factors like business size, industry standards, and changes in technology, you can determine the right frequency that fits your organization’s needs. In the next section, we’ll delve into the key components of a security audit checklist, ensuring that your assessments are thorough and effective.
What Are the Key Components of a Security Audit Checklist?
When it comes to conducting regular security assessments, having a well-structured security audit checklist is essential. This checklist acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the various aspects of your security posture and ensuring that no critical area is overlooked. Based on my experiences, I can attest that a thorough checklist not only simplifies the assessment process but also enhances the effectiveness of your security measures.
Key Components of a Security Audit Checklist
- Network Security
- Firewall Configurations: Check the rules and settings of your firewalls to ensure they are properly configured to block unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Verify that your IDS is operational and regularly updated to detect potential threats.
- Wireless Security: Assess the security of your Wi-Fi networks, including encryption protocols and access controls.
- System Security
- Patch Management: Ensure all systems and software are up-to-date with the latest security patches. This is crucial for mitigating vulnerabilities.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Solutions: Confirm that these solutions are installed, updated, and actively scanning for threats on all devices.
- User Account Management: Review user accounts for proper access controls, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive systems.
- Application Security
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Check if WAFs are in place to protect web applications from common threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Code Reviews: Conduct regular code reviews for custom applications to identify potential vulnerabilities early in the development process.
- Third-Party Software: Assess any third-party applications or plugins for known vulnerabilities and ensure they are regularly updated.
- Physical Security
- Access Controls: Evaluate physical access controls to sensitive areas, including keycard systems, biometric scanners, and visitor logs.
- Surveillance Systems: Ensure that surveillance cameras are operational and positioned effectively to monitor critical areas.
- Environmental Controls: Check for fire suppression systems, temperature controls, and other environmental factors that could affect hardware integrity.
- Personnel Security
- Employee Training: Assess the effectiveness of security awareness training programs for employees. Regular training helps mitigate human errors that can lead to security breaches.
- Background Checks: Review policies regarding background checks for new hires, especially those with access to sensitive information.
- Incident Response Plans: Ensure all employees are aware of their roles in the event of a security incident.
- Compliance
- Regulatory Requirements: Review compliance with relevant regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. This includes ensuring proper data handling practices and documentation.
- Audit Trails: Maintain logs of system access and changes to ensure accountability and traceability in case of an incident.
- Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery
- Backup Procedures: Verify that data backup procedures are in place and tested regularly to ensure data recovery in case of an incident.
- Disaster Recovery Plans: Review disaster recovery plans for effectiveness and ensure they are updated based on recent changes in technology or business operations.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Checklist
In my experience, using a detailed security audit checklist has proven invaluable during assessments. For instance, during one assessment cycle, we discovered that our network firewall configurations were not as robust as we thought. By following our checklist, we identified gaps in our defenses that could have been exploited by attackers. Moreover, having a checklist helps ensure consistency across assessments. It allows you to track improvements over time and provides a clear framework for identifying areas that require additional focus or resources.
Your Roadmap to Stronger Security
In conclusion, a well-structured security audit checklist is an indispensable tool when it comes to conducting regular security assessments. By covering all critical components—from network security to compliance—you can systematically evaluate your organization’s security posture and address vulnerabilities effectively. Next up, we’ll discuss how to prepare for a security assessment so you can maximize its effectiveness.

How to Prepare for a Security Assessment?
Preparing for a security assessment is a crucial step that can significantly impact the effectiveness of conducting regular security assessments. From my experience, the more thorough your preparation, the more insights you’ll gain about your organization’s security posture. Here are practical steps to ensure you’re ready for a successful assessment.
1. Assemble Your Security Team
Before diving into the assessment, gather your security team or designate key personnel responsible for overseeing the process. This team should include individuals from various departments, such as IT, compliance, and operations. Having a diverse team ensures that all aspects of your organization’s security are considered.
- Tip: Schedule a kickoff meeting to discuss the assessment’s scope, objectives, and timeline. This meeting sets expectations and fosters collaboration.
2. Define the Scope of the Assessment
Clearly outline what will be included in the assessment. Will it cover all systems, networks, and applications, or will it focus on specific areas? Defining the scope helps you allocate resources effectively and ensures that critical components are not overlooked.
- Example: If your business has recently implemented new software or systems, make sure these are included in the assessment scope.
3. Review Previous Assessments
If you’ve conducted security assessments in the past, review their findings and recommendations. This review will help you understand previous vulnerabilities and whether they have been addressed. It also provides a baseline for measuring improvements over time.
- Tip: Create a summary document that highlights past vulnerabilities and their current status. This can guide your team during the assessment.
4. Conduct Pre-Assessment Checks
Perform preliminary checks to identify any obvious vulnerabilities before the formal assessment begins. This could involve:
- System Updates: Ensure all systems are updated with the latest patches.
- User Access Reviews: Check user accounts to confirm that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive systems.
- Backup Verification: Make sure your data backup processes are functioning correctly.
These checks can help streamline the formal assessment process and reduce potential findings.
5. Train Your Employees
Educate your employees about the upcoming assessment and its importance. Explain their roles during the process and encourage them to be transparent about any concerns or issues they may have noticed regarding security.
- Example: Consider hosting a brief training session or sending out an informational email to raise awareness about the assessment.
6. Gather Necessary Documentation
Compile all relevant documentation that may be needed during the assessment. This includes:
- Policies and Procedures: Security policies, incident response plans, and compliance documentation.
- Network Diagrams: Visual representations of your network architecture.
- Previous Audit Reports: Any reports from past assessments that can provide valuable context.
Having this information readily available will facilitate a smoother assessment process.
7. Set Up Communication Channels
Establish clear communication channels between your security team and any external assessors (if applicable). Regular updates and open lines of communication can help address any questions or concerns that arise during the assessment.
- Tip: Use project management tools or shared documents to keep everyone informed about progress and findings.
8. Create a Remediation Plan
Before starting the assessment, develop a preliminary remediation plan for addressing any potential vulnerabilities identified during the process. This plan should outline how you will prioritize issues based on risk level and allocate resources for remediation efforts.
Be Proactive in Your Preparation
Thorough preparation is key to maximizing the effectiveness of your security assessments. By assembling a competent team, defining scope, reviewing past assessments, conducting pre-checks, training employees, gathering documentation, setting up communication channels, and creating a remediation plan, you position your organization for success in identifying vulnerabilities and enhancing security measures. Next, we’ll explore what tools and techniques can be used for conducting vulnerability assessments effectively.
What Tools and Techniques Can Be Used for Vulnerability Assessments?
As an experienced entrepreneur and S.E.O expert, I’ve learned that conducting regular security assessments requires a combination of tools and techniques to effectively identify vulnerabilities in your systems. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most commonly used approaches and the tools that can assist in the process.
Automated Vulnerability Scanning
One of the most efficient ways to identify vulnerabilities is through automated vulnerability scanning tools. These tools systematically scan your networks, systems, and applications for known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Some popular options include:
- Nessus: A comprehensive vulnerability scanner that can assess a wide range of systems and applications.
- OpenVAS: An open-source vulnerability scanner that offers a cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Nexpose: A vulnerability management tool that provides detailed reports and remediation guidance.
While automated scanning is a valuable tool, it’s important to note that it has limitations. These tools may not detect all vulnerabilities, especially those that are more complex or require human analysis.
Manual Penetration Testing
In addition to automated scanning, manual penetration testing is another effective technique for identifying vulnerabilities. Penetration testing involves simulating real-world attacks to uncover weaknesses in your security measures. This approach is often conducted by experienced security professionals who use a combination of tools and techniques to assess your systems. Some common tools used in penetration testing include:
- Metasploit: A popular framework for developing and executing exploit code against target systems.
- Kali Linux: A Linux distribution designed for penetration testing and digital forensics, which includes a wide range of security tools.
- Burp Suite: A web application security testing platform that helps identify vulnerabilities in web applications.
Manual penetration testing can provide a more comprehensive assessment of your security posture, as it involves human analysis and creativity. However, it can be time-consuming and requires specialized expertise.
Vulnerability Databases and Threat Intelligence
Staying informed about the latest vulnerabilities and threats is crucial for effective security assessments. Vulnerability databases and threat intelligence services can help you stay ahead of potential attackers. Some useful resources include:
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD): A comprehensive database of publicly disclosed cybersecurity vulnerabilities maintained by the U.S. government.
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE): A list of publicly disclosed cybersecurity vulnerabilities that provides a reference-method for publicly disclosing the existence of vulnerabilities.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: Services like Recorded Future or Anomali that provide real-time threat intelligence to help organizations identify and mitigate risks.
By leveraging these resources, you can stay informed about the latest threats and ensure that your security assessments are up-to-date and effective.
Real-World Example
In my own experience, I’ve seen firsthand how a combination of automated scanning and manual penetration testing can uncover critical vulnerabilities. During one assessment, our team used a combination of Nessus and Metasploit to identify a vulnerability in an outdated web application. Through manual testing, we were able to exploit the vulnerability and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. By addressing this issue promptly, we avoided a potentially devastating data breach that could have had serious consequences for our business and our clients.
Leverage the Right Tools and Techniques
In conclusion, conducting regular security assessments requires a combination of tools and techniques to effectively identify vulnerabilities in your systems. Automated vulnerability scanning, manual penetration testing, and leveraging vulnerability databases and threat intelligence can all contribute to a comprehensive assessment process.
By staying informed about the latest tools and techniques, and adapting your approach to the specific needs of your organization, you can ensure that your security assessments are effective and efficient. In the next section, we’ll discuss how to analyze and report the findings from your security assessments.

How to Analyze and Report Findings from Security Assessments?
Once you’ve completed your conducting regular security assessments, the next critical step is analyzing and reporting your findings. This process is essential for understanding the vulnerabilities identified, prioritizing remediation efforts, and communicating results to stakeholders. Based on my experiences, here’s how to effectively analyze and report your security assessment findings.
1. Organize Your Findings
After conducting the assessment, gather all the data collected from automated scans, manual tests, and any other sources. Organizing this information is crucial for effective analysis. You can categorize findings based on:
- Severity Levels: Classify vulnerabilities as high, medium, or low based on their potential impact on your organization. This helps prioritize which issues need immediate attention.
- Affected Systems: Group findings by the systems or applications they affect. This categorization allows you to see which areas of your organization are most vulnerable.
- Type of Vulnerability: Sort vulnerabilities by type (e.g., software flaws, configuration issues, or policy violations) to identify patterns that may require broader organizational changes.
2. Analyze Vulnerability Impact
For each identified vulnerability, assess its potential impact on your organization. Consider factors such as:
- Data Sensitivity: What type of data could be compromised? For example, personal identifiable information (PII) or financial data typically carries higher risk.
- Likelihood of Exploitation: Evaluate how likely it is that a vulnerability could be exploited based on current threat intelligence and trends in your industry.
This analysis will help you understand the risks associated with each vulnerability and guide your remediation efforts.
3. Develop a Remediation Plan
Once you’ve analyzed the findings, create a remediation plan that outlines how you’ll address each vulnerability. This plan should include:
- Prioritization: Focus on high-severity vulnerabilities first, especially those that could lead to significant data breaches or compliance violations.
- Action Steps: Clearly define what actions need to be taken for each vulnerability (e.g., applying patches, reconfiguring systems, or enhancing security policies).
- Responsible Parties: Assign team members responsible for implementing each action item. Accountability ensures that vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner.
4. Create a Comprehensive Report
A well-structured report is essential for communicating your findings and remediation plans to stakeholders. Your report should include:
- Executive Summary: A brief overview of the assessment’s objectives, methodology, and key findings. This section should be understandable for non-technical stakeholders.
- Detailed Findings: A section that outlines all identified vulnerabilities, their severity levels, affected systems, and recommended actions.
- Visuals: Use charts or graphs to illustrate key points and trends in your findings. Visual aids can help make complex data more digestible.
- Remediation Timeline: Include a timeline for addressing identified vulnerabilities to provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of when improvements will occur.
5. Present Findings to Stakeholders
After compiling your report, present the findings to relevant stakeholders within your organization. This meeting is an opportunity to discuss the implications of the findings and emphasize the importance of addressing vulnerabilities promptly. During the presentation:
- Encourage questions and discussions about potential impacts on business operations.
- Highlight the benefits of remediation efforts in terms of risk reduction and compliance.
Real-Life Example
In one instance at my company, we conducted a thorough security assessment that revealed several critical vulnerabilities in our web application. After analyzing the findings and developing a detailed report, we presented our results to senior management. The executive summary highlighted the potential risks associated with these vulnerabilities—particularly concerning customer data protection. As a result of our presentation, management prioritized funding for necessary upgrades and security enhancements. This experience reinforced my belief in the importance of effective reporting; when stakeholders understand the risks involved, they are more likely to support necessary changes.
Communicate Effectively for Stronger Security
Analyzing and reporting findings from your security assessments is a vital step in enhancing your organization’s security posture. By organizing findings, assessing their impact, developing a remediation plan, creating a comprehensive report, and effectively presenting results to stakeholders, you can ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly and effectively. Next up, we’ll discuss some common vulnerabilities often identified during assessments and how businesses can remediate them.
What Are Common Vulnerabilities Identified in Assessments?
As an experienced entrepreneur and S.E.O expert, I’ve seen firsthand the importance of conducting regular security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and processes. Through these assessments, we often uncover common vulnerabilities that, if left unchecked, can lead to serious security breaches and costly consequences. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most prevalent vulnerabilities identified during security assessments.
1. Unpatched Software and Systems
One of the most common vulnerabilities we encounter is outdated or unpatched software and systems. Software vendors regularly release security updates to address known vulnerabilities, but if these updates are not applied promptly, attackers can exploit these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access to systems and data. This vulnerability is particularly prevalent in legacy systems or software that is no longer actively maintained.
2. Weak or Reused Passwords
Despite ongoing efforts to educate users about the importance of strong passwords, weak or reused passwords remain a significant vulnerability. Attackers often use brute-force attacks or password guessing techniques to gain access to accounts with weak passwords. Additionally, when users reuse the same password across multiple accounts, a single breach can compromise all of their accounts.
3. Misconfigured Systems and Applications
Improper configurations in systems and applications can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. This includes issues such as open ports, default credentials, or overly permissive access controls. Misconfigured firewalls, for example, can allow unauthorized access to internal systems, while improperly configured web applications can be vulnerable to injection attacks.
4. Lack of Employee Security Awareness
Human error is often a contributing factor in security breaches, and a lack of employee security awareness can lead to vulnerabilities. Employees who are not trained to recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, or other security risks can inadvertently expose sensitive information or grant unauthorized access to systems.
5. Inadequate Access Controls
Ineffective access controls can allow unauthorized individuals to gain access to sensitive systems and data. This includes issues such as excessive user privileges, lack of multi-factor authentication, or insufficient monitoring of user activity. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to escalate their privileges and move laterally within an organization’s network.
6. Unprotected Sensitive Data
Sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, or intellectual property, is a prime target for attackers. If this data is not properly secured through encryption, access controls, or secure storage practices, it can be exposed in the event of a breach. Unencrypted data stored on portable devices or transmitted over unsecured channels is particularly vulnerable.
7. Vulnerable Third-Party Software and Services
Many organizations rely on third-party software and services to support their operations, but these external components can introduce vulnerabilities if not properly vetted and monitored. Outdated or unpatched third-party software can provide an entry point for attackers, while poorly configured cloud services can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access.
Real-World Example
In one instance, we conducted a security assessment for a client in the healthcare industry and discovered that their patient records were stored on an unencrypted server. This vulnerability, if exploited, could have led to a massive data breach, exposing sensitive patient information and subjecting the organization to significant legal and financial penalties under HIPAA regulations.
By identifying this vulnerability and working with the client to implement proper encryption and access controls, we were able to mitigate the risk and ensure the protection of patient data.
Proactive Vulnerability Management
By understanding these common vulnerabilities and addressing them through conducting regular security assessments, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of security breaches and protect their critical assets. Regular assessments, combined with proactive vulnerability management practices, can help organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain a strong security posture. In the next section, we’ll discuss how businesses can remediate identified vulnerabilities and strengthen their overall security.
How Can Businesses Remediate Identified Vulnerabilities?
Once vulnerabilities have been identified during conducting regular security assessments, the next critical step is remediation. Addressing these vulnerabilities effectively can significantly enhance your organization’s security posture and protect against potential threats. Based on my experiences, here are actionable strategies for remediating identified vulnerabilities.
Prioritize Vulnerabilities
Not all vulnerabilities pose the same level of risk to your organization. Therefore, it’s essential to prioritize them based on their severity and potential impact. Use a risk assessment framework, such as the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), to evaluate each vulnerability’s likelihood of exploitation and the potential damage it could cause.
- High Priority: Vulnerabilities that could lead to significant data breaches or system compromises should be addressed immediately.
- Medium Priority: These vulnerabilities may not pose an immediate threat but should be remedied within a reasonable timeframe.
- Low Priority: While these vulnerabilities should not be ignored, they can be scheduled for remediation after higher-priority issues are resolved.
Develop a Remediation Plan
Once you’ve prioritized the vulnerabilities, develop a detailed remediation plan that outlines specific actions to address each issue. This plan should include:
- Action Steps: Clearly define what needs to be done for each vulnerability (e.g., applying patches, reconfiguring settings, or enhancing policies).
- Responsible Parties: Assign team members or departments responsible for implementing each action item.
- Timeline: Set realistic deadlines for remediation efforts based on the priority level of each vulnerability.
Implement Technical Controls
Many vulnerabilities can be remediated through technical controls. Here are some common actions to take:
- Patch Management: Regularly update software and systems with the latest security patches. Establish a patch management process to ensure timely updates.
- Access Controls: Review and enforce access controls to limit user privileges based on the principle of least privilege (PoLP). Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible to enhance security.
- Configuration Management: Regularly review and harden system configurations to eliminate misconfigurations that could lead to vulnerabilities.
Conduct Employee Training
Human error is often a significant factor in security breaches, so it’s essential to provide ongoing security awareness training for employees. Training should cover:
- Recognizing Phishing Attempts: Teach employees how to identify phishing emails and social engineering tactics.
- Best Practices for Password Management: Encourage the use of strong, unique passwords and educate employees about password managers.
- Incident Reporting Procedures: Ensure that employees know how to report suspicious activity or potential security incidents promptly.
Monitor and Test Remediation Efforts
After implementing remediation actions, it’s crucial to monitor their effectiveness continually. This can involve:
- Regular Scans: Conduct follow-up vulnerability scans to verify that identified issues have been resolved.
- Penetration Testing: Consider performing penetration tests after remediation efforts to assess whether vulnerabilities have been effectively mitigated.
- Audit Logs: Review system logs for unusual activity that may indicate ongoing vulnerabilities or attempted exploits.
Document Everything
Documentation is key in the remediation process. Keep detailed records of:
- Identified Vulnerabilities: Document all findings from your assessments, including severity levels and affected systems.
- Remediation Actions Taken: Record all actions taken to remediate vulnerabilities, including dates and responsible parties.
- Follow-Up Assessments: Maintain records of follow-up assessments and their results to track progress over time.
Real-Life Example
In one project I managed, our team discovered several high-priority vulnerabilities in a client’s web application during a security assessment. We prioritized these issues based on their potential impact on sensitive customer data. We developed a comprehensive remediation plan that included applying critical patches, enhancing access controls, and providing employee training on secure coding practices. After implementing these changes, we conducted follow-up testing that confirmed the vulnerabilities had been successfully mitigated. This experience reinforced the importance of a structured approach to remediation; by prioritizing actions and documenting our efforts, we not only improved the client’s security posture but also built trust with their customers.
Take Action Against Vulnerabilities
In conclusion, effectively remediating identified vulnerabilities is essential for maintaining a strong security posture after conducting regular security assessments. By prioritizing issues, developing a clear remediation plan, implementing technical controls, conducting employee training, monitoring efforts, and documenting everything, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of security breaches. Next, we’ll explore the role compliance plays in security assessments and how it affects business operations and security posture.
What Role Does Compliance Play in Security Assessments?
Compliance plays a critical role in the realm of cybersecurity and is an essential consideration when conducting regular security assessments. Regulatory frameworks and industry standards dictate how organizations must manage their data and security practices. As an entrepreneur who has navigated these waters, I can attest that understanding compliance requirements not only helps protect your business but also builds trust with clients and stakeholders.
Understanding Compliance in Cybersecurity
Compliance refers to the adherence to laws, regulations, guidelines, and specifications relevant to an organization’s operations. In the context of cybersecurity, compliance often involves:
- Data Protection Regulations: Laws that dictate how organizations must handle sensitive data. Examples include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S.
- Industry Standards: Frameworks that provide guidelines for implementing effective security practices. Common standards include the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for businesses that handle credit card transactions and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework.
Why Compliance Matters
- Legal Obligations
- Many organizations are legally required to comply with specific regulations based on their industry or geographic location. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines, legal action, and even criminal charges.
- Risk Management
- Compliance frameworks often include best practices for risk management, helping organizations identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. By adhering to these guidelines, businesses can reduce their risk of security breaches.
- Customer Trust
- Customers are increasingly concerned about how businesses handle their data. Demonstrating compliance with relevant regulations can enhance customer trust and loyalty. For instance, being GDPR-compliant signals to customers that you take their privacy seriously.
- Competitive Advantage
- In many industries, compliance can serve as a differentiator. Organizations that prioritize compliance may be more appealing to potential clients, especially those in regulated sectors like finance or healthcare.
Integrating Compliance into Security Assessments
To effectively integrate compliance into your conducting regular security assessments, consider the following steps:
- Identify Relevant Regulations
- Determine which regulations apply to your organization based on your industry and geographic location. This will help you understand your compliance obligations.
- Develop a Compliance Checklist
- Create a checklist that aligns with relevant regulations and standards. This checklist should include specific controls and practices that need to be assessed during your security assessments.
- Conduct Gap Analyses
- During your security assessments, perform gap analyses to identify areas where your organization may fall short of compliance requirements. This process can help prioritize remediation efforts.
- Document Compliance Efforts
- Maintain thorough documentation of your compliance efforts, including policies, procedures, training records, and assessment findings. This documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance during audits or regulatory reviews.
- Engage Stakeholders
- Involve key stakeholders from various departments (e.g., IT, legal, compliance) in the assessment process to ensure a comprehensive understanding of compliance requirements.
Real-Life Example
In my experience working with a healthcare organization, we conducted a security assessment that revealed several areas of non-compliance with HIPAA regulations. The assessment identified weaknesses in data encryption practices and employee training on patient data handling. By addressing these vulnerabilities through targeted remediation efforts—such as implementing stronger encryption protocols and enhancing employee training—we were able to bring the organization into compliance while significantly improving its overall security posture. This experience highlighted how integrating compliance into our security assessments not only mitigated risks but also ensured that we were meeting our legal obligations.
Compliance as a Cornerstone of Security
In conclusion, compliance plays a vital role in shaping your organization’s approach to cybersecurity and should be an integral part of your conducting regular security assessments. By understanding relevant regulations, integrating compliance into your assessment processes, and prioritizing adherence to industry standards, you can enhance your organization’s security posture while building trust with clients and stakeholders. Next up, we’ll discuss how businesses can foster a culture of continuous improvement in their security practices to adapt to evolving threats.
How to Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement in Security Practices?
As an experienced entrepreneur and S.E.O expert, I’ve learned that conducting regular security assessments is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to maintaining a strong security posture. To truly protect your organization from evolving threats, it’s essential to foster a culture of continuous improvement in your security practices. This involves ongoing training, regular policy updates, and a proactive approach to addressing vulnerabilities.
Provide Continuous Security Training
Employee education is a critical component of any effective security strategy. Regularly training your staff on best practices, emerging threats, and their role in maintaining a secure environment is essential. Consider the following strategies:
- Implement Mandatory Training: Require all employees to complete security awareness training upon hire and at regular intervals thereafter.
- Use Real-World Examples: Use real-world examples of security incidents to illustrate the importance of security practices and the consequences of negligence.
- Gamify Training: Make training engaging and interactive by incorporating quizzes, simulations, and rewards for participation.
Regularly Review and Update Security Policies
Security policies are the foundation of your organization’s security practices. To ensure they remain effective, regularly review and update them to address evolving threats and changing business needs. This includes:
- Incorporating Lessons Learned: Update policies based on findings from conducting regular security assessments and any security incidents that have occurred.
- Aligning with Industry Standards: Ensure that your policies align with relevant industry standards and best practices.
- Communicating Changes: Clearly communicate policy updates to all employees and provide guidance on how to implement the changes.
Implement Continuous Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is an ongoing process that involves identifying, assessing, and remediating vulnerabilities in your systems and applications. To maintain a proactive approach, consider:
- Automating Vulnerability Scans: Use tools to regularly scan your environment for known vulnerabilities and generate reports for remediation.
- Prioritizing Remediation: Focus on high-risk vulnerabilities first and establish timelines for addressing lower-risk issues.
- Verifying Remediation: Conduct follow-up scans to ensure that vulnerabilities have been effectively remediated.
Foster a Culture of Accountability
Creating a culture of accountability is essential for ensuring that security practices are consistently followed. This involves:
- Defining Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the security-related roles and responsibilities of each employee and department.
- Establishing Metrics: Set measurable goals and metrics for security performance and hold employees accountable for meeting them.
- Recognizing Security Champions: Identify and recognize employees who consistently demonstrate a commitment to security best practices.
Stay Informed About Emerging Threats
Staying informed about emerging threats is crucial for maintaining a proactive security posture. Encourage your team to:
- Subscribe to Security Newsletters: Stay up-to-date on the latest security news, trends, and best practices by subscribing to reputable security newsletters and blogs.
- Attend Security Conferences: Send team members to security conferences and events to network with peers and learn about new security technologies and strategies.
- Participate in Security Communities: Encourage participation in online security communities, such as forums and social media groups, to share knowledge and learn from others in the field.
Real-Life Example
In my own experience, I’ve seen firsthand how fostering a culture of continuous improvement in security practices can pay dividends. When we first started our business, we treated security as a one-time project, conducting an initial assessment and implementing basic security measures. However, as our business grew and the threat landscape evolved, we realized that this approach was no longer sufficient. We began conducting regular security assessments, implementing continuous vulnerability management, and providing ongoing security training to our employees.
By creating a culture of accountability and staying informed about emerging threats, we were able to significantly enhance our security posture and protect our business from potential attacks. This commitment to continuous improvement not only safeguarded our assets but also built trust with our clients and partners.
Embrace a Proactive Approach to Security
Conducting regular security assessments is just the beginning of a comprehensive security strategy. To truly protect your organization from evolving threats, it’s essential to foster a culture of continuous improvement in your security practices. By providing ongoing training, regularly reviewing and updating policies, implementing continuous vulnerability management, fostering a culture of accountability, and staying informed about emerging threats, you can proactively address vulnerabilities and maintain a strong security posture.
Remember, security is an ongoing journey, not a destination. By embracing a proactive approach and continuously improving your practices, you can ensure that your organization remains resilient in the face of ever-changing threats.
Final Thoughts: Strengthening Your Business Against Threats
In today’s digital landscape, conducting regular security assessments is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses of all sizes. By proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of costly data breaches, compliance violations, and reputational damage.
Throughout this blog post, we’ve explored the key aspects of effective security assessments, from understanding the importance of regular assessments to implementing a culture of continuous improvement. We’ve discussed the components of a comprehensive security audit checklist, the tools and techniques used in vulnerability assessments, and strategies for remediating identified vulnerabilities. One of the most critical takeaways is the need for a holistic approach to security. Security assessments should not be viewed as a one-time event but rather as an ongoing process that adapts to evolving threats and changing business needs.
By fostering a culture of security awareness among employees, regularly updating policies and procedures, and staying informed about the latest security trends, organizations can build a strong foundation for protecting their assets. Remember, security is an investment, not a cost. By prioritizing security measures and allocating resources accordingly, businesses can not only safeguard their operations but also gain a competitive advantage in the market. Clients and partners are increasingly looking for organizations that take security seriously and can demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive data.
In conclusion, conducting regular security assessments is a critical component of a comprehensive security strategy. By following the best practices outlined in this blog post and embracing a proactive approach to security, businesses can strengthen their defenses against evolving threats and position themselves for long-term success in the digital age.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.s)
- What is a security audit?
- A security audit is a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s security posture, covering various aspects such as network infrastructure, systems, applications, and physical security measures.
- How often should I conduct a vulnerability assessment?
- The frequency of vulnerability assessments depends on factors such as business size, industry standards, changes in technology, and threat landscape. Generally, it’s recommended to conduct assessments monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, depending on the organization’s specific needs.
- What is included in a security audit checklist?
- A security audit checklist typically includes sections on network security, system security, application security, physical security, personnel security, compliance, and business continuity/disaster recovery.
- What are the benefits of conducting regular security assessments?
- Regular security assessments help identify potential vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, ensure compliance with regulations, enhance overall security posture, and save costs associated with data breaches and security incidents.
- How do I prepare my team for a security assessment?
- To prepare your team, assemble a security team, define the scope of the assessment, review previous assessments, conduct pre-assessment checks, train employees, gather necessary documentation, set up communication channels, and create a remediation plan.
- What tools can assist in conducting vulnerability assessments?
- Tools that can assist in vulnerability assessments include automated scanning tools like Nessus, OpenVAS, and Nexpose, as well as manual penetration testing tools such as Metasploit and Burp Suite.
- How do I analyze the findings from a security assessment?
- To analyze findings, organize the data, assess the impact of vulnerabilities, develop a remediation plan, create a comprehensive report, and present the findings to stakeholders.
- What common vulnerabilities should I be aware of?
- Common vulnerabilities include unpatched software and systems, weak or reused passwords, misconfigured systems and applications, lack of employee security awareness, inadequate access controls, unprotected sensitive data, and vulnerable third-party software and services.
- How can I ensure compliance during security audits?
- To ensure compliance, identify relevant regulations, develop a compliance checklist, conduct gap analyses, document compliance efforts, and engage stakeholders from various departments.
- What steps should I take after identifying vulnerabilities?
- After identifying vulnerabilities, prioritize them based on risk, develop a remediation plan, implement technical controls, conduct employee training, monitor and test remediation efforts, and document everything.



