Introduction
In an increasingly digital world, organizations face a multitude of security threats. While much attention is given to external cyberattacks, one of the most significant risks often lurks within the organization itself: insider threats. These threats arise from individuals who have legitimate access to company resources, such as employees, contractors, or business partners. Whether intentional or accidental, insider threats can lead to severe consequences, including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.Understanding and addressing insider threats is essential for any business aiming to protect its sensitive information and maintain operational integrity.
Insider threats can manifest in various ways—from a disgruntled employee leaking confidential data to an unsuspecting worker inadvertently exposing sensitive information through negligence. This complexity makes it crucial for organizations to adopt a comprehensive approach to risk management.
In this article, we will delve into the nature of insider threats, explore their implications for businesses, and provide actionable strategies for prevention and response. We will cover key topics such as identifying insider threats, implementing effective security measures, fostering a culture of awareness among employees, and developing a robust insider threat response plan.
By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how to protect your organization from within and ensure that your business remains resilient against potential insider attacks. Let’s embark on this journey to strengthen your defenses and safeguard your organization from the risks that lie within.
What Are Insider Threats?
Insider threats are a significant risk for businesses today. They occur when someone within the organization—like an employee, contractor, or partner—misuses their access to harm the company. This can happen intentionally or unintentionally. For example, an employee might steal sensitive data to sell to competitors, or they might accidentally expose confidential information due to negligence. Understanding these threats is crucial for addressing insider threats effectively.
Types of Insider Threats
There are generally two types of insider threats: malicious and unintentional. Malicious insiders deliberately cause harm. They may be disgruntled employees seeking revenge or individuals motivated by financial gain. On the other hand, unintentional threats arise from employees who make mistakes, like sending sensitive emails to the wrong recipient or failing to follow security protocols.In my experience, I once worked with a company that faced a significant insider threat when a trusted employee leaked sensitive client information. This incident not only damaged relationships but also led to financial losses. It highlighted how crucial it is for businesses to focus on preventing insider attacks through proper training and monitoring.
The Importance of Addressing Insider Threats
Addressing insider threats is essential for several reasons:
- Protecting Sensitive Information: Organizations hold vast amounts of data that can be valuable to competitors or cybercriminals. By focusing on addressing insider threats, businesses can safeguard their proprietary information.
- Maintaining Trust: When employees feel secure in their work environment, they are more likely to be productive and loyal. A breach caused by an insider can erode trust among staff and clients alike.
- Financial Implications: The financial fallout from insider attacks can be staggering. According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of an insider threat incident is over $11 million. This figure underscores the need for effective strategies in managing internal risks.
- Legal and Compliance Issues: Many industries have strict regulations regarding data protection. Failing to address insider threats can lead to legal troubles and hefty fines.
Recognizing Insider Threats
Recognizing potential insider threats is key to prevention. Some warning signs include:
- Unusual behavior: Employees accessing data they don’t typically need.
- Sudden changes in performance: A previously engaged employee becomes disengaged or starts acting suspiciously.
- Increased complaints about job dissatisfaction: This might indicate a potential malicious intent.
To effectively address these signs, businesses should implement monitoring systems that help track user behavior without infringing on privacy rights.
Tools for Monitoring Employee Behavior
Several tools can assist in identifying potential insider threats:
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): These tools analyze user activities and flag anomalies that could indicate a threat.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions help prevent unauthorized data transfers, ensuring sensitive information remains secure.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security data from across the organization, providing insights into potential risks.
In my previous role at a tech company, we implemented a UBA tool that significantly improved our ability to detect unusual patterns in employee behavior. This proactive approach allowed us to address potential issues before they escalated into serious problems.
Understanding what insider threats are is the first step toward addressing insider threats effectively. By recognizing the types of threats, their implications, and how to identify them, businesses can take proactive measures to safeguard their operations. Remember, preventing insider attacks isn’t just about technology; it’s also about fostering a culture of security awareness among employees.

Image: Types if insider threats
Why Is Addressing Insider Threats Essential for Your Business?
Addressing insider threats is not just a good practice; it’s a necessity for any business that wants to thrive in today’s digital landscape. The consequences of ignoring these threats can be severe, affecting everything from financial stability to reputation. In this section, we’ll explore why addressing insider threats should be a top priority for every organization.
The Impact on Organizational Integrity and Trust
When insider threats occur, they can severely undermine the integrity of an organization. Employees who feel unsafe or distrustful may become disengaged, leading to decreased productivity. This environment can foster more insider threats, creating a vicious cycle. By actively addressing insider threats, businesses can cultivate a culture of trust and security.In my experience, I once consulted for a mid-sized firm that faced significant internal strife after an insider threat incident. An employee leaked sensitive information to a competitor. This breach not only damaged client relationships but also led to high turnover rates as employees felt insecure about their jobs. Addressing insider threats proactively could have prevented this situation.
Financial Implications of Insider Attacks
The financial repercussions of insider attacks are staggering. According to the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of an insider threat incident is over $11 million. This figure includes direct costs like data recovery and legal fees, as well as indirect costs such as lost business and damage to reputation. By focusing on preventing insider attacks, companies can save significant amounts of money.For example, I worked with a financial services company that invested in comprehensive training programs aimed at managing internal risks. They reported a 30% reduction in incidents related to insider threats within the first year. This proactive approach not only saved them money but also improved employee morale.
Case Studies of Businesses Affected by Insider Threats
Real-world examples highlight the importance of addressing insider threats. Take the case of a major retail chain that suffered a data breach due to an employee’s negligence. An employee accidentally shared confidential customer data with unauthorized personnel. The result? A massive lawsuit and loss of customer trust.Another example is a tech company that faced significant backlash when an employee stole proprietary software code and sold it to competitors. The fallout included legal battles and a tarnished reputation, which took years to rebuild. These cases emphasize the need for businesses to adopt strategies focused on preventing insider attacks.
Legal and Compliance Issues
In many industries, failing to address insider threats can lead to legal complications. Organizations must comply with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, which mandate strict data protection measures. If an insider threat leads to a data breach, companies could face hefty fines and legal action.By managing internal risks effectively, businesses can ensure compliance with these regulations. Investing in robust security measures not only protects sensitive information but also safeguards against potential legal issues.
Building a Resilient Organization
To build resilience against insider threats, companies must prioritize security training and awareness programs. Employees should be educated about the risks associated with sharing sensitive information and the importance of following security protocols. Regular training sessions can help reinforce these messages.In my experience, implementing such programs has proven beneficial. One company I worked with saw a marked improvement in employee awareness after conducting quarterly training sessions focused on addressing insider threats.
Addressing insider threats is essential for safeguarding your business from various risks—financial losses, reputational damage, and legal complications. By recognizing the importance of addressing insider threats, organizations can create a secure environment that fosters trust and productivity among employees.
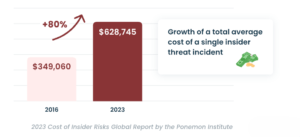
Image: Financial losses associated with insider threats.
How Can Businesses Identify Insider Threats?
Identifying insider threats is a crucial step in addressing insider threats effectively. Since these threats often originate from within the organization, they can be challenging to detect. However, with the right strategies and tools, businesses can uncover potential risks before they escalate into serious incidents. In this section, we’ll explore how organizations can identify insider threats and implement measures to prevent insider attacks.
Key Indicators to Watch For
Recognizing the signs of insider threats is the first line of defense. Some key indicators include:
- Unusual Access Patterns: If an employee accesses files or systems that are outside their normal job responsibilities, it could be a red flag. For instance, if a marketing employee starts accessing sensitive financial data, it’s worth investigating.
- Behavioral Changes: Sudden changes in behavior can indicate potential insider threats. An engaged employee may become withdrawn or start making unusual requests for access to sensitive information. Monitoring these changes is essential in managing internal risks.
- Increased Data Transfers: If an employee suddenly begins transferring large amounts of data, especially if it’s outside normal business hours, this could signal a potential threat. Keeping track of data transfers can help identify suspicious activities.
- Frequent Complaints or Grievances: Employees who express dissatisfaction with their jobs may be more likely to engage in harmful behaviors. Regularly checking in with staff and addressing grievances can help mitigate this risk.
In my experience, I once worked with a company that implemented a monitoring system to track user access patterns. This system flagged unusual access attempts, allowing the security team to investigate further and prevent potential breaches.
Tools and Technologies for Monitoring Employee Behavior
Several tools can assist businesses in identifying insider threats:
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): UBA tools analyze user activity over time and establish a baseline of normal behavior. When deviations occur, these tools alert security teams to investigate further.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor data transfers and prevent unauthorized sharing of sensitive information. This technology plays a vital role in preventing insider attacks by ensuring that data remains secure.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems aggregate security data from various sources within the organization. By analyzing this data in real-time, businesses can identify potential threats as they arise.
When I was part of a cybersecurity team at a large corporation, we utilized UBA tools that significantly improved our ability to detect anomalies in user behavior. This proactive monitoring allowed us to address potential insider threats before they could cause harm.
Importance of a Proactive Approach
A proactive approach is essential when it comes to identifying insider threats. Waiting for an incident to occur before taking action can lead to severe consequences. Instead, businesses should regularly review their security protocols and update them as needed.Conducting regular internal audits can help identify vulnerabilities within the organization. These audits should assess not only technical controls but also employee behavior and adherence to security policies.Additionally, fostering open communication about security concerns is vital. Employees should feel comfortable reporting suspicious behavior without fear of retaliation. Creating an environment where security is prioritized helps in managing internal risks effectively.
Training Employees on Threat Recognition
Training employees on how to recognize potential insider threats is another crucial step in prevention. Regular training sessions should cover topics like:
- Identifying suspicious behavior
- Understanding the importance of data protection
- Reporting procedures for suspected insider threats
By educating employees about the risks associated with insider threats, organizations empower them to act as the first line of defense. In my experience, companies that invest in regular training see significant improvements in their ability to detect and respond to potential threats.
Identifying insider threats requires vigilance and proactive measures. By recognizing key indicators, utilizing effective monitoring tools, and fostering a culture of security awareness, businesses can significantly enhance their ability to address insider threats before they escalate into serious issues. Remember, the goal is not just to react but to create an environment where potential risks are identified and mitigated early on.
Image: Graphic showing key indicators of insider threats.
What Strategies Can Be Implemented to Address Insider Threats?
Addressing insider threats effectively requires a multifaceted approach. Organizations must implement comprehensive strategies that encompass technology, policies, and employee engagement. In this section, we will discuss various strategies that businesses can adopt to address insider threats, prevent insider attacks, and manage internal risks.
Developing a Comprehensive Risk Management Plan
A solid risk management plan is the foundation for addressing insider threats. This plan should include:
- Risk Assessment: Regularly evaluate the potential risks associated with insider threats. Identify critical assets and processes within the organization that could be vulnerable.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit employee access to sensitive information based on their roles. The principle of least privilege should guide these decisions, allowing employees access only to the data necessary for their jobs.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Establish regular monitoring and auditing processes to track user activities. This includes reviewing access logs and identifying any unusual patterns that may indicate a threat.
In my experience, I worked with a company that revamped its risk management plan after experiencing an insider threat incident. By conducting thorough risk assessments and implementing stricter access controls, they significantly reduced their vulnerability to future attacks.
Conducting Regular Internal Audits
Regular internal audits are essential for addressing insider threats. These audits should assess both technical controls and employee behavior. Key components of an effective audit include:
- Reviewing access logs for unusual activities.
- Evaluating compliance with security policies.
- Identifying gaps in training or awareness programs.
By conducting these audits, organizations can identify potential weaknesses in their security posture and take corrective action before an incident occurs.
Implementing Strict Access Controls
Implementing strict access controls is crucial for preventing insider attacks. Access should be granted based on the principle of least privilege, meaning employees only have access to the information necessary for their roles. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.Additionally, organizations should regularly review and update access permissions as employees change roles or leave the company. In my previous role at a tech firm, we conducted quarterly reviews of user access rights, which helped us quickly identify and revoke unnecessary permissions.
Establishing Clear Policies and Procedures
Clear policies and procedures are vital for managing internal risks effectively. Organizations should develop comprehensive security policies that outline acceptable use of company resources, data protection measures, and reporting procedures for suspected insider threats.These policies should be communicated to all employees during onboarding and reinforced through regular training sessions. In my experience, having well-defined policies helps create a culture of accountability among employees.
Fostering a Culture of Security Awareness
Creating a culture of security awareness is essential for addressing insider threats. Employees should feel empowered to report suspicious behavior without fear of retaliation. Regular training sessions can help reinforce the importance of security practices.Encouraging open communication about security concerns fosters trust within the organization. Employees who feel comfortable discussing potential risks are more likely to report suspicious activities early on.I recall working with a client who implemented a “security champions” program, where select employees were trained as security advocates within their teams. This initiative not only increased awareness but also created a network of trusted individuals who could address concerns quickly.
Utilizing Technology for Threat Detection
Technology plays a crucial role in preventing insider attacks. Businesses should invest in tools that help monitor user behavior and detect anomalies in real-time:
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): UBA tools analyze user activities over time and establish baselines for normal behavior. When deviations occur, alerts are triggered for further investigation.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor data transfers and prevent unauthorized sharing of sensitive information, helping organizations protect against insider threats.
In my experience implementing these technologies, I found that they significantly enhanced our ability to detect potential threats early on, allowing us to respond proactively.
Addressing insider threats requires a comprehensive strategy that includes risk management planning, regular audits, strict access controls, clear policies, fostering a culture of security awareness, and utilizing technology for threat detection. By implementing these strategies effectively, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to insider threats while promoting a secure work environment.

Image: Steps in developing a risk management plan.
How to Foster a Culture of Security Awareness?
Fostering a culture of security awareness is crucial for addressing insider threats effectively. When employees understand the importance of security and their role in protecting sensitive information, they become active participants in safeguarding the organization. In this section, we will explore practical strategies for creating a security-conscious workplace that helps prevent insider attacks and manage internal risks.
Training Programs for Employees
Regular training programs are essential for building security awareness among employees. These programs should cover:
- Understanding Insider Threats: Employees need to know what insider threats are, how they can occur, and the potential consequences for the organization.
- Recognizing Red Flags: Training should help employees identify suspicious behavior or activities that could indicate an insider threat. For example, if someone is accessing files unrelated to their job, it should raise concerns.
- Reporting Procedures: Employees must understand how to report suspicious activities safely and confidentially. Clear reporting channels encourage employees to speak up without fear of retaliation.
In my experience, I implemented a training program at a previous company that significantly increased employee awareness about insider threats. After the first session, we noticed more employees reporting unusual behavior, which allowed us to address potential issues before they escalated.
Encouraging Open Communication
Creating an environment where open communication is valued is vital for addressing insider threats. Employees should feel comfortable discussing security concerns with their managers or IT teams. Here are some ways to promote open communication:
- Regular Check-Ins: Managers should have regular one-on-one meetings with team members to discuss any concerns related to security or workplace dynamics.
- Anonymous Feedback Channels: Providing anonymous channels for reporting concerns can help employees voice their worries without fear of being identified.
- Security Forums: Hosting regular forums or town hall meetings focused on security can encourage dialogue about best practices and emerging threats.
I once worked with a client who established a monthly security forum where employees could share experiences and discuss potential risks. This initiative not only improved awareness but also fostered a sense of community around security issues.
Role of Leadership in Promoting Security
Leadership plays a critical role in fostering a culture of security awareness. When leaders prioritize security, it sets the tone for the entire organization. Here are some ways leaders can promote security:
- Lead by Example: Leaders should model good security practices by following policies and procedures themselves. This demonstrates commitment to security at all levels.
- Recognize and Reward Good Practices: Acknowledging employees who demonstrate strong security practices encourages others to follow suit. Consider implementing a reward system for teams that excel in maintaining security protocols.
- Communicate the Importance of Security: Leaders should regularly communicate the significance of addressing insider threats and how everyone has a role in protecting the organization.
In my experience, I’ve seen organizations thrive when leadership actively engages in promoting security awareness. One company I worked with had its CEO host quarterly meetings focused on cybersecurity, which significantly boosted employee engagement around the topic.
Implementing Security Policies
Clear and accessible security policies are essential for fostering a culture of awareness. Employees should have easy access to these policies and understand their importance. Key elements include:
- Acceptable Use Policies: Outline what constitutes acceptable behavior regarding company resources and data protection.
- Incident Response Procedures: Clearly define steps employees should take when they suspect an insider threat or data breach.
- Regular Policy Reviews: Policies should be reviewed regularly to ensure they remain relevant and effective against evolving threats.
In my previous roles, I found that companies with well-defined policies experienced fewer incidents related to insider threats because employees were aware of the expectations set forth by the organization.
Fostering a culture of security awareness is vital for effectively addressing insider threats within any organization. By implementing regular training programs, encouraging open communication, involving leadership, and establishing clear policies, businesses can create an environment where employees actively participate in safeguarding sensitive information. This proactive approach not only helps prevent insider attacks but also strengthens the overall security posture of the organization.
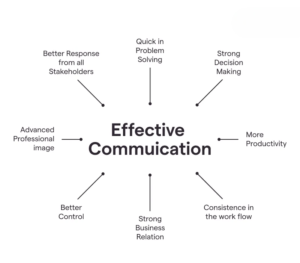
Image: key elements of effective communication strategies in promoting security awareness.
What Are the Best Practices for Preventing Insider Attacks?
Preventing insider attacks is essential for safeguarding your organization’s sensitive information and maintaining operational integrity. By implementing best practices tailored to addressing insider threats, businesses can significantly reduce their risk exposure. In this section, we will explore effective strategies and techniques that organizations can adopt to prevent insider attacks and manage internal risks effectively.
Implementing Effective Internal Controls
One of the most critical steps in addressing insider threats is establishing robust internal controls. These controls help ensure that employees can only access the data necessary for their roles. Key components include:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement a system that grants access based on job responsibilities. Employees should have access only to the information they need to perform their tasks.
- Regular Access Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of user access rights to ensure they remain appropriate as roles change. This practice helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Segregation of Duties: Divide responsibilities among different employees to minimize the risk of fraud or error. For example, the person responsible for approving transactions should not be the same person processing them.
In my experience, I once worked with a financial institution that implemented RBAC and saw a significant reduction in unauthorized access attempts. This proactive measure was instrumental in preventing insider attacks.
Regularly Updating Security Protocols
Security protocols should never be static; they must evolve with emerging threats. Regular updates are crucial for ensuring that your organization remains protected against insider threats. Consider these practices:
- Conduct Threat Assessments: Regularly assess potential insider threats and update security protocols accordingly. This includes evaluating new technologies and changing business processes.
- Stay Informed About Emerging Threats: Keep abreast of industry trends and common tactics used in insider attacks. This knowledge can help you adapt your security measures proactively.
- Engage with Cybersecurity Experts: Collaborate with cybersecurity professionals who can provide insights into best practices and emerging threats relevant to your industry.
In my previous role, we established a routine where our security team reviewed protocols quarterly, which allowed us to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities.
Utilizing Technology for Threat Detection
Leveraging technology is essential for effectively addressing insider threats. Various tools can help organizations monitor user behavior and detect anomalies:
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): UBA tools analyze user activities over time, establishing baselines for normal behavior. When deviations occur, alerts are triggered for further investigation.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions monitor data transfers and prevent unauthorized sharing of sensitive information, helping organizations protect against insider threats.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems aggregate security data from various sources within the organization, providing insights into potential risks in real-time.
In one organization I assisted, implementing UBA tools led to early detection of unusual activities, allowing the security team to intervene before any significant damage occurred.
Conducting Background Checks During Hiring Processes
One proactive measure in preventing insider attacks is conducting thorough background checks during the hiring process. This step can help identify potential red flags before an employee joins the organization:
- Criminal History Checks: Review candidates’ criminal histories to assess any past behavior that may indicate a risk.
- Employment Verification: Confirm previous employment details to ensure candidates have a reliable work history.
- Reference Checks: Speak with previous employers or colleagues to gain insights into the candidate’s character and work ethic.
In my experience, companies that conducted comprehensive background checks reported fewer incidents related to insider threats, as they were able to make more informed hiring decisions.
Creating a Strong Incident Response Plan
Even with preventive measures in place, it’s essential to prepare for potential incidents involving insider threats. A strong incident response plan should include:
- Clear Procedures: Define clear steps employees should take if they suspect an insider threat or data breach occurs.
- Designated Response Team: Establish a dedicated team responsible for investigating incidents related to insider threats and coordinating responses.
- Regular Drills: Conduct regular drills to ensure all employees understand their roles in responding to potential incidents effectively.
When I worked at a tech company, we developed an incident response plan that included regular training exercises. This preparation ensured that employees knew how to respond quickly and effectively when faced with a potential threat.
Preventing insider attacks requires a comprehensive approach that includes effective internal controls, regular updates to security protocols, leveraging technology for threat detection, conducting thorough background checks during hiring processes, and creating a strong incident response plan. By implementing these best practices focused on addressing insider threats, organizations can significantly reduce their risk exposure while fostering a secure working environment for all employees.
Image: Insider threat motivation.
How to Manage Internal Risks Effectively?
Managing internal risks is a critical component of addressing insider threats. By implementing effective risk management strategies, organizations can identify vulnerabilities and take proactive measures to mitigate potential insider attacks. In this section, we will explore practical approaches to effectively manage internal risks and enhance overall security.
Creating a Risk Assessment Framework
A robust risk assessment framework is essential for identifying and prioritizing potential insider threats. This framework should include:
- Identifying Critical Assets: Determine which assets—such as sensitive data, intellectual property, or financial information—are most critical to the organization. Understanding what needs protection is the first step in managing internal risks.
- Evaluating Threats and Vulnerabilities: Assess potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities within the organization. This includes both external threats and those that may arise from within the organization.
- Prioritizing Risks: Rank identified risks based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This prioritization helps organizations focus their resources on the most significant threats.
In my experience, I worked with a healthcare organization that implemented a comprehensive risk assessment framework. By identifying critical assets and prioritizing risks, they were able to allocate resources effectively and address vulnerabilities before they became significant issues.
Continuous Monitoring and Review
Effective risk management requires continuous monitoring and regular review of security measures. Organizations should establish processes for:
- Ongoing Risk Assessment: Regularly revisit the risk assessment framework to account for changes in the business environment, technology, or employee behavior.
- Monitoring User Activities: Utilize tools like User Behavior Analytics (UBA) to continuously monitor user activities for any unusual patterns that may indicate insider threats.
- Reviewing Security Policies: Periodically review and update security policies to ensure they remain relevant and effective against evolving insider threats.
In a previous role, we implemented a continuous monitoring program that allowed us to identify potential risks in real-time. This proactive approach enabled us to address issues before they escalated into serious incidents.
Engaging Employees in Risk Management
Employees play a vital role in managing internal risks. Engaging them in the process can enhance awareness and foster a culture of security. Here are some strategies:
- Involve Employees in Risk Assessments: Encourage employees to participate in identifying potential risks within their departments. They often have valuable insights into vulnerabilities that may not be apparent at higher levels.
- Provide Training on Risk Awareness: Conduct regular training sessions focused on risk management practices. Employees should understand how their actions can impact organizational security.
- Encourage Reporting of Concerns: Create an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious behavior or concerns about security without fear of retaliation.
I recall working with a client who established cross-departmental teams to assess risks collaboratively. This approach not only improved awareness but also empowered employees to take ownership of their roles in maintaining security.
Implementing Incident Response Plans
Having an effective incident response plan is crucial for managing internal risks associated with insider threats. Key components include:
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Define roles for team members involved in incident response, ensuring everyone knows their responsibilities during an incident.
- Communication Protocols: Establish communication protocols for notifying relevant stakeholders during an incident, including management, IT, and legal teams.
- Post-Incident Reviews: After an incident occurs, conduct a thorough review to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement in the response plan.
In my previous experience, we developed an incident response plan that included regular drills and post-incident reviews. This preparation ensured our team was ready to respond effectively when faced with actual incidents.
Utilizing Technology for Risk Management
Technology can significantly enhance efforts to manage internal risks related to insider threats:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions help monitor data transfers and prevent unauthorized sharing of sensitive information, thereby reducing the risk of insider attacks.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware, helping organizations detect potential insider threats quickly.
- Automated Reporting Tools: Implement tools that automate the reporting of suspicious activities or policy violations, allowing for quicker responses to potential insider threats.
In one organization I assisted, integrating DLP solutions helped them prevent several unauthorized data transfers by alerting the security team in real-time when sensitive information was accessed improperly.
Effectively managing internal risks involves creating a comprehensive risk assessment framework, engaging employees in risk management practices, implementing incident response plans, and leveraging technology for enhanced monitoring and detection. By focusing on these strategies centered around addressing insider threats, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability while fostering a secure workplace environment for all employees.
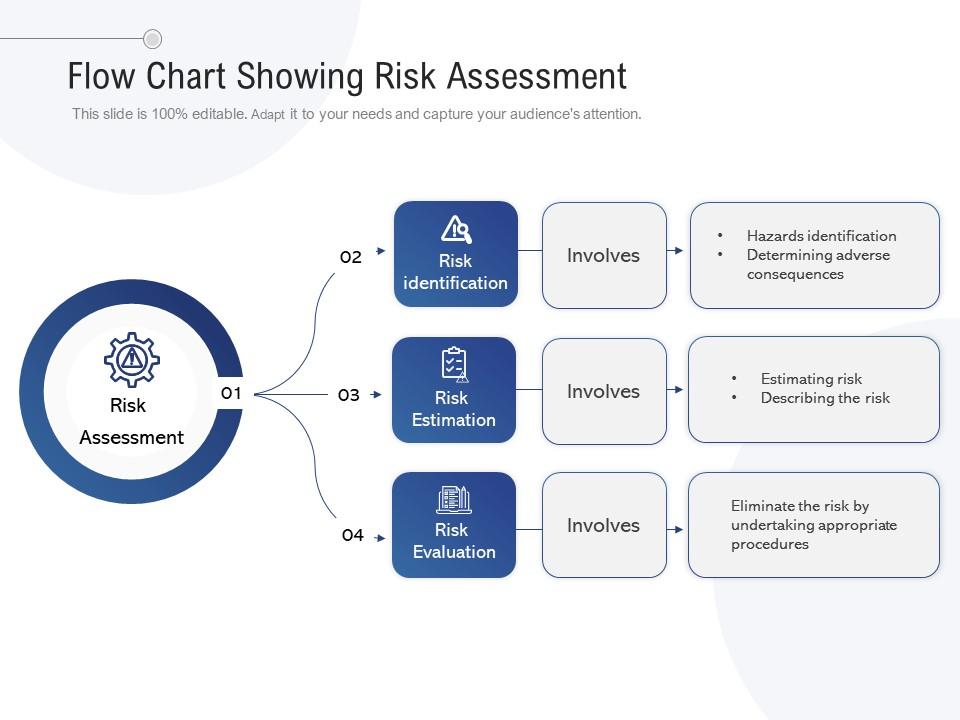
Image: Flowchart illustrating the steps in a risk assessment framework.
What Should Be Included in an Insider Threat Response Plan?
An effective insider threat response plan is essential for addressing insider threats and mitigating the impact of potential incidents. This plan outlines the steps an organization should take when an insider threat is suspected or detected. In this section, we will explore the critical components of a comprehensive insider threat response plan that helps prevent insider attacks and manage internal risks effectively.
Clear Procedures for Reporting Suspicion
The first step in an insider threat response plan is establishing clear procedures for reporting suspicious activities. Employees need to know how to report their concerns quickly and confidentially. Key elements include:
- Defined Reporting Channels: Create multiple channels for reporting, such as a dedicated email address, a hotline, or an anonymous reporting tool. This ensures that employees feel safe when voicing their concerns.
- Guidelines for Reporting: Provide employees with guidelines on what constitutes suspicious behavior and how to document their observations. This can include unusual access patterns, changes in employee behavior, or unauthorized data transfers.
- Training on Reporting Procedures: Regularly train employees on the reporting process, ensuring they understand how to act if they suspect an insider threat.
In my experience, I once worked with a company that implemented a straightforward reporting process. As a result, employees felt more empowered to report suspicious activities, which led to early detection of potential threats.
Designated Response Team
Having a designated response team is crucial for managing insider threats effectively. This team should be responsible for investigating reports of suspicious behavior and coordinating the organization’s response. Key roles within this team may include:
- Incident Response Manager: This individual oversees the investigation and ensures that all necessary steps are followed according to the response plan.
- IT Security Personnel: IT specialists should be involved in assessing the technical aspects of the incident, including data breaches or unauthorized access to systems.
- Legal and Compliance Representatives: Legal experts can provide guidance on regulatory requirements and potential legal implications arising from the incident.
In one organization I supported, forming a dedicated response team significantly improved their ability to handle insider threats. The team worked collaboratively to assess incidents and implement corrective actions swiftly.
Communication Protocols
Effective communication is vital during an insider threat incident. Establishing clear communication protocols ensures that all relevant stakeholders are informed and coordinated in their responses:
- Internal Communication Plan: Define how information will be shared internally among team members during an incident. This includes regular updates on the investigation’s progress.
- External Communication Strategy: If necessary, outline how to communicate with external parties, such as clients or regulatory bodies, while maintaining confidentiality.
- Post-Incident Communication: After resolving an incident, communicate lessons learned and any changes to policies or procedures to all employees.
When I was part of a security team at a large corporation, we developed a communication plan that outlined who needed to be informed at each stage of an incident response. This clarity helped streamline our efforts and minimize confusion during critical moments.
Investigation Procedures
A well-defined investigation procedure is essential for assessing the nature and scope of an insider threat incident:
- Gathering Evidence: Outline steps for collecting evidence related to the suspected incident, including logs of user activity, emails, and other relevant documentation.
- Conducting Interviews: Define how interviews with involved parties will be conducted while ensuring confidentiality and compliance with company policies.
- Documenting Findings: Maintain thorough documentation throughout the investigation process to ensure transparency and facilitate any necessary follow-up actions.
In my previous roles, I found that having clear investigation procedures allowed teams to respond quickly and effectively when incidents occurred, minimizing potential damage from insider threats.
Post-Incident Review
After addressing an insider threat incident, conducting a post-incident review is crucial for continuous improvement:
- Analyzing the Incident: Review what happened during the incident, including how it was detected, how it was handled, and what could have been done differently.
- Identifying Lessons Learned: Discuss what lessons were learned from the incident and how they can inform future prevention strategies.
- Updating Policies and Procedures: Based on findings from the review, update security policies and procedures as needed to strengthen defenses against future insider threats.
In one organization I assisted with post-incident reviews, we identified several areas for improvement in our training programs based on lessons learned from previous incidents. This proactive approach helped reduce future vulnerabilities significantly.
An effective insider threat response plan is essential for successfully addressing insider threats within any organization. By establishing clear reporting procedures, designating a response team, implementing communication protocols, defining investigation procedures, and conducting post-incident reviews, businesses can enhance their ability to respond swiftly and effectively to potential incidents. These measures not only help prevent insider attacks but also contribute to a culture of security awareness throughout the organization.

Image: Documenting suspicious activities.
Conclusion: Strengthening Your Business from Within
In today’s digital landscape, addressing insider threats is more critical than ever. As organizations increasingly rely on technology and data, the potential for insider attacks grows. These threats can stem from trusted employees, contractors, or partners who misuse their access to harm the organization intentionally or unintentionally. However, by implementing comprehensive strategies and fostering a culture of security awareness, businesses can significantly reduce their vulnerability to these risks.
Recap of Key Points
Throughout this article, we’ve explored various aspects of insider threats, including:
- Understanding Insider Threats: Recognizing the types of insider threats and their potential impact on an organization is the first step toward prevention.
- Importance of Addressing Insider Threats: The financial, reputational, and legal implications of insider attacks underscore the need for proactive measures.
- Identifying Insider Threats: By monitoring user behavior and recognizing key indicators, organizations can detect potential threats before they escalate.
- Strategies for Prevention: Implementing effective internal controls, conducting regular audits, and utilizing technology are essential for preventing insider attacks.
- Fostering a Culture of Security Awareness: Engaging employees in security practices and promoting open communication can create a more secure work environment.
- Managing Internal Risks: Establishing a risk assessment framework and continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities helps organizations stay ahead of potential threats.
- Developing an Insider Threat Response Plan: A well-defined response plan ensures that organizations can react quickly and effectively when incidents occur.
The Path Forward
Moving forward, it’s crucial for organizations to remain vigilant in their efforts to address insider threats. Here are some actionable steps to consider:
- Invest in Training: Regularly update training programs to keep employees informed about emerging threats and best practices for data protection.
- Enhance Monitoring Tools: Utilize advanced technologies like User Behavior Analytics (UBA) and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions to continuously monitor user activities.
- Review Policies Regularly: Ensure that security policies are reviewed and updated frequently to adapt to changing business environments and technological advancements.
- Encourage Reporting: Create an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious behavior without fear of repercussions.
By taking these steps, organizations can strengthen their defenses against insider threats while fostering a culture of security awareness among employees.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, addressing insider threats is not just about preventing attacks; it’s about building a resilient organization that prioritizes security at all levels. By understanding the risks, implementing effective strategies, and fostering a culture of awareness, businesses can protect their assets and ensure long-term success. Remember, a proactive approach to security is always more effective than a reactive one.
FAQ
1. What are the most common types of insider threats?
Insider threats typically fall into two categories: malicious insiders and unintentional insiders. Malicious insiders intentionally cause harm, often motivated by revenge or financial gain. Unintentional insiders, on the other hand, are employees who may inadvertently expose sensitive information or violate security protocols due to negligence or lack of awareness.
2. How can I recognize the signs of an insider threat?
Recognizing the signs of an insider threat involves monitoring for unusual behaviors. Key indicators include:
- Unusual access patterns: Employees accessing files or systems unrelated to their job roles.
- Behavioral changes: A previously engaged employee becomes withdrawn or starts acting suspiciously.
- Increased data transfers: Sudden spikes in data movement, especially outside normal working hours.
- Frequent complaints: Employees expressing dissatisfaction or frustration with their jobs may be more likely to engage in harmful behavior.
3. What role does employee training play in preventing insider attacks?
Employee training is crucial for preventing insider attacks as it educates staff about the risks associated with insider threats. Training helps employees recognize suspicious behavior, understand security protocols, and know how to report concerns effectively. Regular training sessions reinforce the importance of security practices and create a culture of vigilance within the organization.
4. How often should businesses conduct internal audits for risk management?
Internal audits should be conducted at least annually, but more frequent audits are advisable, especially after significant changes in personnel, technology, or business processes. Regular audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies, making it easier to address potential insider threats proactively.
5. What technologies can help in detecting insider threats?
Several technologies can assist in detecting insider threats effectively:
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA): Analyzes user activities over time and establishes baselines for normal behavior. Alerts are triggered when deviations occur.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Monitors data transfers and prevents unauthorized sharing of sensitive information.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Aggregates security data from various sources and provides real-time analysis to detect potential insider threats.
6. How can I create a culture of security awareness in my organization?
Creating a culture of security awareness involves several strategies:
- Foster open communication about security concerns and encourage employees to report suspicious activities without fear of retaliation.
- Implement regular training sessions focused on recognizing insider threats and following security protocols.
- Engage leadership in promoting security awareness by modeling good practices and reinforcing the importance of data protection.
7. What steps should I take if I suspect an insider threat?
If you suspect an insider threat, take the following steps:
- Report your concerns through established channels within your organization.
- Document any suspicious behavior you’ve observed, including dates, times, and specific actions.
- Avoid confronting the suspected individual directly; instead, allow your organization’s designated response team to investigate.
8. How can I balance employee privacy with security measures?
Balancing employee privacy with security measures requires transparency and clear policies. Implement monitoring tools that respect privacy rights while still providing necessary oversight. Communicate clearly with employees about what monitoring entails and ensure that policies are accessible and understood by all staff members.
9. Are there legal implications related to managing insider threats?
Yes, failing to address insider threats can lead to significant legal implications, including liability for data breaches or non-compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. Organizations must ensure that they have appropriate measures in place to protect sensitive information and respond effectively to incidents.
10. How can small businesses effectively address insider threats?
Small businesses can effectively address insider threats by implementing basic security measures such as:
- Establishing clear access controls based on employee roles.
- Conducting regular training sessions focused on cybersecurity awareness.
- Developing clear policies regarding data protection and incident reporting.
- Utilizing affordable monitoring tools to safeguard against potential insider threats.




