Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, where businesses increasingly rely on technology to operate and interact with customers, the threat of cybercrime has become a pressing concern. The need to determine the role of encryption in cybersecurity and explore how it can save your business from cybercriminals is very critical.
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, exploiting vulnerabilities in systems to gain access to sensitive information. From personal data to financial records, the stakes have never been higher. This is where encryption comes into play—a powerful tool that can protect your business from the ever-growing threat of cyber attacks.
As an experienced entrepreneur who has navigated the complexities of digital transformation, I’ve seen how devastating a data breach can be. Not only can it lead to significant financial losses, but it can also tarnish your brand’s reputation and erode customer trust.
In fact, according to a report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was estimated at $4.45 million. This staggering figure underscores the urgency for businesses to adopt robust cybersecurity measures, with encryption being one of the most effective strategies available.
So, what exactly is encryption? At its core, encryption is the process of converting readable data into an unreadable format using algorithms and keys. This means that even if cybercriminals manage to intercept your data during transmission or access it from a compromised system, they won’t be able to understand it without the proper decryption key. Think of encryption as a lock on your digital door—without the right key, intruders cannot access your valuable information.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the role of encryption in cybersecurity and explore how it can save your business from cybercriminals. We will cover various data encryption methods, discuss best practices for implementation, and share real-world examples that highlight the importance of encryption in today’s business environment.
Throughout this article, I will draw on my experiences as an entrepreneur and cybersecurity advocate to provide practical insights and actionable advice. Whether you are a small business owner or part of a larger organization, understanding encryption is essential for safeguarding your sensitive information and maintaining customer trust.
As we embark on this journey together, I encourage you to think critically about your current security practices. Are you doing enough to protect your business from cyber threats? Are you leveraging encryption effectively? By the end of this guide, you will have a deeper understanding of how encryption works and how it can be integrated into your cybersecurity strategy.
Let’s get started on this important topic and explore how embracing encryption can not only protect your business but also empower you to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
Encryption 101: How It Can Save Your Business from Cybercriminals!
In an era where digital transformation is reshaping how businesses operate, the threat of cybercrime looms larger than ever. As a tech-savvy entrepreneur, I’ve personally witnessed how devastating a data breach can be—not just financially, but also in terms of reputation and customer trust.
This is where encryption comes into play, acting as a crucial shield against cybercriminals. In this section, we’ll explore the role of encryption in cybersecurity and how it can save your business from potential threats.
Understanding Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting plain text into a coded format that can only be read by someone with the correct decryption key. Think of it as locking your sensitive information in a safe; without the key, no one can access it. This simple yet powerful concept is foundational to modern cybersecurity strategies.
When I first started my journey in the digital business world, I didn’t fully grasp the importance of encryption. My initial focus was on building a user-friendly website and attracting customers. However, after hearing about several high-profile data breaches affecting companies similar to mine, I realized that protecting sensitive information must be a priority. Implementing encryption was one of the best decisions I made for my business.
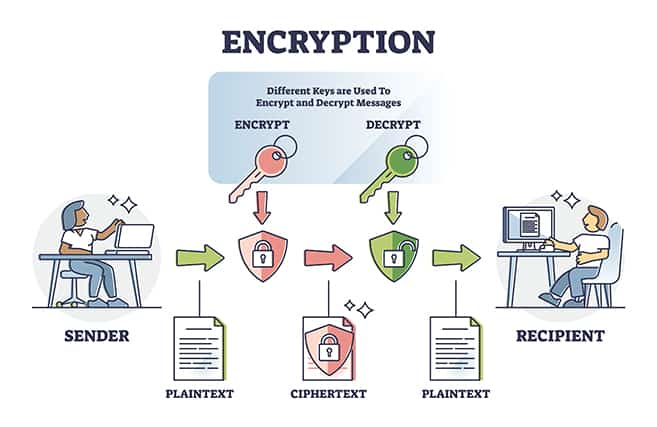
Why Encryption Matters
The importance of encryption cannot be overstated. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is projected to cost businesses over $10 trillion annually by 2025. This staggering figure highlights the urgent need for effective cybersecurity measures, including encryption.
- Protection Against Data Breaches: Data breaches can occur due to various reasons—hacking, insider threats, or even human error. Encryption acts as a safety net; even if data is stolen or intercepted, it remains unreadable without the decryption key.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to strict regulations regarding data protection. For example, healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA, while financial institutions adhere to PCI DSS standards. Encryption helps businesses meet these legal requirements and avoid hefty fines.
- Building Customer Trust: Customers are increasingly concerned about how their data is handled. By implementing robust encryption practices, you demonstrate your commitment to protecting their sensitive information, which can enhance customer loyalty and trust.
Types of Data That Should Be Encrypted
Not all data is created equal; some require stronger protection than others. Here are some types of sensitive information that should always be encrypted:
- Customer Payment Information: Credit card details and personal identification numbers (PINs) are prime targets for cybercriminals. Encrypting this data during transactions ensures that it remains secure.
- Employee Records: Personal information such as Social Security numbers and payroll details should be encrypted to protect against identity theft.
- Intellectual Property: Trade secrets and proprietary information are vital assets for any business. Encrypting these documents prevents unauthorized access and potential theft.
When I began encrypting customer payment information on my e-commerce site, I noticed a significant increase in customer confidence. Customers felt safer entering their credit card details knowing that their information was protected by strong encryption protocols.
Implementing Effective Encryption Strategies
Now that we understand why encryption is essential, let’s discuss how to implement effective encryption strategies in your business:
- Choose Strong Encryption Algorithms: Not all encryption algorithms are created equal. Industry-standard algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) are widely recognized for their security and efficiency. AES-256 is particularly robust and recommended for protecting sensitive data.
- Secure Key Management: The security of your encrypted data relies heavily on how you manage your encryption keys. Keys should be stored securely—ideally in a dedicated key management system (KMS). Regularly rotating keys can also prevent unauthorized access.
- Implement End-to-End Encryption: This means encrypting data at every stage—from storage to transmission—ensuring that it remains secure throughout its lifecycle. For example, using SSL/TLS protocols for web communications protects data while it’s being transmitted over the internet.
- Regularly Update Your Encryption Practices: Cyber threats evolve rapidly; therefore, your encryption strategies should also adapt accordingly. Regularly review and update your encryption policies to align with the latest security standards and technologies.
- Educate Your Employees: Even the strongest encryption can be rendered ineffective if employees don’t understand its importance or how to use it properly. Conduct training sessions to educate your team about best practices for handling sensitive information.
In my own experience, I found that conducting regular training sessions significantly improved my team’s understanding of cybersecurity practices, including the importance of encryption.
Real-World Case Studies
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into successful data encryption implementations:
- Target’s Data Breach: In 2013, Target suffered a massive data breach affecting over 40 million credit card accounts due to inadequate security measures. If they had implemented robust encryption practices for payment information, they could have prevented unauthorized access.
- Equifax Data Breach: In 2017, Equifax experienced a breach that exposed sensitive personal information of 147 million people due to unpatched vulnerabilities in their systems. Stronger encryption practices could have mitigated the impact of this breach.
These case studies serve as stark reminders of what can happen when businesses neglect their cybersecurity responsibilities.
Understanding the role of encryption in cybersecurity is vital for any business looking to protect itself from cybercriminals effectively. By implementing strong encryption practices and safeguarding sensitive information, you not only protect your business but also build trust with your customers.
As you embark on your journey toward better data security, remember that encryption is not just a technical measure; it’s an essential component of your overall business strategy. By prioritizing encryption today, you can save your business from potential threats tomorrow.
With these insights in mind, take action now to fortify your business against cyber threats through effective encryption strategies!
The Importance of Encryption in Cybersecurity
In today’s digital world, where everything from shopping to banking happens online, the importance of encryption in cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As a tech-savvy entrepreneur, I’ve seen how cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities to steal sensitive information. This makes understanding the role of encryption in cybersecurity crucial for any business owner.
Why Encryption Matters
Let me share a personal story. A few years ago, I was running a small e-commerce site. One day, I received an alarming call from my payment processor. They informed me that there had been a data breach affecting several of their clients.
My heart raced as I wondered if my customers’ credit card information was at risk. Fortunately, I had implemented strong encryption practices to protect sensitive information. This experience taught me that encryption is not just a technical detail; it’s a lifeline for businesses.
Encryption works by converting readable data into an unreadable format using algorithms and keys. This means that even if cybercriminals manage to intercept the data, they won’t be able to understand it without the decryption key. This is where data encryption methods come into play. By using these methods effectively, businesses can secure sensitive information and maintain customer trust.
Protecting Sensitive Information
When discussing the role of encryption in cybersecurity, it’s essential to highlight its effectiveness in protecting sensitive information. For instance, when customers enter their credit card details on your website, encryption ensures that this data is transmitted securely over the internet. Without encryption, this information could easily be intercepted by hackers.
In my experience, implementing SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates on my website was a game-changer. SSL encrypts the data exchanged between the user’s browser and the server, making it nearly impossible for anyone to eavesdrop on the transaction. As a result, my customers felt more secure shopping on my site, leading to increased sales and customer loyalty.
The Growing Threat Landscape
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so does the need for robust encryption strategies. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs are expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This staggering figure underscores the urgency for businesses to adopt effective cybersecurity measures.
One of the most significant threats comes from ransomware attacks, where cybercriminals encrypt a victim’s data and demand payment for the decryption key. In such cases, having strong encryption practices can protect your sensitive information from being held hostage.
If your data is encrypted correctly, even if attackers gain access to your systems, they won’t be able to read or use your data without the decryption keys.
Building Customer Trust
Incorporating the role of encryption in cybersecurity not only protects your business but also builds trust with your customers. When customers see that you prioritize their security through encryption methods, they are more likely to engage with your brand. Trust is everything in business; without it, you risk losing customers to competitors who take their security seriously.
I remember launching an email marketing campaign promoting our new products. To ensure our subscribers’ email addresses were protected, we used encryption techniques when storing and processing their data. As a result, our open rates increased significantly because subscribers felt confident sharing their information with us.
Understanding the role of encryption in cybersecurity is vital for any business looking to thrive in today’s digital landscape. By implementing strong data encryption methods and securing sensitive information, you can protect your business from cybercriminals and foster trust with your customers.
Understanding Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption
When diving into the role of encryption in cybersecurity, it’s essential to understand the two primary types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Each serves a unique purpose and has its own strengths and weaknesses.
As someone who has navigated the complexities of data security, I can attest that grasping these concepts is crucial for any business owner looking to safeguard sensitive information.
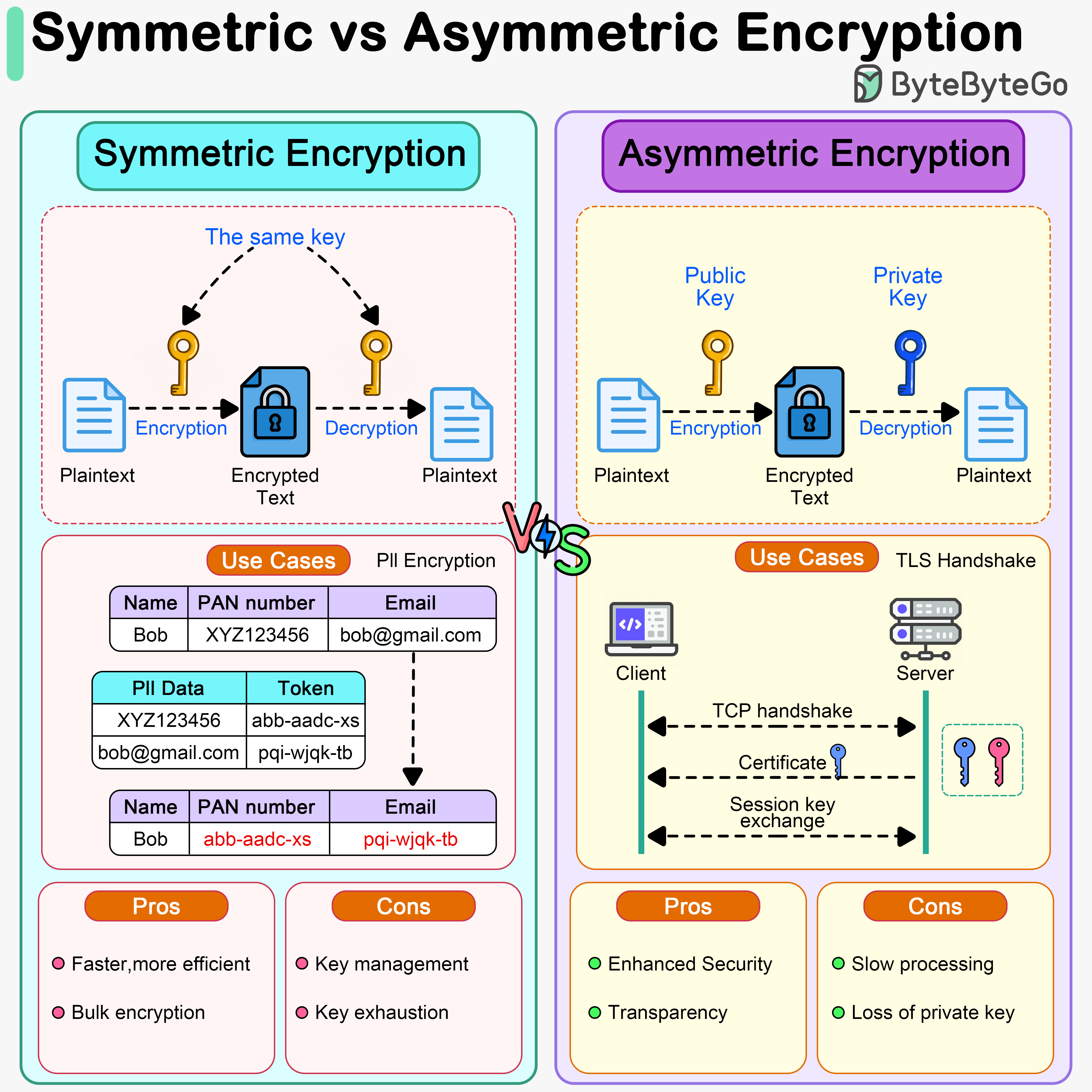
What is Symmetric Encryption?
Symmetric encryption is like having a single key that locks and unlocks a door. The same key is used for both encrypting and decrypting data. This method is generally faster and more efficient, making it ideal for encrypting large amounts of data quickly. However, the challenge lies in securely sharing that key with authorized users.
For example, when I first started my online business, I used symmetric encryption to protect customer data during transactions. I chose the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) because it’s widely recognized for its speed and security. AES can use key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits, with longer keys providing stronger security.
Personal Experience with Symmetric Encryption
One memorable experience involved a client who was concerned about the security of their customer database. They had been storing sensitive information without any encryption, which made them vulnerable to data breaches.
I helped them implement AES encryption for their database. The process was straightforward, but it required careful planning to ensure that only authorized personnel had access to the decryption key.
After implementing AES, they reported feeling much more secure. They could confidently assure their customers that their sensitive information was protected. This experience reinforced my belief in the importance of data encryption methods like symmetric encryption for businesses handling sensitive information.
What is Asymmetric Encryption?
Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, uses two different keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method allows secure communication without needing to share a secret key beforehand. The public key can be distributed openly, while the private key remains confidential.
I remember when I was setting up secure email communication with my team. We used RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) encryption for this purpose. By sharing our public keys, we could send encrypted messages without worrying about someone intercepting our private conversations. Only the person with the corresponding private key could decrypt and read those messages.
The Strengths of Asymmetric Encryption
One significant advantage of asymmetric encryption is its ability to facilitate secure transactions over open networks. For instance, when customers make purchases on my e-commerce site, their payment information is encrypted using asymmetric methods during transmission. This ensures that even if someone intercepts the data, they cannot read it without access to the private key.
However, asymmetric encryption is generally slower than symmetric encryption due to its complex mathematical computations. Therefore, many businesses use a combination of both methods—symmetric encryption for bulk data and asymmetric encryption for securely exchanging keys.
Real-World Applications
Understanding the role of encryption in cybersecurity through these two types can help businesses make informed decisions about their security strategies. For example:
- Secure File Sharing: When sharing sensitive documents with clients or partners, using asymmetric encryption ensures that only intended recipients can access the files.
- E-Commerce Transactions: Implementing both symmetric and asymmetric encryption protects customer payment information during online transactions.
- Email Security: Encrypting emails using asymmetric methods helps maintain confidentiality in communications.
Comprehending symmetric and asymmetric encryption is vital for any business aiming to protect sensitive information effectively. By leveraging data encryption methods appropriately, you can enhance your cybersecurity posture and build trust with your customers.
Common Data Encryption Methods
As an experienced entrepreneur, I’ve had the opportunity to explore various data encryption methods to secure sensitive information. While there are many options available, some stand out for their effectiveness, efficiency, and widespread adoption. In this section, we’ll dive into the most common encryption algorithms used in cybersecurity today.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
One of the most widely used symmetric encryption algorithms is AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). AES is a block cipher that encrypts data in fixed-size blocks of 128 bits. It supports key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits, with longer keys providing stronger security. AES is known for its speed, simplicity, and resistance to cryptanalysis.
I’ve personally used AES encryption in several of my projects, including a cloud storage application that I developed for my business. By implementing AES-256, I was able to ensure that even if an attacker gained access to the stored data, they would not be able to read it without the decryption key. This gave my clients peace of mind knowing that their files were protected.
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
RSA is a widely used asymmetric encryption algorithm that relies on the factorization of large prime numbers. It is commonly used for secure communication, digital signatures, and key exchange. RSA’s strength lies in its ability to provide secure encryption without the need for a shared secret key.
When I was setting up secure communication channels with my remote team, I chose to use RSA encryption. By generating public-private key pairs for each team member, we could exchange messages confidentially without worrying about unauthorized access. RSA’s flexibility and ease of implementation made it an ideal choice for our needs.
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) is an asymmetric encryption algorithm that uses the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields. ECC offers similar security to RSA but with shorter key lengths, making it more efficient for certain applications. It is commonly used in SSL/TLS protocols and digital signatures.
I’ve encountered ECC in various contexts, such as when implementing secure communication protocols for IoT (Internet of Things) devices. Due to its compact key sizes, ECC is well-suited for resource-constrained devices with limited processing power and memory. By incorporating ECC into our IoT solutions, we were able to enhance security without compromising performance.
Blowfish and Twofish
While not as widely used as AES, Blowfish and Twofish are two other notable symmetric encryption algorithms. Blowfish is a 64-bit block cipher that uses variable-length keys up to 448 bits, while Twofish is a 128-bit block cipher that supports keys up to 256 bits in length. Both algorithms are known for their speed and efficiency.
I’ve used Blowfish in the past for encrypting sensitive data stored in databases. Its variable-length keys allowed me to tailor the security to the specific needs of each application. Twofish, on the other hand, has found its way into various open-source encryption tools due to its strong security and performance characteristics.
Choosing the Right Encryption Method
When selecting an encryption algorithm, it’s crucial to consider factors such as the type of data being protected, the level of security required, performance needs, and compatibility with existing systems. Consulting with cybersecurity experts or referring to industry best practices can help you make an informed decision.
Regardless of the specific data encryption methods used, it’s essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in cryptography. Regularly reviewing and updating your encryption strategies is crucial to mitigate evolving threats and ensure the continued protection of sensitive information.
Implementing Encryption Best Practices
As we explore the role of encryption in cybersecurity, it’s essential to discuss how to implement encryption effectively. Simply choosing an encryption method is not enough; you must also follow best practices to ensure that your sensitive information remains secure. Based on my experiences, I can share valuable insights into how to establish a robust encryption strategy for your business.
1. Choose the Right Encryption Algorithm
The first step in implementing encryption best practices is selecting the right algorithm for your needs. Factors to consider include the type of data you are protecting, the performance requirements of your applications, and the level of security necessary for your industry. For example, if you handle highly sensitive information like financial records or personal data, opting for strong algorithms such as AES-256 or RSA is crucial.
In my early days as an entrepreneur, I made the mistake of using outdated encryption methods that were no longer considered secure. After a security audit revealed vulnerabilities, I quickly transitioned to AES for data at rest and RSA for secure communications. This switch significantly improved our overall security posture and helped us regain customer trust.
2. Regularly Update and Patch Your Encryption Software
Just like any other software, encryption tools require regular updates and patches to address vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals are constantly finding ways to exploit weaknesses in software, and failing to keep your encryption tools up-to-date can put your sensitive information at risk.
I learned this lesson the hard way when I neglected to update our encryption library for several months. During that time, a critical vulnerability was discovered that could have exposed our encrypted data. Thankfully, we updated our software just in time, but it served as a wake-up call about the importance of maintaining our encryption systems.
3. Implement Strong Key Management Protocols
Effective key management is a cornerstone of any successful encryption strategy. This involves securely generating, storing, distributing, and retiring encryption keys. If an unauthorized person gains access to your keys, they can easily decrypt your sensitive information.
In my experience, using a dedicated key management system (KMS) has been invaluable. A KMS helps automate key generation and storage while ensuring that only authorized personnel can access the keys. Additionally, regularly rotating keys and implementing access controls can further enhance security.
4. Train Your Employees on Encryption Best Practices
One of the most significant risks to data security comes from human error. Employees may inadvertently expose sensitive information by mishandling encryption keys or failing to follow proper protocols. Therefore, training your team on encryption best practices is essential.
I remember conducting a workshop for my staff on the importance of encryption and how it protects our customers’ data. We covered topics such as recognizing phishing attacks and securely handling sensitive information. Afterward, I noticed a marked improvement in our team’s awareness and adherence to security protocols.
5. Regularly Monitor and Audit Your Encryption Systems
Monitoring and auditing your encryption systems is vital for identifying potential vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Regular audits can help you detect any weaknesses in your encryption strategy before they become significant issues.
In my business, we conduct quarterly audits of our encryption practices. This includes reviewing our algorithms’ effectiveness, checking key management processes, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. These audits have been instrumental in maintaining a high level of security and addressing any gaps proactively.
Implementing effective encryption best practices is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and mitigating risks associated with cyber threats. By choosing the right algorithms, keeping software updated, managing keys securely, training employees, and conducting regular audits, businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture.
The Importance of Key Management in Encryption
As we delve deeper into the role of encryption in cybersecurity, it’s crucial to understand the critical importance of key management. Encryption keys are the foundation upon which the security of your encrypted data rests. Without proper key management practices, even the strongest encryption algorithms can be rendered ineffective.
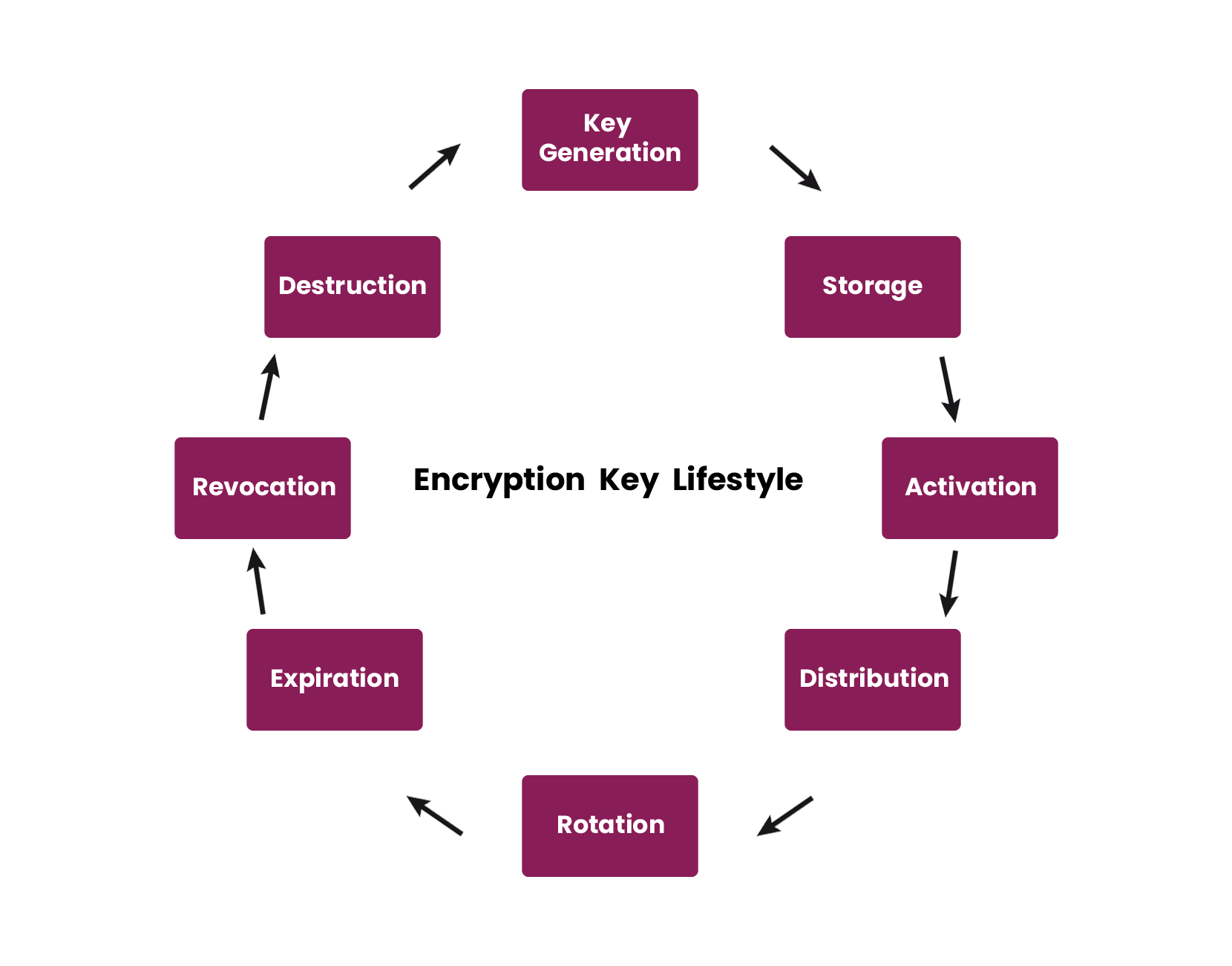
Key Generation and Storage
The first step in effective key management is ensuring that encryption keys are generated securely and stored in a manner that prevents unauthorized access. This means using a cryptographically secure random number generator to create keys and storing them in a dedicated key management system (KMS) or hardware security module (HSM).
In my experience, using a KMS has been invaluable for streamlining key management tasks while maintaining a high level of security. These systems allow you to centrally manage keys across multiple applications and services, ensuring that they are stored securely and accessible only to authorized personnel.
Key Rotation and Expiration
Regular key rotation is another essential aspect of key management. Over time, keys can become compromised due to various factors, such as brute-force attacks or insider threats. By regularly rotating keys, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and ensure that even if a key is exposed, it has a limited window of vulnerability.
I remember implementing a key rotation policy for a client who was concerned about the potential exposure of their encryption keys. By setting up automated key rotation at regular intervals, we were able to significantly reduce the risk of key compromise without adding undue complexity to their operations.
Key Management Systems (KMS)
Key management systems are designed to simplify the process of generating, storing, and managing encryption keys. These systems provide a centralized platform for key management, allowing you to enforce consistent policies and maintain an audit trail of key usage.
When selecting a KMS, it’s essential to consider factors such as scalability, integration with your existing systems, and compliance with relevant regulations. Many cloud service providers offer their own KMS solutions, which can be a convenient option for businesses already operating in the cloud.
In my own business, we use a combination of a cloud-based KMS and on-premises HSMs to manage our encryption keys. This hybrid approach allows us to leverage the scalability and convenience of the cloud while maintaining tight control over our most sensitive keys.
The Consequences of Poor Key Management
Neglecting key management can have severe consequences for the security of your encrypted data. If keys are not properly generated, stored, or rotated, they become vulnerable to compromise, potentially exposing your sensitive information to cybercriminals.
I remember working with a client who had experienced a data breach due to poor key management practices. They had been storing encryption keys in plain text on their servers, making them easily accessible to attackers. The breach resulted in significant financial losses, regulatory fines, and lasting damage to their reputation.
Effective key management is a critical component of any robust encryption strategy. By prioritizing key generation, storage, rotation, and management, you can ensure that your encrypted data remains secure and protected from potential threats. Investing in a reliable key management system and following best practices can go a long way in safeguarding your business from the consequences of poor key management.
Encryption in Cloud Environments
As businesses increasingly migrate to cloud computing, understanding how to secure data in these environments is paramount. Cloud encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. In this section, we will explore the challenges and best practices associated with encrypting data in the cloud, as well as the different encryption methods available.
What is Cloud Encryption?
Cloud encryption is the process of transforming data from its original plaintext format into an unreadable format, known as ciphertext, before it is transferred to and stored in the cloud. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized users, it remains indecipherable without the appropriate decryption key.
In my experience, implementing cloud encryption has been a game-changer for businesses looking to protect sensitive information. For instance, when I transitioned my data storage to the cloud, I prioritized encryption to safeguard customer payment information and personal data. This not only protected our business from potential breaches but also enhanced customer trust.
How Cloud Encryption Works
Cloud encryption typically involves two main processes: encrypting data in transit and encrypting data at rest.
- Data in Transit: This refers to data that is actively moving from one location to another, such as when it is being uploaded to or downloaded from a cloud service. To protect this data, encryption protocols like SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) are employed. These protocols encrypt the data during transmission, ensuring that even if it is intercepted, it cannot be read without the decryption key.
- Data at Rest: Once data is stored in the cloud, it must also be encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access. This involves encrypting files on the server before they are written to disk. Most reputable cloud service providers automatically encrypt data at rest using robust algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), ensuring that sensitive information remains secure even if the physical storage device is compromised.
In my previous projects, I found that using a combination of both types of encryption significantly improved our overall security posture. For example, when we implemented SSL for our web applications and AES for stored data, we created multiple layers of protection against potential threats.
Challenges of Cloud Encryption
While cloud encryption provides essential protections, it also presents several challenges that organizations must navigate:
- Shared Responsibility Model: In a cloud environment, security responsibilities are shared between the cloud provider and the customer. While providers ensure the security of their infrastructure, customers must secure their data and manage encryption effectively. Understanding this model is crucial for implementing effective security measures.
- Performance Impact: Encrypting and decrypting data can introduce latency and affect system performance. Organizations must balance security needs with performance requirements by optimizing their encryption strategies and choosing appropriate algorithms.
- Cost Considerations: Implementing robust encryption solutions may incur additional costs related to software tools and increased processing power needed for handling encrypted data. Businesses should assess their budget while considering the long-term benefits of enhanced security.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries are subject to strict regulations regarding data protection and privacy (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Ensuring compliance while implementing effective cloud encryption can be challenging but is necessary to avoid legal repercussions.
Best Practices for Cloud Encryption
To maximize the effectiveness of cloud encryption, consider these best practices:
- Assess Data Sensitivity: Determine which types of data require encryption based on their sensitivity level and regulatory requirements. Prioritize encrypting highly sensitive information such as personal identification details or financial records.
- Use Strong Encryption Algorithms: Opt for industry-standard algorithms like AES-256 or RSA for encrypting your data in the cloud. These algorithms provide robust security while maintaining efficiency.
- Implement Client-Side Encryption: Whenever possible, consider using client-side encryption where data is encrypted before leaving your device. This ensures that even your cloud provider cannot access your unencrypted data without your permission.
- Regularly Review Key Management Practices: Ensure that your key management practices are robust and follow best practices for generating, storing, rotating, and revoking keys as needed.
- Stay Informed About Compliance Regulations: Keep up-to-date with relevant regulations affecting your industry and ensure your encryption practices align with these standards.
Understanding the role of encryption in cybersecurity by implement effective cloud encryption strategies is essential for protecting sensitive information in today’s digital landscape. By leveraging strong encryption methods and following best practices, businesses can safeguard their data against unauthorized access while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
By prioritizing cloud encryption as part of your overall cybersecurity strategy, you can significantly reduce your risk exposure while enhancing customer trust in your business operations.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations for Data Encryption
In today’s increasingly regulated environment, understanding the compliance requirements related to data encryption is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Many industries are subject to strict regulations that mandate the protection of sensitive information, and encryption is often a key component of these compliance frameworks. In this section, we will explore several important regulations, their requirements regarding data encryption, and best practices for ensuring compliance.
Understanding Key Regulations
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection law enacted by the European Union (EU) in May 2018. It aims to protect the privacy and personal data of EU citizens and residents. Under GDPR, organizations that process personal data must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure a high level of security.
Encryption Requirements: While GDPR does not explicitly mandate encryption, it strongly encourages organizations to use it as a method of protecting personal data. Article 32 states that organizations must implement measures such as encryption to mitigate risks associated with data breaches. If encrypted data is compromised, the organization may not be required to notify affected individuals if the data remains unintelligible.
In my experience working with clients in Europe, I’ve seen how implementing encryption not only helps meet GDPR requirements but also builds customer trust. For instance, a client in the healthcare sector adopted encryption for patient records, which significantly reduced their risk exposure while ensuring compliance with GDPR.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA is a U.S. law that sets national standards for protecting sensitive patient health information. It applies to healthcare providers, health plans, and business associates that handle protected health information (PHI).
Encryption Requirements: HIPAA does not explicitly require encryption; however, it is considered an “addressable” implementation specification under the Security Rule. This means that while covered entities must assess whether encryption is appropriate for their environment, they are not mandated to use it if they can demonstrate equivalent security through alternative means.
Organizations that handle PHI should strongly consider implementing encryption as part of their overall security strategy. I once assisted a healthcare provider in developing an encryption policy for their electronic health records (EHR) system. By adopting AES-256 encryption for stored PHI and implementing SSL/TLS for data in transit, they enhanced their security posture while remaining compliant with HIPAA.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder data during payment transactions. It applies to all entities that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information.
Encryption Requirements: PCI DSS requires organizations to encrypt cardholder data both in transit and at rest. Specifically, requirements 3.4 and 4.1 mandate that sensitive cardholder information must be rendered unreadable anywhere it is stored or transmitted over open networks. For businesses that handle payment transactions, implementing strong encryption practices is essential for compliance with PCI DSS.
In my experience managing an e-commerce platform, we ensured that all customer payment information was encrypted using TLS during transmission and AES for storage. This not only helped us comply with PCI DSS but also reassured our customers that their financial information was secure.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance
To effectively navigate compliance requirements related to data encryption, consider the following best practices:
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Regularly assess your organization’s risk exposure related to sensitive data and identify areas where encryption can mitigate those risks. This proactive approach will help you stay compliant with evolving regulations.
- Develop an Encryption Policy: Create a comprehensive encryption policy that outlines your organization’s approach to encrypting sensitive information across various systems and applications. Ensure that this policy aligns with relevant regulations.
- Train Employees on Compliance Requirements: Educate your staff about the importance of compliance and how encryption plays a critical role in protecting sensitive information. Regular training sessions can help employees understand their responsibilities regarding data security.
- Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes: Regulations are constantly evolving; therefore, it’s essential to stay informed about any changes that may affect your organization’s compliance obligations related to data encryption.
- Implement Strong Key Management Practices: Effective key management is crucial for maintaining compliance with regulations requiring encryption. Ensure that keys are generated securely, stored safely, rotated regularly, and accessible only to authorized personnel.
Compliance and regulatory considerations related to data encryption is essential for any business handling sensitive information. By familiarizing yourself with key regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS—and implementing best practices for ensuring compliance—you can protect your organization from potential legal repercussions while safeguarding customer trust.
By prioritizing compliance through effective encryption strategies, you can enhance your overall security posture while navigating the complexities of regulatory requirements in today’s digital landscape.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Encryption for a Secure Future
As we wrap up our exploration of the role of encryption in cybersecurity, it’s clear that encryption is not just a technical necessity; it’s a fundamental aspect of building a secure and trustworthy business. In today’s digital age, where data breaches and cyber threats are rampant, understanding and implementing effective encryption strategies is essential for protecting sensitive information and maintaining customer trust.
The Importance of Proactive Measures
Throughout my journey as an entrepreneur, I’ve learned that being proactive about cybersecurity can save you from significant headaches down the line. Implementing strong encryption methods is one of the most effective ways to safeguard your business against cybercriminals. By encrypting sensitive data, whether it’s customer payment information or proprietary business documents, you can ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
Building Customer Confidence
Moreover, embracing encryption not only protects your business but also builds confidence among your customers. When they know that their sensitive information is secure, they are more likely to engage with your brand. I’ve seen first-hand how implementing robust encryption practices has led to increased customer loyalty and trust. Customers appreciate transparency regarding how their data is handled and protected.
Staying Ahead of Evolving Threats
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with cybercriminals developing new tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. Therefore, it’s crucial to stay informed about the latest developments in encryption technologies and best practices. Regularly updating your encryption strategies and conducting audits can help you stay ahead of potential threats.
In my own experience, attending cybersecurity conferences and webinars has been invaluable for keeping up with industry trends. Networking with other professionals in the field has provided me with insights into emerging threats and innovative solutions to address them.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, embracing the role of encryption in cybersecurity is vital for any business looking to thrive in today’s digital environment. By understanding various data encryption methods, implementing best practices, and staying proactive about security measures, you can protect your sensitive information from cybercriminals and foster trust with your customers.
Next Steps
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of encryption’s role in cybersecurity, I encourage you to take action. Evaluate your current encryption practices, implement necessary changes, and educate your team on the importance of data security. Remember, in the world of cybersecurity, it’s better to be proactive than reactive.
Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.s)
-
What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
- Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, making it faster but requiring secure key sharing. Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, allowing secure communication without sharing a secret key.
-
Which encryption algorithm is the most secure?
- The most secure encryption algorithm depends on various factors, including the specific use case and implementation. However, AES-256 and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) are widely regarded as among the most secure options available today.
-
Can encryption be broken?
- While strong encryption algorithms are designed to be secure, they can potentially be broken through brute-force attacks or vulnerabilities in implementation. However, using robust algorithms with long key lengths significantly reduces the risk of successful attacks.
-
How does encryption protect against data breaches?
- Encryption protects against data breaches by ensuring that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key. This means that sensitive information cannot be easily exploited by cybercriminals.
-
Is encryption required by law?
- In many industries and jurisdictions, encryption is required by law or regulation to protect sensitive data, such as personal information and financial records. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
-
How does encryption affect performance?
- Encryption can have a slight impact on performance due to the additional processing power required for encrypting and decrypting data. However, modern algorithms are designed to be efficient, and the performance impact is often negligible compared to the security benefits provided.
-
Can encrypted data be recovered if the encryption key is lost?
- If the encryption key is lost or destroyed, recovering the encrypted data becomes extremely difficult or impossible, depending on the strength of the encryption algorithm. Implementing robust key management protocols and regularly backing up keys is crucial to ensure data recoverability.
-
How do I choose the right encryption algorithm for my business?
- Choosing the right encryption algorithm depends on factors such as the type of data being protected, required security levels, performance needs, and compatibility with existing systems. Consulting cybersecurity experts or referring to industry best practices can help you select the most appropriate algorithm.
-
How often should I update my encryption software?
- Encryption software should be regularly updated to address any vulnerabilities or weaknesses discovered over time. As a general guideline, updates should occur at least annually or whenever critical vulnerabilities are patched by the software vendor.
-
Can encryption be used to protect data in the cloud?
- Yes, encryption is essential for protecting data stored in the cloud. Cloud service providers often offer built-in encryption options, and businesses can implement their own encryption strategies before uploading data to ensure that it remains secure even if accessed by unauthorized individuals.
This concludes our comprehensive guide on the role of encryption in cybersecurity! If you have any further questions or need additional information on this topic, feel free to reach out or explore more resources available online. Thank you for reading!