Introduction
In today’s digital age, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. With businesses increasingly relying on technology and the internet, the threats posed by cybercriminals have also escalated. Organizations of all sizes face risks ranging from data breaches to ransomware attacks, making it essential to establish robust cybersecurity measures. This is where developing a cybersecurity policy becomes crucial.
Developing a cybersecurity policy is not merely a regulatory requirement; it is a strategic imperative that helps protect sensitive information and maintain customer trust. A well-crafted policy outlines how an organization will safeguard its digital assets, ensuring that employees understand their roles in mitigating risks. However, creating such a policy can be complex and daunting, especially for those unfamiliar with cybersecurity principles.
This blog post aims to simplify the process of creating comprehensive cybersecurity policies. We will explore essential components, common pitfalls to avoid, and best practices for engaging stakeholders throughout the development process. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how to draft effective security policies tailored to your organization’s specific needs.
As we delve into this topic, we will address key questions such as: What are the core elements of an effective cybersecurity policy? Why is drafting security policies essential? How can organizations ensure compliance and effectiveness? These questions will guide our exploration of developing a cybersecurity policy, providing you with actionable insights to enhance your organization’s security posture.
In an era where cyber threats are ever-evolving, being proactive about cybersecurity is not just wise—it’s necessary. Let’s embark on this journey to empower your organization with the knowledge and tools needed to create a resilient cybersecurity framework.
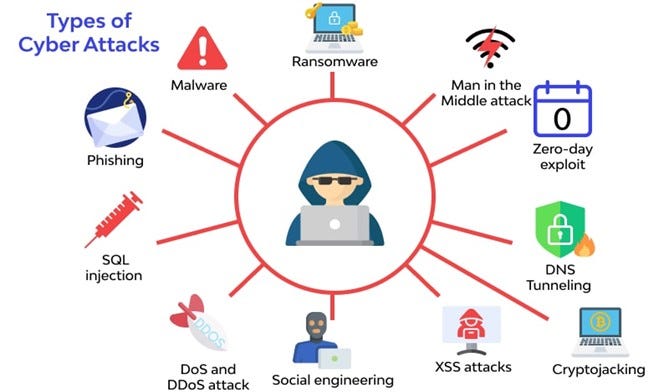
Image: Types of cyberthreats
What is Involved in Developing a Cybersecurity Policy?
Developing a cybersecurity policy is crucial for any business today. With the rise of digital threats, having a solid plan can protect your organization from significant risks. So, what exactly does it involve? Let’s break it down.
Understanding the Basics
At its core, developing a cybersecurity policy means creating a framework that outlines how your organization will protect its digital assets. This includes data, networks, and systems from cyber threats. A comprehensive policy serves as a roadmap for your employees, guiding them on how to handle sensitive information and respond to security incidents.In my experience, the first step in developing a cybersecurity policy is to assess your current security posture. This means looking at what you already have in place and identifying any gaps. For example, when I first started drafting security policies for my business, I realized we had no clear guidelines on password management. This oversight could have led to serious vulnerabilities.
Key Components of a Cybersecurity Policy
When developing a cybersecurity policy, several key components must be included:
- Purpose and Scope: Clearly define why the policy exists and what it covers. This helps everyone understand its importance.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assign specific roles to team members. For instance, who will monitor security incidents? Who will manage updates? Clearly defined roles make it easier to hold people accountable.
- Policy Statement: This is the heart of your document. It should outline your organization’s commitment to cybersecurity and the measures you will take to protect data.
- Incident Response Plan: What happens if there’s a breach? Developing a clear incident response plan is critical. It should detail steps to take when an incident occurs, including who to notify and how to mitigate damage.
- Training and Awareness: Regular training sessions are essential for ensuring that employees understand the policies in place. When I implemented training programs in my company, I noticed a significant decrease in security incidents.
Importance of Developing a Cybersecurity Policy
Developing a cybersecurity policy isn’t just about compliance; it’s about building trust with your customers and stakeholders. A well-crafted policy demonstrates that your organization takes security seriously. It can also help you avoid costly breaches that can damage your reputation.Moreover, developing a cybersecurity policy helps create a culture of security within your organization. When employees see that their company prioritizes cybersecurity, they are more likely to follow best practices in their daily activities.
The Role of Drafting Security Policies
Drafting security policies is an ongoing process. As technology evolves, so do threats. Therefore, it’s essential to regularly review and update your policies. In my journey of developing a cybersecurity policy, I learned that involving various departments in drafting security policies leads to more comprehensive coverage.For example, when drafting our data protection policy, I collaborated with the IT department and legal team. Their insights were invaluable in ensuring we met both technical requirements and legal obligations.
Developing a cybersecurity policy involves understanding your organization’s needs and creating a structured approach to protect against cyber threats. By including essential components like purpose, roles, and an incident response plan, you can create a robust framework that enhances your organization’s security posture.As you embark on this journey of developing a cybersecurity policy, remember that it’s not just about writing documents; it’s about fostering a culture of security awareness among all employees.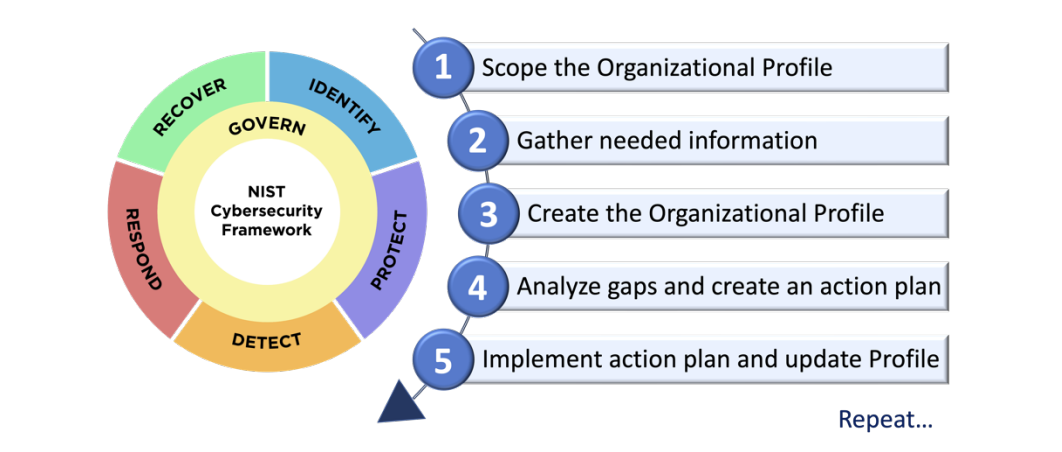
Image: NIST Cybersecurity Policy Framework
Why is Drafting Security Policies Essential?
Drafting security policies is a fundamental aspect of developing a cybersecurity policy. It lays the groundwork for how your organization will respond to threats and manage its digital assets. But why is this process so essential? Let’s explore the critical reasons behind drafting security policies and how they contribute to a robust cybersecurity framework.
The Foundation of Cybersecurity
At its core, drafting security policies provides a structured approach to managing risks. When you commit to developing a cybersecurity policy, you’re essentially creating a blueprint for your organization’s security practices. This blueprint helps everyone understand their roles in protecting sensitive information.In my experience, when I first started drafting security policies, I underestimated their importance. Initially, I thought simply having antivirus software was enough. However, after facing a minor security incident, I realized that without clear policies, our team was unsure how to respond effectively. This incident highlighted the need for comprehensive guidelines that everyone could follow.
Benefits of Drafting Security Policies
- Clarity and Consistency: One of the primary benefits of drafting security policies is that it brings clarity. Employees know what is expected of them when they handle sensitive data. This consistency reduces the chances of human error, which is often the weakest link in cybersecurity.
- Risk Mitigation: By clearly outlining procedures for various scenarios—like data breaches or phishing attempts—drafting security policies helps mitigate risks. For example, when we developed our incident response plan as part of our cybersecurity policy, we significantly improved our ability to react quickly to potential threats.
- Compliance and Legal Protection: Many industries have legal requirements for data protection. Drafting security policies ensures that your organization complies with these regulations. This compliance not only protects your organization from legal issues but also builds trust with clients who expect their data to be handled securely.
Engaging Stakeholders in the Drafting Process
An often-overlooked aspect of drafting security policies is stakeholder engagement. Involving various departments in the process can lead to more effective policies. When I was developing a cybersecurity policy for my business, I made it a point to include input from IT, HR, and even marketing teams.This collaboration was invaluable. For instance, the HR team provided insights into employee training needs, while IT identified technical vulnerabilities we hadn’t considered. By drafting security policies with input from multiple perspectives, we created a more comprehensive approach that addressed diverse concerns.
The Role of Continuous Improvement
Drafting security policies is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. As technology evolves and new threats emerge, your policies must adapt accordingly. Regularly reviewing and updating your policies ensures they remain relevant and effective.In my journey of developing a cybersecurity policy, I learned that feedback from employees is crucial for continuous improvement. After implementing our initial draft, we conducted surveys to gather insights on how well the policies were understood and followed. This feedback allowed us to make necessary adjustments and enhance clarity.
Drafting security policies is essential for any organization committed to developing a cybersecurity policy. It provides clarity, mitigates risks, ensures compliance, and fosters collaboration among departments. By engaging stakeholders in this process and committing to continuous improvement, you can create effective policies that protect your organization from cyber threats.As you embark on the journey of drafting security policies, remember that these documents are living tools that evolve with your organization’s needs and the ever-changing digital landscape.

Image: Compliance Checklist for Security Policies
How to Start Drafting Security Policies?
Starting the process of drafting security policies can feel overwhelming, especially if you’re new to developing a cybersecurity policy. However, breaking it down into manageable steps can make it much easier. In this section, we’ll explore how to effectively begin drafting security policies that will protect your organization’s digital assets.
Step 1: Identify Business Needs
The first step in developing a cybersecurity policy is to identify your organization’s specific needs. This involves understanding the types of data you handle, the potential threats you face, and the regulatory requirements that apply to your industry. For instance, if your business deals with sensitive customer information, your policies must address how to protect that data.
When I began drafting security policies for my company, I conducted a thorough assessment of our data landscape. I mapped out all the sensitive information we collected and stored, which helped me understand where our vulnerabilities lay. This initial assessment was crucial in shaping our cybersecurity policy.
Step 2: Secure Management Approval
Once you have a clear understanding of your business needs, the next step is to secure management approval. Developing a cybersecurity policy requires resources and commitment from leadership. Presenting your findings and proposed policies to management can help gain their support.
In my experience, I found that presenting data on potential risks and compliance requirements was effective in securing buy-in from management. When they understood the implications of not having robust security policies, they were more willing to allocate resources for development and training.
Step 3: Gather Stakeholder Input
Engaging various stakeholders is vital when drafting security policies. Involving different departments—such as IT, HR, and legal—ensures that your policies are comprehensive and practical. Each department brings unique insights that can enhance the effectiveness of your cybersecurity policy.
For example, when I was drafting our security policies, I held workshops with team members from different departments. This collaborative approach not only helped us identify potential gaps but also fostered a sense of ownership among employees regarding the policies we were creating.
Step 4: Drafting the Policy Document
Now comes the actual drafting of the policy document. Start with a clear structure that includes sections like purpose, scope, roles and responsibilities, and procedures for handling incidents. Use simple language to ensure everyone can understand the document easily.
As I drafted our cybersecurity policy, I focused on making it user-friendly. I included bullet points for key procedures and used straightforward language to explain complex concepts. This clarity has proven essential in ensuring that employees know how to follow the guidelines laid out in the policy.
Step 5: Review and Revise
Once you have a draft ready, it’s time for review and revision. Share the draft with stakeholders for feedback. This collaborative review process helps identify any unclear sections or areas that need more detail.
In my journey of developing a cybersecurity policy, I learned that feedback is invaluable. After circulating our draft policy among team members, we received constructive criticism that led to significant improvements. For instance, we added examples of phishing emails to help employees recognize potential threats more easily.
Step 6: Finalize and Communicate
After making necessary revisions based on feedback, finalize your security policy document. The next step is communication. Ensure all employees are aware of the new policies through training sessions and internal communications.When we rolled out our finalized cybersecurity policy, we organized training sessions to explain its importance and how it would affect daily operations. These sessions were crucial in fostering a culture of security awareness within our organization.
Starting the process of drafting security policies involves several key steps: identifying business needs, securing management approval, gathering stakeholder input, drafting the document, reviewing it thoroughly, and communicating it effectively across the organization. By following these steps diligently, you can create a robust cybersecurity policy that safeguards your organization against digital threats.As you embark on this journey of developing a cybersecurity policy through effective drafting practices, remember that collaboration and clarity are key components in ensuring success.

Image: Example of a Cybersecurity Policy Document
What Are the Core Elements of Organizational Security Plans?
When developing a cybersecurity policy, understanding the core elements of organizational security plans is essential. These elements form the backbone of your security strategy and guide how your organization will protect its digital assets. In this section, we’ll explore these critical components and how they contribute to developing a comprehensive cybersecurity policy.
1. Purpose and Scope
The first element of any organizational security plan is a clear statement of purpose and scope. This section outlines why the policy exists and what it covers. It sets the stage for everything that follows.When I was developing a cybersecurity policy for my business, I realized that clearly defining the purpose helped everyone understand its importance. For example, our purpose statement emphasized our commitment to protecting sensitive customer data and maintaining trust. This clarity motivated employees to take the policy seriously.
2. Roles and Responsibilities
Next, it’s vital to define roles and responsibilities within your organizational security plan. This element ensures that everyone knows their specific duties regarding cybersecurity. Assigning clear roles helps create accountability.In my experience, when drafting security policies, I found it helpful to create a chart outlining who is responsible for various tasks. For instance, our IT team was tasked with monitoring systems for vulnerabilities, while HR was responsible for employee training on security protocols. This division of labor made it easier to manage our cybersecurity efforts effectively.
3. Policy Statement
The policy statement is the heart of your organizational security plan. It should articulate your organization’s commitment to cybersecurity and outline the measures you will take to protect data. This statement should be concise yet comprehensive.When I crafted our policy statement, I focused on making it clear and actionable. It included commitments to regular updates of our systems, employee training programs, and incident response procedures. A strong policy statement reinforces the importance of cybersecurity throughout the organization.
4. Risk Assessment Procedures
A crucial component of developing a cybersecurity policy is establishing risk assessment procedures. These procedures help identify potential threats and vulnerabilities within your organization’s systems.In my journey of drafting security policies, I learned that conducting regular risk assessments is vital. We implemented a process where we reviewed our systems quarterly to identify new risks or changes in existing ones. This proactive approach allowed us to adjust our policies accordingly and stay ahead of potential threats.
5. Incident Response Plan
An effective incident response plan is another core element of organizational security plans. This plan outlines how your organization will react in the event of a cyber incident, such as a data breach or ransomware attack.When I developed our incident response plan, I included specific steps for reporting incidents, assessing damage, and communicating with stakeholders. Having this plan in place ensured that when we faced a minor breach, we could respond quickly and effectively without panic.
6. Training and Awareness Programs
Training and awareness are essential components of any organizational security plan. Regular training ensures that employees understand the policies in place and know how to follow them.I found that implementing ongoing training programs significantly improved our overall security posture. We held monthly sessions that covered various topics, such as recognizing phishing attempts and safe data handling practices. These sessions not only educated employees but also fostered a culture of security awareness within our organization.
7. Review and Update Procedures
Finally, establishing procedures for regularly reviewing and updating your organizational security plan is crucial for its long-term effectiveness. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, so your policies must adapt accordingly.In my experience, we set up an annual review process for our cybersecurity policy. During this review, we assessed whether our policies were still relevant based on emerging threats or changes in technology. This practice ensured that we remained vigilant against potential risks.
Understanding the core elements of organizational security plans is vital when developing a comprehensive cybersecurity policy. By clearly defining purpose and scope, roles and responsibilities, policy statements, risk assessment procedures, incident response plans, training programs, and review processes, you can create a robust framework that protects your organization from cyber threats.As you work on developing a cybersecurity policy that includes these core elements, remember that collaboration among departments is key to ensuring its success.
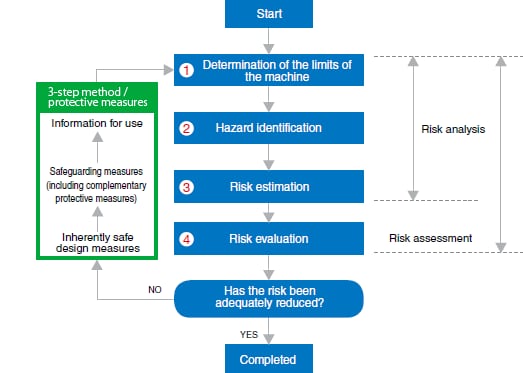
Image : Risk Assessment Process Flowchart
How to Ensure Compliance and Effectiveness?
Ensuring compliance and effectiveness in your cybersecurity policy is crucial for protecting your organization from cyber threats. A well-developed policy is only as good as its implementation and adherence. In this section, we will explore strategies to ensure that your cybersecurity policy remains compliant with regulations and effective in safeguarding your digital assets.
1. Regular Audits and Assessments
One of the most effective ways to ensure compliance and effectiveness is through regular audits and assessments. These processes help identify areas where your cybersecurity policy may be lacking or where updates are necessary.In my experience, conducting bi-annual audits of our cybersecurity practices proved invaluable. During these audits, we reviewed our policies against current regulations and industry standards. This practice not only ensured compliance but also highlighted areas for improvement in our developing a cybersecurity policy framework.
2. Employee Training and Awareness
Training is essential for ensuring that employees understand the policies in place and how to follow them. Regular training sessions help reinforce the importance of compliance and keep everyone informed about new threats.When I first implemented a training program focused on drafting security policies, I noticed a significant increase in employee awareness. We included real-world scenarios in our training, which helped staff recognize potential threats like phishing attacks. By making training engaging and relevant, we fostered a culture of security that encouraged compliance with our cybersecurity policy.
3. Clear Communication Channels
Establishing clear communication channels is vital for ensuring that employees know where to go for questions or concerns regarding the cybersecurity policy. When employees feel comfortable asking questions, they are more likely to adhere to the guidelines.In my organization, we created a dedicated channel on our internal communication platform for cybersecurity-related inquiries. This allowed employees to ask questions anonymously if they preferred, fostering an environment where they felt safe discussing their concerns about compliance with the organizational security plans.
4. Incident Reporting Mechanisms
Having a clear incident reporting mechanism is essential for ensuring compliance with your cybersecurity policy. Employees should know how to report suspicious activities or potential breaches without fear of repercussions.When developing our incident reporting process, I made sure it was straightforward and accessible. We implemented an online form that employees could fill out anonymously. This approach encouraged more people to report incidents, leading to quicker responses and better overall security.
5. Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of your systems is crucial for maintaining compliance and effectiveness in your cybersecurity policy. Implementing tools that monitor network activity can help detect potential threats before they escalate into serious incidents.In my experience, investing in monitoring software significantly improved our ability to respond to threats proactively. We could identify unusual activity patterns in real-time, allowing us to take immediate action to mitigate risks associated with our developing a cybersecurity policy.
6. Feedback Loops
Creating feedback loops within your organization can help ensure that your cybersecurity policy remains effective over time. Regularly soliciting input from employees can provide valuable insights into how well the policies are working in practice.I found that conducting quarterly surveys allowed us to gather feedback on our drafting security policies from those who were directly affected by them. Employees shared their thoughts on what worked well and what needed improvement, which helped us refine our approach continuously.
7. Compliance with Legal Requirements
Finally, it’s essential to stay informed about legal requirements related to data protection and cybersecurity within your industry. Ensuring compliance with these regulations not only protects your organization but also builds trust with clients.In my journey of developing a cybersecurity policy, I made it a priority to stay updated on changes in legislation affecting our industry. For example, when GDPR was introduced, we revised our policies accordingly to ensure compliance with its stringent data protection requirements.
Ensuring compliance and effectiveness in your cybersecurity policy involves regular audits, employee training, clear communication channels, incident reporting mechanisms, continuous monitoring, feedback loops, and adherence to legal requirements. By implementing these strategies as part of your developing a cybersecurity policy, you can create a robust framework that protects your organization from cyber threats while fostering a culture of security awareness among employees.As you work towards enhancing compliance and effectiveness in your organizational security plans, remember that ongoing commitment from all levels of the organization is crucial for success.

Image: Employee Training Session on Cybersecurity Policies
What Types of Cybersecurity Policies Should You Consider?
When developing a cybersecurity policy, it’s essential to recognize that not all policies are created equal. Different types of cybersecurity policies serve various purposes and address specific aspects of your organization’s security needs. In this section, we’ll explore the primary types of cybersecurity policies you should consider when drafting your organizational security plans.
1. Program Policies
Program policies provide a high-level overview of your organization’s approach to cybersecurity. These policies outline the overall objectives and strategies for managing cybersecurity risks across the organization.In my experience, having a well-defined program policy was crucial when I began developing a cybersecurity policy for my company. It set the tone for our entire security framework and communicated our commitment to protecting sensitive information. A solid program policy should include the organization’s mission regarding cybersecurity, key objectives, and the roles of various teams in achieving these goals.
2. Issue-Specific Policies
Issue-specific policies focus on particular areas of concern within your organization’s cybersecurity landscape. These policies address specific threats or vulnerabilities that may arise, providing detailed guidelines on how to manage them.For example, when drafting security policies related to data protection, I created an issue-specific policy that outlined how we would handle sensitive customer information. This policy included guidelines on data encryption, access controls, and procedures for data disposal. By addressing specific issues in detail, we ensured that employees understood their responsibilities in protecting sensitive data.
3. System-Specific Policies
System-specific policies are designed to protect specific systems or technologies within your organization. These policies provide detailed instructions on how to secure particular systems, such as servers, databases, or applications.When I developed our system-specific policies, I focused on our cloud storage solution. We needed clear guidelines on how employees should access and use this system securely. Our policy included details about user authentication, data sharing protocols, and regular system audits. By creating system-specific policies, we could ensure that our security measures were tailored to the unique needs of each technology we used.
4. Acceptable Use Policies (AUP)
An Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) outlines the acceptable behaviors and practices for using organizational resources, including computers, networks, and internet access. This policy sets clear expectations for employees regarding what constitutes appropriate use.
In my organization, we implemented an AUP to prevent misuse of company resources and ensure compliance with our developing a cybersecurity policy. The AUP included guidelines on internet usage, email etiquette, and social media conduct while representing the company. By establishing clear boundaries, we minimized risks associated with inappropriate use of technology.
5. Incident Response Policies
Incident response policies outline the procedures your organization will follow in the event of a cybersecurity incident or breach. These policies are critical for ensuring a swift and effective response to minimize damage.
When I was drafting our incident response policy, I focused on creating a step-by-step guide for employees to follow in case of a breach. This included reporting procedures, roles and responsibilities during an incident, and communication protocols with external stakeholders. Having a clear incident response policy in place allowed us to react quickly when we faced a minor security issue.
6. Data Protection Policies
Data protection policies are essential for organizations handling sensitive information. These policies outline how data should be collected, stored, processed, and disposed of securely.In my experience with developing a cybersecurity policy focused on data protection, I learned that clarity is key. Our data protection policy included guidelines on data classification, access controls based on roles, and procedures for data retention and disposal. By establishing these protocols, we ensured compliance with regulations while safeguarding our customers’ information.
7. Remote Work Policies
With the rise of remote work, having a dedicated remote work policy is increasingly important. This policy outlines security measures employees must follow when working from home or other non-office locations.
When I implemented remote work policies in my organization during the pandemic, I emphasized secure connections through VPNs and proper device management practices. This included guidelines on using personal devices for work-related tasks and securing home networks against potential threats. By addressing remote work specifically in our organizational security plans, we maintained security standards even outside the office environment.
There are several types of cybersecurity policies you should consider when developing your organizational security plans: program policies, issue-specific policies, system-specific policies, acceptable use policies (AUP), incident response policies, data protection policies, and remote work policies. Each type serves a unique purpose in enhancing your overall cybersecurity posture.As you embark on drafting these various types of security policies as part of your developing a cybersecurity policy, remember that clarity and specificity are essential for ensuring compliance and effectiveness across your organization.
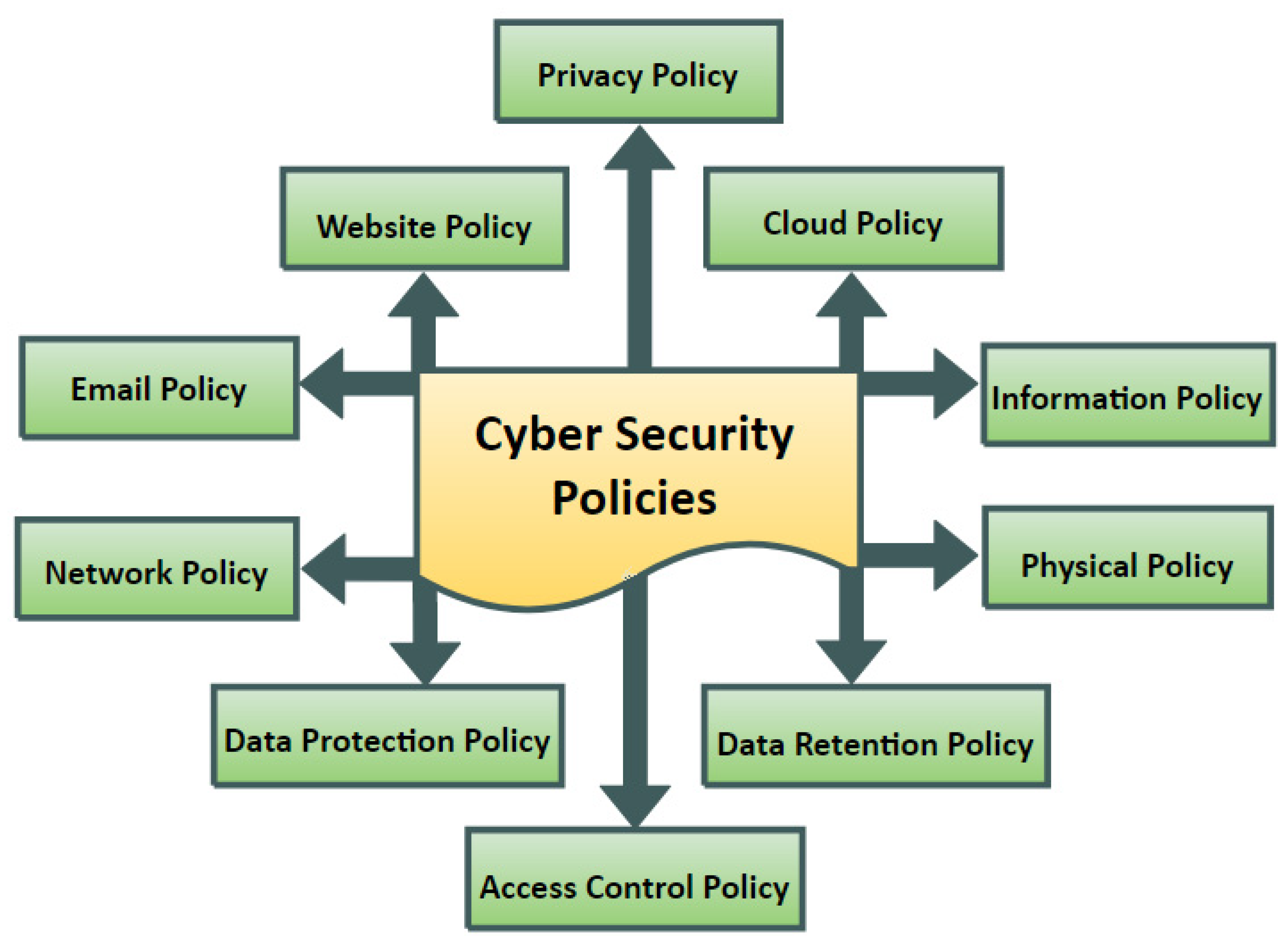
Image: Overview of Cybersecurity Policy Types
How to Engage Stakeholders in the Policy Development Process?
Engaging stakeholders in the policy development process is crucial for creating effective cybersecurity policies. Their insights and experiences can significantly enhance the quality and applicability of your policies. In this section, we will explore strategies for effectively engaging stakeholders when developing your cybersecurity policy.
1. Identify Key Stakeholders
The first step in engaging stakeholders is to identify who they are. Key stakeholders typically include representatives from various departments, such as IT, HR, legal, finance, and operations. Each department brings unique perspectives that can help shape your developing a cybersecurity policy.
In my experience, I found it helpful to create a stakeholder map that outlined who should be involved in the policy development process. For instance, IT personnel can provide technical insights about potential vulnerabilities, while HR can address training and compliance issues. By recognizing the importance of diverse input, you can ensure a well-rounded approach to your cybersecurity policies.
2. Communicate the Importance of Engagement
Once you’ve identified stakeholders, it’s essential to communicate why their engagement is vital. Explain how their input will influence the effectiveness of the cybersecurity policy and how it will impact their departments.
When I initiated the policy development process in my organization, I held an introductory meeting to discuss the importance of collaboration. I emphasized that developing a robust cybersecurity policy is not just an IT issue; it affects everyone in the organization. This approach helped foster a sense of ownership among stakeholders, motivating them to contribute actively.
3. Conduct Workshops and Brainstorming Sessions
Organizing workshops and brainstorming sessions is an effective way to engage stakeholders in the policy development process. These interactive sessions allow participants to share their ideas and concerns openly.During my journey of drafting security policies, I facilitated several workshops with different departments. For example, in one session focused on incident response policies, we discussed various scenarios and how each department would respond. This collaborative effort not only generated valuable insights but also helped build relationships among team members who might not typically work together.
4. Gather Feedback Throughout the Process
Engaging stakeholders is not a one-time event; it should be an ongoing process. Regularly soliciting feedback throughout the development stages ensures that everyone feels heard and valued.After drafting initial sections of our cybersecurity policy, I circulated them among stakeholders for feedback. This iterative approach allowed us to refine our policies based on real-world experiences and concerns from various departments. For example, input from HR led us to include more comprehensive training requirements in our organizational security plans.
5. Create Drafts for Review
Once you have gathered initial feedback, create drafts of your cybersecurity policies for stakeholders to review. Providing a tangible document allows stakeholders to see how their input has been incorporated and gives them an opportunity to suggest further improvements.
When I distributed our draft cybersecurity policy for review, I encouraged stakeholders to provide comments directly on the document. This collaborative review process made it easier for everyone to see how their contributions shaped the final product.
6. Foster Open Communication Channels
Establishing open communication channels is essential for keeping stakeholders engaged throughout the policy development process. Encourage them to ask questions or express concerns at any time.
In my organization, we set up a dedicated email address and an online forum where stakeholders could share their thoughts or ask questions about the cybersecurity policy development process. This openness fostered trust and encouraged more active participation from all involved.
7. Acknowledge Contributions
Finally, acknowledging stakeholder contributions is vital for maintaining engagement throughout the process. Recognizing their efforts reinforces the value of collaboration and encourages continued participation.When we finalized our cybersecurity policy, I made it a point to thank everyone who contributed during our meetings and reviews publicly. This acknowledgment not only boosted morale but also created a sense of community around our shared goal of enhancing organizational security.
Engaging stakeholders in the policy development process is essential for creating effective cybersecurity policies. By identifying key stakeholders, communicating the importance of engagement, conducting workshops, gathering feedback throughout the process, creating drafts for review, fostering open communication channels, and acknowledging contributions, you can ensure that your developing a cybersecurity policy reflects the needs and concerns of your entire organization.
As you work on engaging stakeholders in your organizational security plans, remember that collaboration leads to stronger policies that better protect your organization from cyber threats.

Image: Stakeholder Engagement Workshop
What Common Mistakes Should Be Avoided in Policy Development?
Developing a cybersecurity policy is a complex process, and there are several common pitfalls that organizations often encounter. Avoiding these mistakes can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your developing a cybersecurity policy and ensure that it meets the needs of your organization. In this section, we will discuss some of the most frequent errors and how to steer clear of them.

Image: Common Mistakes in Policy Development
1. Lack of Clarity and Specificity
One of the most significant mistakes in policy development is failing to provide clear and specific guidelines. Vague policies can lead to confusion among employees, resulting in inconsistent practices and potential security vulnerabilities.
In my experience, when I first drafted our cybersecurity policy, I realized that some sections were too ambiguous. For instance, our initial guidelines on password management didn’t specify the required length or complexity. After receiving feedback, we revised this section to include clear requirements, which helped employees understand exactly what was expected of them.
2. Ignoring Employee Input
Another common mistake is neglecting to involve employees in the policy development process. Employees are often on the front lines and can provide valuable insights into potential risks and practical solutions.When I was developing our organizational security plans, I initially overlooked the importance of gathering input from staff. After realizing this mistake, I organized focus groups to discuss their experiences with existing policies. This engagement not only improved our policies but also made employees feel valued and more likely to adhere to them.
3. Overcomplicating Policies
While it’s essential to be thorough in your cybersecurity policy, overcomplicating it can lead to confusion and frustration among employees. Policies should be straightforward and easy to understand.In my early attempts at drafting security policies, I included too much technical jargon, which alienated many employees. After revising our documents to use simpler language and clearer examples, we noticed a marked improvement in compliance rates. Remember, your goal is to create a document that everyone can easily follow.
4. Failing to Align with Business Objectives
Cybersecurity policies should align with your organization’s overall business objectives. Failing to do so can result in policies that are irrelevant or impractical for daily operations.When I began developing our cybersecurity policy, I ensured that it directly supported our business goals. For example, since we aimed to enhance customer trust through data protection, our policy included strict guidelines on handling sensitive information. This alignment made the policy more relevant and easier for employees to embrace.
5. Neglecting Regular Updates
Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, and so should your policies. A common mistake is failing to review and update policies regularly to reflect new threats or changes in technology.In my experience, we established a schedule for reviewing our cybersecurity policy annually. This practice allowed us to adapt our policies based on emerging threats and changes in regulations. By making regular updates a priority, we ensured that our developing a cybersecurity policy remained effective over time.
6. Lack of Training and Awareness Programs
Another critical mistake is not providing adequate training and awareness programs for employees regarding the cybersecurity policy. Even the best-written policies are ineffective if employees do not understand them or know how to implement them.I learned this lesson firsthand when we rolled out our initial cybersecurity policy without sufficient training. Many employees were unsure about their responsibilities, leading to lapses in compliance. After implementing regular training sessions that focused on real-world applications of the policy, we saw a significant increase in adherence.
7. Not Testing Incident Response Plans
Having an incident response plan is crucial, but failing to test it regularly is a common oversight. Testing helps ensure that everyone knows their roles during an incident and can respond effectively.
When developing our incident response plan as part of our organizational security plans, we conducted tabletop exercises simulating various scenarios. These tests revealed gaps in our plan that we could address before an actual incident occurred. Regular testing not only improves preparedness but also builds confidence among team members.
Avoiding common mistakes in policy development is essential for creating an effective cybersecurity policy. By ensuring clarity and specificity, involving employee input, simplifying language, aligning with business objectives, regularly updating policies, providing adequate training, and testing incident response plans, you can enhance your organization’s security posture significantly.As you work on your developing a cybersecurity policy, remember that learning from these mistakes will help you create a more robust framework that protects your organization from cyber threats.
How to Communicate the Policy Across the Organization?
Effectively communicating your cybersecurity policy across the organization is just as important as developing it. A well-crafted policy is only useful if employees understand it and know how to implement it in their daily activities. In this section, we will explore strategies for effectively communicating your developing a cybersecurity policy to ensure that all employees are informed and engaged.
1. Use Multiple Communication Channels
To reach all employees effectively, utilize multiple communication channels. Different people prefer different methods of receiving information, so using a variety of platforms can enhance understanding and retention.In my experience, we employed several channels to communicate our cybersecurity policy. We used email announcements, internal newsletters, and company-wide meetings to share key information. Additionally, we created an intranet page dedicated to the policy, where employees could easily access the document and related resources. This multi-channel approach ensured that everyone had the opportunity to engage with the material.
2. Simplify Language and Format
When communicating your cybersecurity policy, it’s essential to use clear and straightforward language. Avoid technical jargon that may confuse employees who are not familiar with cybersecurity concepts.When I first communicated our policy, I noticed that some sections were too complex for many staff members. After revising the document to simplify the language and format, we found that employees were more receptive to the information. Using bullet points, headings, and visuals helped break down complex ideas into digestible pieces, making it easier for everyone to understand their responsibilities.
3. Conduct Training Sessions
Training sessions are a vital component of communicating your cybersecurity policy. These sessions provide an opportunity for employees to learn about the policy in detail and ask questions in real time.I found that hosting interactive training sessions significantly improved employee engagement with our organizational security plans. During these sessions, we covered key aspects of the policy and included scenarios for discussion. This hands-on approach encouraged participation and helped reinforce the importance of adhering to the policy.
4. Create Quick Reference Guides
Developing quick reference guides or cheat sheets can be an effective way to communicate essential points from your cybersecurity policy. These guides should summarize key procedures and responsibilities in a concise format. For example, we created a one-page quick reference guide that highlighted critical aspects of our incident response plan. This guide was distributed to all employees and posted in common areas around the office. Having this resource readily available made it easier for staff to remember their roles during a security incident.
5. Foster a Culture of Open Communication
Encouraging open communication about cybersecurity can help create a culture where employees feel comfortable discussing concerns or asking questions about the policy. This openness promotes understanding and compliance.
In my organization, we established regular check-in meetings focused on cybersecurity topics. During these meetings, team members could share their thoughts on the policy and any challenges they faced in following it. This practice not only provided valuable feedback but also reinforced our commitment to maintaining a secure environment.
6. Highlight Real-World Examples
Using real-world examples can help illustrate the importance of your cybersecurity policy and make it more relatable for employees. Sharing stories about recent security incidents—whether from your organization or others—can emphasize why adherence is crucial.When communicating our cybersecurity policy, I shared case studies of companies that faced significant breaches due to non-compliance with their policies. These stories resonated with employees and highlighted the potential consequences of neglecting security protocols.
7. Regularly Reinforce Key Messages
Communication shouldn’t be a one-time event; it should be an ongoing process. Regularly reinforcing key messages about your cybersecurity policy can help keep it top-of-mind for employees.In my experience, we included reminders about our cybersecurity practices in monthly newsletters and during team meetings. Additionally, we celebrated “Cybersecurity Awareness Month” with activities designed to engage employees and reinforce their understanding of our policies.
Effectively communicating your cybersecurity policy across the organization is essential for ensuring compliance and fostering a culture of security awareness. By using multiple communication channels, simplifying language, conducting training sessions, creating quick reference guides, fostering open communication, highlighting real-world examples, and regularly reinforcing key messages, you can ensure that all employees are informed and engaged with your developing a cybersecurity policy.As you work on communicating your organizational security plans, remember that clarity and consistency are key components in achieving widespread understanding and adherence.

Image: Security awareness training
What Are the Key Challenges in Implementing Cybersecurity Policies?
Implementing cybersecurity policies is a critical step in safeguarding your organization from cyber threats. However, this process often comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges can help you proactively address them and ensure a smoother implementation of your developing a cybersecurity policy. In this section, we will explore some of the key challenges organizations face when implementing cybersecurity policies and how to overcome them.
1. Resistance to Change
One of the most common challenges in implementing cybersecurity policies is resistance to change among employees. When new policies are introduced, some staff may feel overwhelmed or skeptical about the need for additional security measures.
In my experience, I faced resistance when we rolled out our updated cybersecurity policy. Many employees were accustomed to their previous routines and were hesitant to adopt new practices. To address this challenge, I organized informational sessions that explained the reasons behind the changes and how they would benefit both the organization and employees personally. By highlighting the importance of cybersecurity in protecting their jobs and data, we were able to reduce resistance significantly.
2. Lack of Awareness and Training
Another significant challenge is the lack of awareness and training regarding cybersecurity policies. Employees may not fully understand the policies or their importance, leading to non-compliance.To combat this issue, I implemented a comprehensive training program that included regular workshops and online courses focused on our organizational security plans. These sessions provided employees with practical knowledge about the policies and how to apply them in their daily work. Regular training not only increased awareness but also empowered employees to take ownership of their roles in maintaining security.
3. Insufficient Resources
Implementing effective cybersecurity policies often requires adequate resources—both financial and human. Organizations may struggle if they do not allocate sufficient resources for training, technology, or personnel dedicated to cybersecurity efforts.
In my organization, we initially faced budget constraints that limited our ability to invest in necessary security tools. To address this challenge, I prepared a proposal outlining the potential risks of inadequate resources and the long-term benefits of investing in cybersecurity. This approach helped secure additional funding for training programs and security software, ultimately strengthening our overall security posture.
4. Complexity of Policies
Cybersecurity policies can sometimes be overly complex or technical, making it difficult for employees to understand and follow them effectively. If policies are too complicated, compliance may suffer.To mitigate this challenge, I focused on simplifying our policy documents during development. We used clear language, visual aids, and examples to make the policies more accessible. Additionally, we created quick reference guides that summarized key points for easy recall. This simplification made it easier for employees to grasp their responsibilities under our developing a cybersecurity policy.
5. Integration with Existing Processes
Integrating new cybersecurity policies into existing workflows can be challenging. Employees may find it difficult to adjust their routines or may not see how the new policies fit into their daily tasks.When implementing our cybersecurity policy, I worked closely with department heads to identify areas where integration could be improved. We held collaborative meetings to discuss how best to incorporate security practices into existing processes without disrupting productivity. By aligning our security measures with daily operations, we made it easier for employees to adopt new practices seamlessly.
6. Keeping Up with Evolving Threats
Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field, with new threats emerging regularly. Keeping your policies up-to-date with these changes can be a significant challenge for organizations. To address this issue, I established a routine review process for our cybersecurity policy that included monitoring industry trends and emerging threats. We scheduled bi-annual reviews where we assessed our policies against current risks and made necessary updates. This proactive approach ensured that our organizational security plans remained relevant and effective over time.
7. Measuring Compliance and Effectiveness
Finally, measuring compliance with cybersecurity policies can be challenging. Without proper metrics or assessments in place, it can be difficult to determine whether employees are following the guidelines effectively.In my experience, we implemented regular audits and assessments as part of our compliance strategy. These audits allowed us to evaluate adherence to our policies and identify areas needing improvement. Additionally, we conducted anonymous surveys to gather employee feedback on their understanding of the policies and any challenges they faced in following them.
Implementing cybersecurity policies comes with several key challenges: resistance to change, lack of awareness and training, insufficient resources, complexity of policies, integration with existing processes, keeping up with evolving threats, and measuring compliance effectiveness. By recognizing these challenges early on and developing strategies to address them as part of your developing a cybersecurity policy, you can enhance your organization’s overall security posture.
As you work through these implementation challenges related to your organizational security plans, remember that communication, training, and collaboration are vital components in ensuring success.

Image: Team Meeting Addressing Implementation Challenges
Final Thoughts on Creating Comprehensive Cybersecurity Policies
Creating comprehensive cybersecurity policies is a vital undertaking for any organization looking to protect its digital assets and maintain trust with customers and stakeholders. As we conclude this exploration of developing a cybersecurity policy, let’s summarize the key takeaways and emphasize the importance of a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
The Importance of a Strong Foundation
A well-developed cybersecurity policy serves as the foundation for your organization’s security posture. It outlines the strategies, responsibilities, and procedures necessary to protect sensitive information from cyber threats. Throughout my journey in drafting security policies, I learned that having a strong foundation is crucial. This foundation not only guides employees in their daily tasks but also helps establish a culture of security awareness throughout the organization.
Engaging Stakeholders
One of the most critical aspects of developing effective cybersecurity policies is engaging stakeholders across all levels of the organization. By involving various departments—such as IT, HR, legal, and operations—you can ensure that your policies are comprehensive and practical. In my experience, collaboration leads to better insights and more robust policies that address the unique needs of your organization.
Continuous Improvement
Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort; it requires continuous improvement. As threats evolve, so too must your policies. Regularly reviewing and updating your cybersecurity policy ensures that it remains relevant and effective. I established a routine for bi-annual reviews in my organization, allowing us to adapt to new risks and technologies. This proactive approach has been instrumental in maintaining our security posture.
Training and Awareness
Implementing a cybersecurity policy is only effective if employees understand it and know how to follow it. Regular training and awareness programs are essential for educating staff about their roles in maintaining security. In my experience, engaging training sessions that include real-world scenarios significantly improve compliance rates. Employees are more likely to adhere to policies when they understand their importance and how they apply to their daily tasks.
Communication is Key
Effective communication is crucial for ensuring that all employees are aware of the cybersecurity policies in place. Utilizing multiple communication channels—such as emails, meetings, and quick reference guides—can help reinforce key messages. Additionally, fostering an open environment where employees feel comfortable discussing security concerns encourages adherence to policies.
Measuring Success
Finally, measuring the effectiveness of your cybersecurity policies is essential for ongoing success. Regular audits, assessments, and feedback loops can help you identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance. In my organization, we implemented anonymous surveys to gather employee insights on our policies, which provided valuable information for refining our approach.
Developing comprehensive cybersecurity policies is an ongoing journey that requires commitment from all levels of the organization. By focusing on stakeholder engagement, continuous improvement, training and awareness, effective communication, and measuring success, you can create a robust framework that protects your organization from cyber threats.
As you embark on your own journey of developing a cybersecurity policy, remember that the landscape of cybersecurity is ever-changing. Stay vigilant, remain adaptable, and prioritize security as an integral part of your organizational culture.
FAQ Section
1. What is the first step in developing a cybersecurity policy?
The first step in developing a cybersecurity policy is to assess your organization’s current security posture. This involves identifying the types of data you handle, understanding potential threats, and evaluating existing security measures. This assessment provides a foundation for creating a policy that addresses specific vulnerabilities and aligns with business needs.
2. How often should cybersecurity policies be reviewed?
Cybersecurity policies should be reviewed at least annually or whenever significant changes occur within the organization or the threat landscape. Regular reviews help ensure that your policies remain relevant and effective in addressing new risks, technologies, and regulatory requirements.
3. Who should be involved in drafting security policies?
Key stakeholders from various departments should be involved in drafting security policies. This typically includes representatives from IT, HR, legal, finance, and operations. Involving diverse perspectives ensures that the policies are comprehensive and practical for all areas of the organization.
4. What are common types of cybersecurity policies?
Common types of cybersecurity policies include:
- Program Policies: High-level guidelines outlining overall cybersecurity objectives.
- Issue-Specific Policies: Focused on particular risks or areas of concern (e.g., data protection).
- System-Specific Policies: Addressing security measures for specific systems or technologies.
- Acceptable Use Policies (AUP): Guidelines on the appropriate use of organizational resources.
- Incident Response Policies: Procedures for responding to cybersecurity incidents.
- Data Protection Policies: Guidelines for handling sensitive information securely.
- Remote Work Policies: Security measures for employees working outside the office.
5. How can I ensure employee compliance with security policies?
To ensure employee compliance with security policies, provide regular training sessions that explain the importance of the policies and how they apply to daily tasks. Establish clear communication channels for questions and concerns, and reinforce key messages through ongoing reminders and updates.
6. What are the consequences of not having a cybersecurity policy?
Not having a cybersecurity policy can lead to increased risks of data breaches, regulatory penalties, loss of customer trust, and reputational damage. Without clear guidelines, employees may not know how to handle sensitive information or respond to security incidents effectively.
7. How do I assess the effectiveness of my cybersecurity policy?
Assessing the effectiveness of your cybersecurity policy involves conducting regular audits and assessments to evaluate adherence to the policy. Additionally, gather feedback from employees through surveys or focus groups to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the policy is understood and followed.
8. What legal requirements should I consider when drafting my policy?
When drafting your cybersecurity policy, consider industry-specific regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), or PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). These regulations govern data protection and privacy standards relevant to your organization.
9. How can technology assist in implementing security policies?
Technology can assist in implementing security policies by automating compliance monitoring, facilitating training programs, and providing tools for incident detection and response. For example, security information and event management (SIEM) systems can help monitor network activity for potential threats in real-time.
10. Where can I find templates for drafting security policies?
Many organizations offer free resources online for drafting security policies, including templates and guidelines. You can also consult industry associations or hire professionals specializing in cybersecurity policy development to create tailored documents that meet your organization’s specific needs.



